

ソニーCSL:成層圏や低軌道でTCP/IP通信実現(動画):
Sony CSL: TCP / IP in the stratosphere and low earth orbit:
Sony CSL:在平流层和近地轨道实现 TCP/IP 通信:
ーJAXAと技術 を共同開発ー
ー完全データファイル転送の実証に成功ー
ソニーCSL
JAXA1月27日、
「成層圏/低軌道における光通信事業」に不可欠な、
「エラー環境下での完全なデータファイル転送技術」の実証に成功した。
- エラーが発生しやすい、
- 低品質な通信環境を模擬することで、
- 地上実験により実証に成功した。
「高高度自由空間光通信」の実用化:
成層圏や宇宙といった、高高度自由空間光通信の実用化においては、
「通信機器の軽量化や省電力化、通信の高速化」が求められる。
エラー環境下でのファイル転送技術:
受信機器が、レーザー光を安定受信することは、極めて難しい。
- 通信機器間では、機体の姿勢変動により、
- 送信側機器の射出レーザー光を、
- 受信機器側で安定して正確に受信できない。
TCP/IPプロトコルの適用:
「受信機機内や環境に起因したノイズで、デジタル信号の符号誤り」が多く生じる。
「安定的通信品質での利用を前提としているTCP/IPプロトコル」を適用できない。
ソニーCSLとJAXAが開発:
低軌道衛星同士や、成層圏無人機との間で利用可能な、
光インターネットサービス事業を目指し、J-SPARCを進めて技術開発してきた。
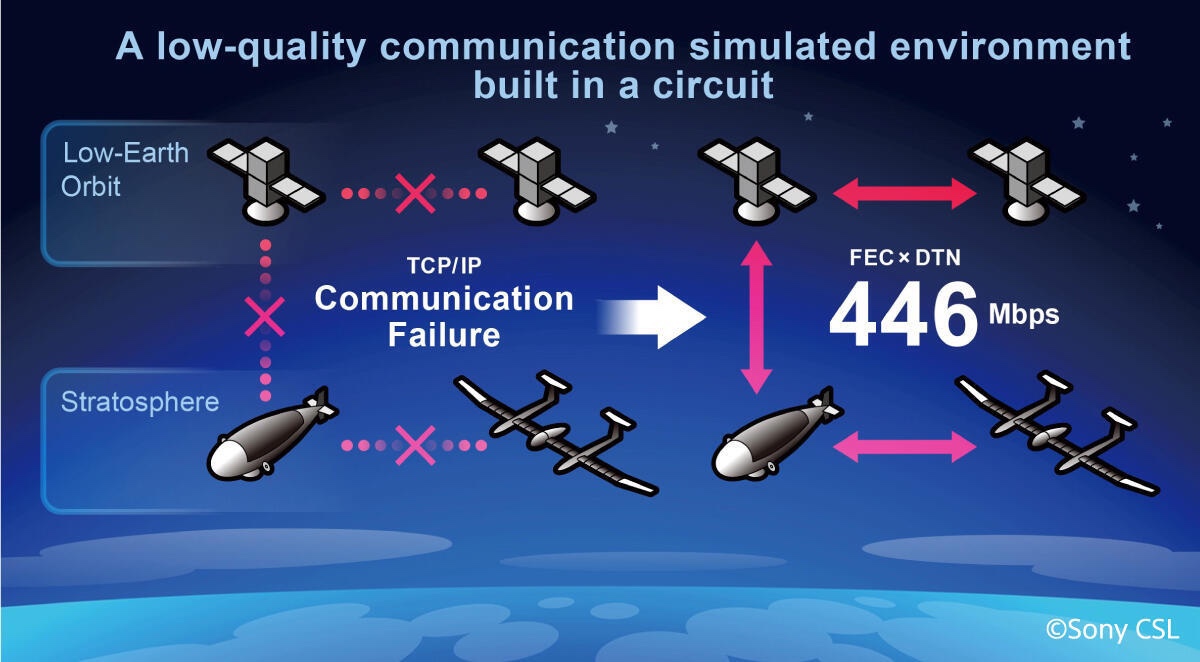
今回の実証実験:
Gigabit Ethernet回線を実験的に構築、自由空間光通信の符号誤り率を模擬して、
低品質で、インターネット通信が不可能な通信環境を作成した。
446Mbpsの完全ファイル転送:
ソニーCSLとJAXA:
446Mbpsの通信速度で無欠損の完全データのファイル転送に成功したのだ。
レーザー光読取技術をベース:
ソニーグループがBlu-ray Disc・光デバイスで長年培ったレーザー光読み取り技術をベースにした。
ソニーCSL:
レーザー光読み取りでの、誤り訂正(FEC)技術を開発した。JAXA:
JAXAが保有する遅延途絶耐性ネットワーク(DTN)技術を組み合わせた。両者の2信号処理技術を用いることで実現した。
高速/大容量/低消費電力通信の実現:
- 低軌道や成層圏における、
- 2地点間光インターネットに必要な、
- 高速/大容量/低消費電力の通信の実現できる。
今後、
- 低軌道衛星コンステレーションや、
- 成層圏無人機の光端末間通信サービスに、
- 幅広く事業展開できることが期待される。
– PC Watch
https://pc.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/news/1383828.html
Sony CSL and JAXA Successfully Demonstrate Complete Data File Transfer in Error-Prone Environment, Forming Technical Foundations for Internet Service in Stratosphere & Outer Space
January 27, 2022
JAXA
Sony CSLas part of JAXA’s Space Innovation through Partnership and Co-creation (J-SPARC)1 program,
have successfully conducted an experiment to transfer a complete data file in a simulated low-quality and error-prone communications environment.
Accomplishing transfer data in a strict environment is key to future stratospheric and low-Earth orbit optical communications,
Sony CSL and JAXA have established the technical foundations for the commercialization of this technology.
For free-space optical communication to become practical in the extreme altitudes of the stratosphere and beyond,
communications equipment must be compact, energy-efficient, and capable of fast transmission speeds.
Additionally, the long distances between communications devices mean that
any changes to their orientation
can result in laser signals from the sending device not being stably received by the receiving device.Signal noise
could also occur in the environment and the receiving device causing signal errors.Because of these factors,
the standard internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) is unable to secure stable communications link between devices in such environments.The partnership between Sony CSL and JAXA
aims to establish an optical internet service between low orbit satellites and unmanned aircraft for stratospheric telecommunications.
An experimental environment with the bit error rate of free-space optical communication built on a Gigabit Ethernet line
was simulated in such a manner that communications through general Internet communication was impossible due to low quality.
The data file was successfully transferred, complete and uncorrupted, at a speed of 446 Mbps2 under such conditions.
This result indicates
the possibility for high-quality and high-speed communications similar to a terrestrial internet service, albeit free-space optical communication.The communication
was done using a signal processing method which combines Sony CSL’s Forward Error Correction (FEC),which is based on the Sony Group laser reading technology that has been refined through the development of optical technologies such as Blu-ray, and JAXA’s Delay/Disruption-Tolerant Networking (DTN).
With this successful demonstration,
a solution is in sight to the high speed, high bandwidth, and low energy consumption requirements of point-to-point optical internet service in the stratosphere or low-Earth orbit.We expect this to lead to future business development opportunities for communication services,
such as small optical communication terminals installed on low-Earth orbit satellite constellations,5 or unmanned aircraft for stratospheric telecommunications.