JAEA:生分解性・高強度ゲルを開発:クエン酸や水から(動画):
JAEA: Biodegradable, high-strength gel: From citric acid, water:
JAEA:开发出可生物降解的高强度凝胶:由柠檬酸,水等制成。
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)、
東京都立産業技術研究センター(都産技研)、
東京大学10月30日、環境にやさしい高強度ゲル材料「凍結架橋セルロースナノファイバーゲル」の開発に成功したと発表した。
- 木材の「セルロースナノファイバー」と
- レモンに含まれるクエン酸、
- そして水から構成される。
セルロースナノファイバー:
「カルボキシメチルセルロース(CMC)ナノファイバー」は、食品添加剤や化粧品の増粘剤としても利用されている安全性の高い素材だ。
その分子中には、有機化合物の反応性官能基のひとつである「カルボキシル基」を持つ。
ほかの物質と反応させて、ゲルやフィルムを作製することが可能だ。
今回の研究:
CMCナノファイバーとクエン酸が、実験に用いられることとなった。
-20℃の環境で、
凍結させられたCMCナノファイバー溶液に
クエン酸溶液を混ぜて、
-4℃の環境で溶かした。
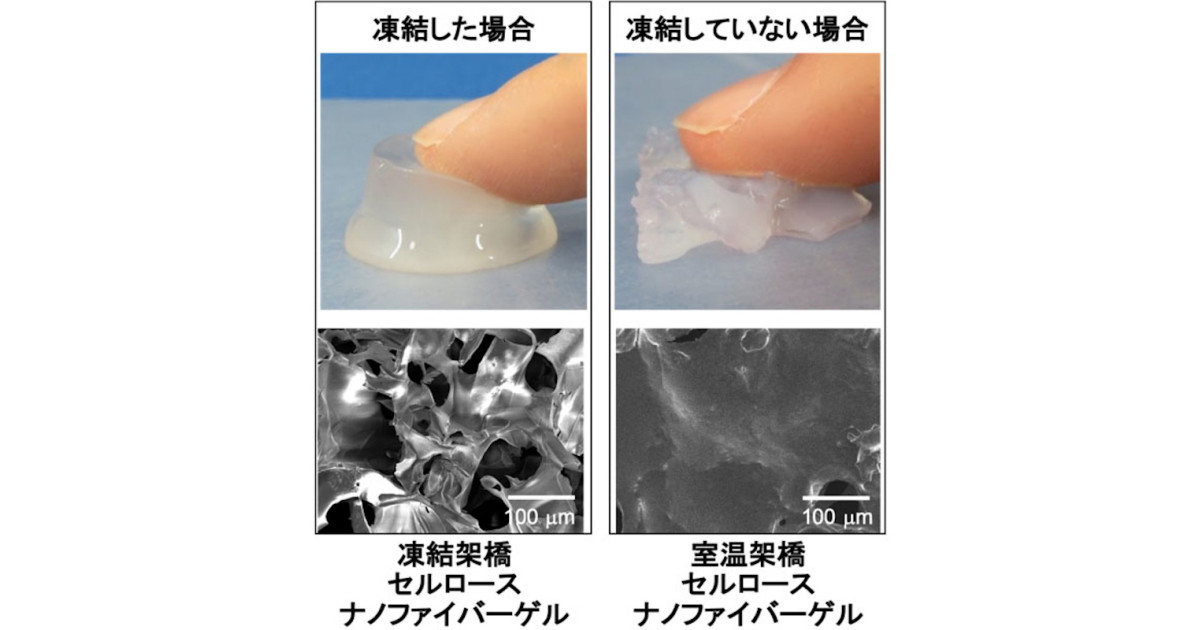
結果、氷が溶けると同時に白く不透明なハイドロゲル、
凍結架橋CNFゲルの形成が確認されたという。
凍結架橋CNFゲルの保水性を調べた結果、
「全体の重さの約95%もの水を、ゲル内部に含めることができること」が判明した。
詳細は、国際学術誌「ACS Applied Polymer Materials」のオンライン版に掲載された。
マイナビニュース
https://news.mynavi.jp/article/20201104-1452145/
Eco-friendly Carboxymethyl Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels Prepared via Freeze Cross-Linking and Their Applications
Abstract
We developed a cross-linking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize
a carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel
with high water content (>94%),
high compressive strength (>80 MPa),
and high compressive recoverability.
The hydrogels
were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol.The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure with a pore diameter of approximately 80 μm, which resembled the ice crystal structure.
The stress–strain curves of the hydrogel during repeated compression up to 80% strain
were similar over three cycles, which indicated that their cross-linked structure had high stability to compressive stress.
ACS Applied Polymer Materials