COVID-19:タカラバイオのPCR検査、2時間で5000件:米FDAに緊急申請
COVID-19: PCR test of Takara Bio, 5000 cases in 2 hours: Urgent application to US FDA
COVID-19:Takara Bio PCR测试,在2小时内进行5000次:紧急申请美国FDA
COVID-19:
Takara Bio USA:
6月9日、米国子会社が、「新型コロナウイルス感染の有無を調べるPCR検査の効率を大幅に上げる手法を開発した」と明らかにした。
最大5千件を2時間で検査できる。
米FDAに、緊急使用許可を申請中で、6月中にも、承認される見通しという。
新PCR検査手法:
タカラバイオの米子会社(Takara Bio USA)とバイオシンタグマ(bioSyntagma)が、既存の装置と試薬を組み合わせ、共同開発した。
現在、米国で主流の手法と比べ、大幅な検査のスピードアップが可能。
この手法の権利については、バイオシンタグマが保有している。
タカラバイオは「日本での展開は考えていない」とのこと。
京都新聞
https://www.kyoto-np.co.jp/articles/-/272636
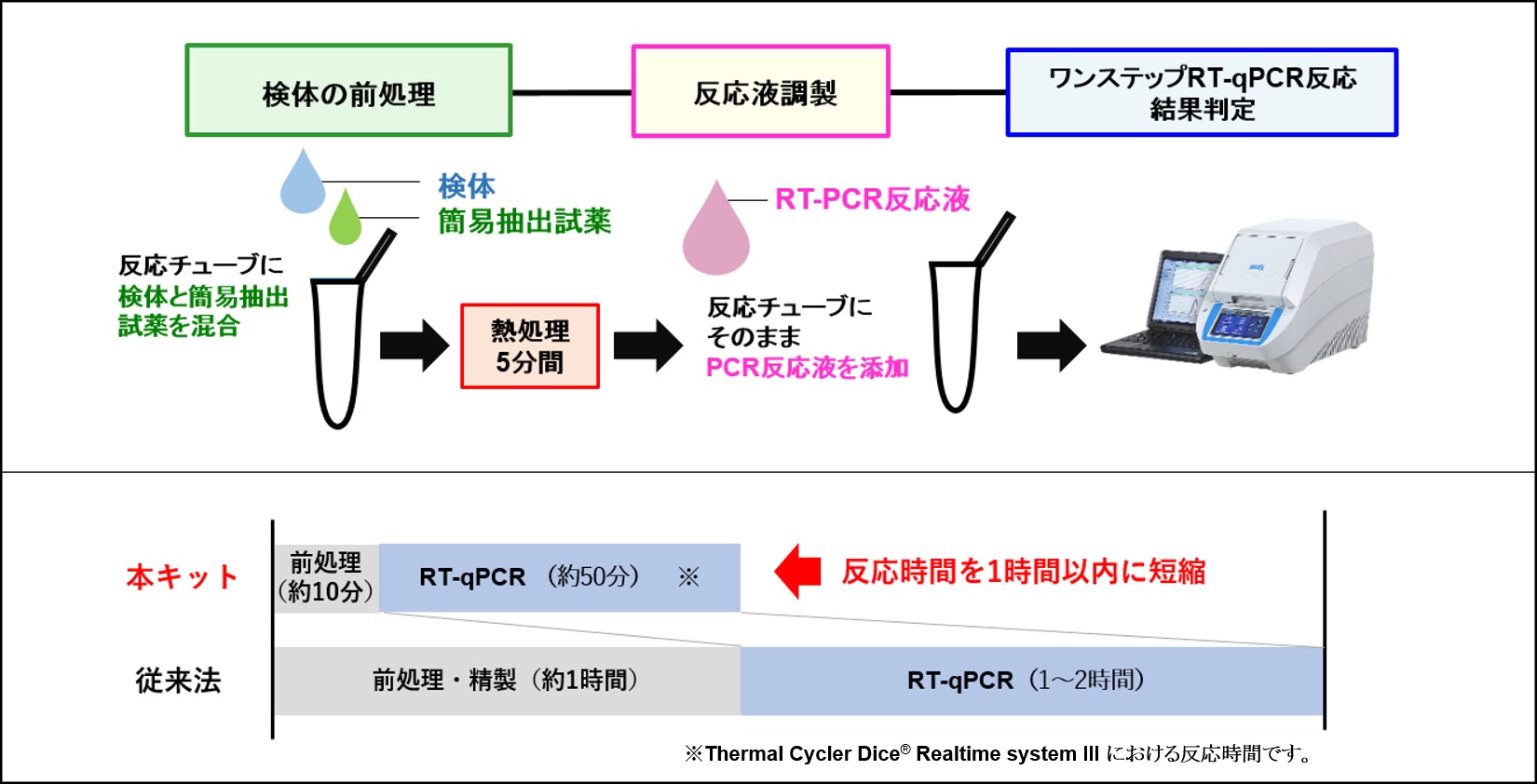
新型コロナウイルスの ハイスループット PCR 検査法を開発
タカラバイオ株式会社の米国子会社である Takara Bio USA, Inc.(米国カリフォルニア 州、以下 TBUSA 社)
2020 年 6 月8日(現地時間)に、新型コロナウイルスのハイスルー プット PCR 検査法の開発に関するプレスリリースを行いました。
https://ir.takara-bio.co.jp/ja/news_all/news_IR/auto_20200610441125/pdfFile.pdf
Takara Bio USA, Inc. and bioSyntagma, Inc. develop method for large-scale automated COVID-19 testing
DATE: June 8, 2020
AUTHOR: Takara Bio USA, Inc.
CATEGORIES: Press release
Mountain View, CA—
June 8, 2020—
Takara Bio USA, Inc. (TBUSA), a pioneering life science instrument and reagent company and wholly owned subsidiary of Takara Bio Inc.,
collaborated with bioSyntagma, Inc. and their partners to develop and validate a new high-throughput method for detecting SARS-CoV-2.
The method
employs automation technology and reagents from TBUSA to detect viral RNA via real-time PCR and will enable rapid, large-scale testing of thousands of patient samples per day.
The method uses TBUSA’s SmartChip real-time PCR instrument, chips, and reagents to run 5,184 reactions per chip in less than 30 minutes of direct hands-on time.
Each reaction is at nanoliter scale, which reduces variability via elimination of the standard preamplification step and reduces costs via decreased reagent volume.
The trusted SmartChip Real-Time PCR System is already widely used for detection of antibiotic and antimicrobial resistance around the world, and is ideally suited to address the major need for rapid and accurate SARS-CoV-2 detection.
President of TBUSA Carol Lou states,
As shelter-in-place orders are lifted, controlling the COVID-19 pandemic will depend on our ability to detect SARS-CoV-2 from a large number of samples with precision, reproducibility, and speed.
To support this effort,
we optimized our existing chemistries and developed SmartChip protocols that maximize the number of samples processed while minimizing costs.
The work we have accomplished with bioSyntagma, plus their partners’ further development of diagnostic tests based on our work, will contribute to comprehensive and faster detection of COVID-19.
Scottsdale-based bioSyntagma
is a biotech spinoff of Arizona State University and serves as the development and validation partner of P2 Diagnostics, LLC.
The new SmartChip testing method
will be adopted by this and other molecular testing labs that are certified by CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) and therefore eligible to develop and perform COVID-19 diagnostic tests.
“The rapid development of this novel COVID-19 detection method
was made possible through a highly productive collaboration between bioSyntagma and TBUSA,
and the results of this effort will soon have an impact on the ability to detect SARS-CoV-2 in nasal and saliva samples from many patients,
said David Richardson, CEO of bioSyntagma.
bioSyntagma and partners
are seeking an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA for COVID-19 detection using the TBUSA SmartChip method.
Ipsum Diagnostics, LLC and Hackensack University Medical Center—two of TBUSA’s customers in the US—
have already obtained EUAs for their COVID-19 tests using Takara Bio’s one-step RT-PCR reagents.