東大:パワー半導体向け高効率放熱を実現:ヒートスプレッダー(動画):
Tokyo Univ:High-efficient heat dissipation for power semicon:Heat spread:
东京大学:实现功率半导体的高效散热:散热器
ー高電圧・大電流を扱うパワー半導体向けー
東京大学大学院
塩見淳一郎教授研究グループは、高電圧・大電流を扱うパワー半導体向けの高効率な放熱構造を開発した。
発熱体と加熱器の間に挟んで熱を拡散するヒートスプレッダーとして利用できる。
パワー半導体向け
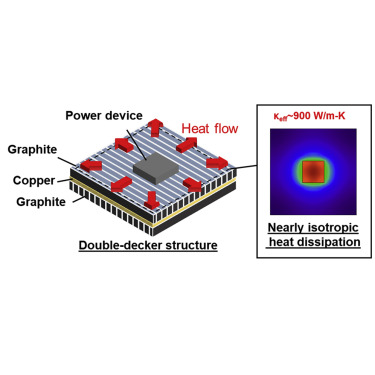
高効率な放熱構造比較的安価なグラファイトを用い、3次元的な熱流制御を行うことで実現した。
- 高放熱効率と低コスト化を両立し、
- 次世代パワー半導体の高集積化や、
- コスト低減につながると期待される。
高熱伝導率・ヒートスプレッダー:
パワー半導体の出力上昇や小型化に伴い、
一般に使用されている銅より、高熱伝導率のヒートスプレッダーが求められている。
グラファイトの熱伝導率:
- グラファイトの熱伝導率は、
- 面内方向には高いが、
- 面直方向には低いため、
グラファイトは、「等方的な放熱が必要なパワー半導体向け」には使えなかった。
研究グループ:
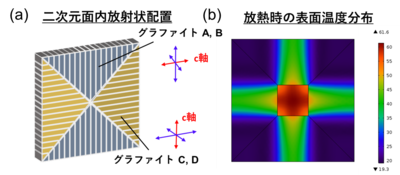
熱流制御によりグラファイトに等方的で高い熱伝導率を持たせる方法を考案した。
その結果、
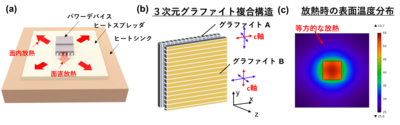
3次元空間で配向の異なる二つのグラファイト材を重ねた構造が、
1・5倍以上高い放熱性能を持つことが分かった。
放熱実験の結果:
これを用いて3次元空間でデバイス放熱実験をした。
- 放熱実験での熱伝導率が、
- 900ワット/メートル・ケルビンで、
- 等方性材料と同等の性能を示した。
既存の銅の熱伝導率は、400ワット/メートル・ケルビンにとどまる。
ニュースイッチ
グラファイトを用いた3次元的な熱流制御により、超高性能ヒートスプレッダを実現
~パワー半導体の高効率放熱への活用に期待~
発表のポイント:
◆グラファイトの熱伝導率は面内方向には高いが、面直方向には低い。
その為、「等方的な放熱が要求されるパワー半導体(注1)の熱マネージメントへの利用」は困難でした。
◆「異なる向きのグラファイト材」を加工して、3次元的に組み立てた。
更に、銅と一体焼成して接合した。
ことで、実効的に等方的な放熱性を付与することに成功しました。
◆実装を模擬した放熱試験を実施した。
「熱伝導率900 W/m-Kの等方性材料と同等の、非常に高い放熱性能」を実現しました。
https://www.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/foe/press/setnws_202110221318571011060492.html
Ultra-high-performance heat spreader based on a graphite architecture with three-dimensional thermal routing
Summary
To meet the increasing demand for highly efficient heat dissipation in power electronics,
a heat spreader
that has significantly greater isotropic thermal conductivity than the commonly used copper (400 W/m·K) should be developed.Although graphite
is a promising candidate because of its high basal-plane thermal conductivity,its application is restricted by its low c axis thermal conductivity.
This issue can be resolved
by transforming graphite into an isotropic thermal conductor by building a structure that can effectively route heat in all three dimensions.
Herein,
we develop a double-decker structurewith differently oriented graphite layers to realize high heat dissipation from a local heat source.
The critical issue of bonding the graphite layers is overcome by a high-temperature process using Cu as the binding layer.
The graphite/Cu composite efficiently
dissipates heat nearly isotropically and performs as well as an isotropic conductor with a thermal conductivity of 900 W/m·K.
ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666386421003398