

SPring-8:東北大、放射光のマルチビーム化成功:動的3D観察/ミリ秒で実現:
SPring-8: Tohoku Univ succeeds in synchrotron radiation multi-beam: Dynamic 3D /millisecond order:
SPring-8:东北大学成功实现同步辐射多光束:动态3D观测/毫秒级
SPring-8:
【発表の要点】
- 従来のX線CTでは、「多くの角度から投影像を取得するために試料を非常に高速に回転する必要」
- 試料を回転せずに、ミリ秒オーダー/X線CTの実現可能な、放射光マルチビーム化技術開発に、世界ではじめて成功
- 「流動性のある試料や生きた生物の動的3D観察がミリ秒オーダーで可能」、広い分野への応用展開が期待
【概要】
- 東北大学:矢代准教授、
- 東京学芸大学:Wolfgang Voegeli准教授、
- 筑波大学 :工藤教授、
- 高輝度光科学研究センター:梶原主幹研究員
共同研究グループ:
試料を回転せずに、「ミリ秒オーダー/X線CTを実現するための、放射光マルチビーム化」に、世界ではじめて成功しました。
本研究成果により、「流動性のある試料/生きた生物など、動的3D観察」が、ミリ秒オーダーで可能となります。
応用分野:
- 様々な試料環境の導入も、可能
- 物質・生命科学の基礎研究から
- 産業応用に至る広い分野への
応用展開が期待されます。
本研究成果は、学術誌「Optica」に2020年5月12日付でオンライン公開されました。
TOHOKU UNIVERSITY-
https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/japanese/2020/05/press20200513-01-CT.html
ミリ秒X線CTのための放射光マルチビーム化に成功
~試料の回転要らず動的3D観察を可能に~
研究成果:
矢代准教授らの共同研究グループは、
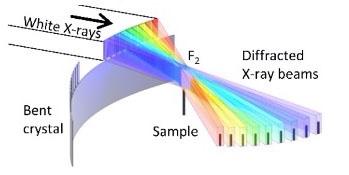
- 図1に示すような放射光をマルチビーム化するためのX線光学系を開発。
- 1 ms(ミリ秒)の撮影時間で三次元再構成ができることを世界ではじめて実証。
X線CTの特徴:
X線CTに用いられている透過力の高いX線は、一般に物質との相互作用が小さい。
そのため、可視光の鏡による反射のように、伝播方向を容易に制御することができません。
本研究では:
- 図1左上の形状の薄い単結晶を微細加工により作製、
- 図1左下のように双曲面上に湾曲させ、
- 図1右のように三段に配置することにより、
「±70°の投影方向をカバーするマルチビーム光学系の開発」に成功しました。
事例の説明:
- 図2左に投影像の例を、
- 図2右に三次元再構成結果の例を示します。
SPring-8:
実験は大型放射光施設SPring-8(注2)のビームラインBL28B2の放射光を用いて行いました。
この放射光マルチビーム化技術を用いると、多くの方向からの投影像を同時に取得可能。
試料を回転せずに、ミリ秒オーダーのX線CTを、実現できます。
三次元に再構成:
なお、図2右の三次元再構成には、わずか数10方向の投影像から画像再構成が可能。
最先端の圧縮センシング(注3)に基づくアルゴリズムを使用します。
今後の展望:
- 流動性のある試料や生きた生物など、動的3D観察がミリ秒オーダーで可能。
- また様々な試料環境の導入も可能。
物質・生命科学の基礎研究から産業応用に至る広い分野への波及効果が期待されます。
例えば:
- ポリマー材料や接着界面の破壊過程の研究、
- 生きた昆虫の3D観察による動的バイオミメティクス(注4)研究、
様々な応用展開を期待しています。
— SPring-8 Web Site
http://www.spring8.or.jp/ja/news_publications/press_release/2020/200513_1/
Unlocking the gate to the millisecond CT
Many will undergo a CT scan at some point in their lifetime – being slid in and out of a tunnel as a large machine rotates around.
X-ray computed tomography, better known by its acronym CT, is a widely used method of obtaining cross-sectional images of objects.
Now a research team – led by Tohoku University Professor, Wataru Yashiro –
has developed a new method using intense synchrotron radiation that produces higher quality images within milliseconds.
High-speed, high-resolution X-ray CT
is currently possible using intense synchrotron radiation.
However, this requires samples to be rotated at high speed to obtain images from many directions. This would make CT scans more akin to a rollercoaster ride!
Extreme rotation also makes controlling the temperature or atmosphere of the sample impossible.
Nevertheless, the research team
solved this conundrum by creating an optical system that splits single synchrotron X-ray beams into many.
These beams then shine onto the sample from different directions at the same time; thus, negating the need to rotate the sample.
SPring-8 Web Site
http://www.spring8.or.jp/en/news_publications/press_release/2020/200513_1/?set_language=en&cl=en