岡山大学、異分野基礎科学研究所、村岡祐治准教授

図1. Qカーボンの表面像。フィラメント状の明るい部分がQカーボン
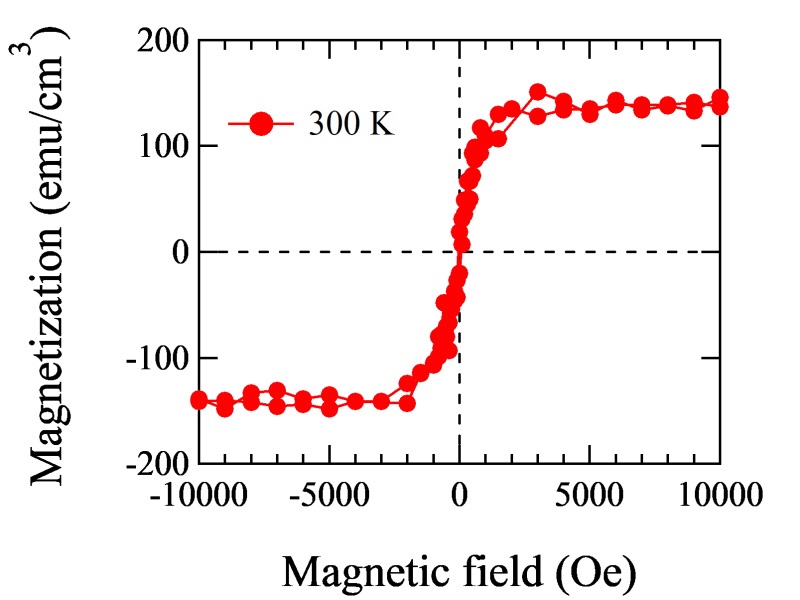
図2. Qカーボンの室温強磁性的振舞い。
岡山大:新素材Qカーボン再現:a KrF excimer laser(動画):
Okayama Univ.: Reproducing new material Q carbon: a KrF excimer laser:
冈山大学:用KrF准分子激光器成功地生产了新的碳材料Q碳
ーエネルギー材料としての展開に期待ー
岡山大:
2020年07月30日
◆発表の要点
世界に先駆けて、
- 新しい炭素材料Qカーボンの再現に成功。
- Qカーボン作製には、原料炭素・熱的性質、
- 照射レーザーの強さを、厳密に制御することが重要、
Qカーボンを用いた省エネやエネルギーに関する研究が加速されると期待されます。
岡山大学:村岡研究グループ
世界に先駆けて、作製が非常に難しい新しい炭素材料Qカーボンの作製を再現することに成功しました。
また、Qカーボンの作製方法を確立するための指針を示しました。
研究成果は、2020年6月25日、科学雑誌「Carbon」電子版に掲載されました。
Qカーボン:
2015年に報告された新しい炭素同素体です。
- 室温強磁性、
- わずかなエネルギーでの発光、
- ダイヤモンドを凌ぐ硬度、
- ホウ素ドープ(添加)による超伝導など
独特の特性を示します。
従来:Qカーボンの作製例はない
レーザーを使った極短時間のプロセスで、Qカーボンを作製することは可能。
しかし、その作製は、極めて難しい。
これまで発見者グループ以外に、Qカーボンの作製例はありません。
今回:初めてQカーボンの作製を実現
今回、研究グループはナノ秒レーザーを使用した作製プロセスを開発。
特に、冷却度に着目して実験を行いました。
作製の結果:
「溶融炭素の急冷度を厳密に制御すること」で、Qカーボンを作製に成功しました。
Qカーボンの作製には、
- 原料炭素の熱的性質と
- 照射レーザーの強さを
- 厳密に制御することが重要であることを明らかにしました。
岡山大学
http://www.okayama-u.ac.jp/tp/release/release_id751.html
Formation of Q-carbon by adjusting sp3 content in diamond-like carbon films and laser energy density of pulsed laser annealing
Abstract
In this study, we prepared Q-carbon by adjusting the sp3 content in diamond-like carbon (DLC) films and the laser energy density of pulsed laser annealing (PLA).
The amorphous DLC films
were fabricated on sapphire Al2O3(0001) substrates using a pulsed laser deposition technique with a KrF excimer laser (λ = 248 nm).
The sp3 content in the films
varied between 20% and 42% by changing the laser energy density. Subsequently, PLA was performed on the DLC films by using the KrF excimer laser with energy densities between 0.5 and 1.2 J/cm2.
The prepared films
were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and magnetization measurements.
Consequently, for the combination of 20% sp3 content and laser density of 1.0 J/cm2, as well as 42% sp3 and 0.5 J/cm2,
the films showed the characteristic features of Q-carbon:
filamentary nanostructures, the presence of a T band in the Raman spectrum, room-temperature ferromagnetic behavior, and ∼80% sp3 content.
The results indicate that Q-carbon
can be obtained by using a proper combination of sp3 content in DLC films and an appropriate PLA energy density.
This study provides important guidance for establishing a preparation method for Q-carbon.
ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0008622320305923