

-与JAXA共同开发技术-
-完整数据文件传输成功演示-
索尼 CSL
日本宇宙航空研究开发机构
1月27日,
“平流层/近地轨道光通信业务”不可或缺
成功演示“错误环境下完整的数据文件传输技术”。
容易出错,
通过模拟低质量的通信环境
地面实验演示成功。
“高空自由空间光通信”的实际使用:
在平流层、太空等高空自由空间光通信的实际应用中,
要求“通信设备的轻量化、省电化、通信的高速化”。
错误环境下的文件传输技术:
接收装置稳定地接收激光束是极其困难的。
通信设备之间,由于飞机姿态的变化
发射装置的发射激光,
接收设备侧无法实现稳定准确的接收。
TCP/IP协议的应用:
经常发生“由于接收机内部和环境引起的噪声导致的数字信号中的信号错误”。
“以使用稳定的通信质量为前提的 TCP/IP 协议”不能应用。
由 Sony CSL 和 JAXA 开发:
在低地球轨道卫星之间和平流层无人机之间可用,
针对光互联网服务业务,我们推广了J-SPARC并开发了技术。
本演示实验:
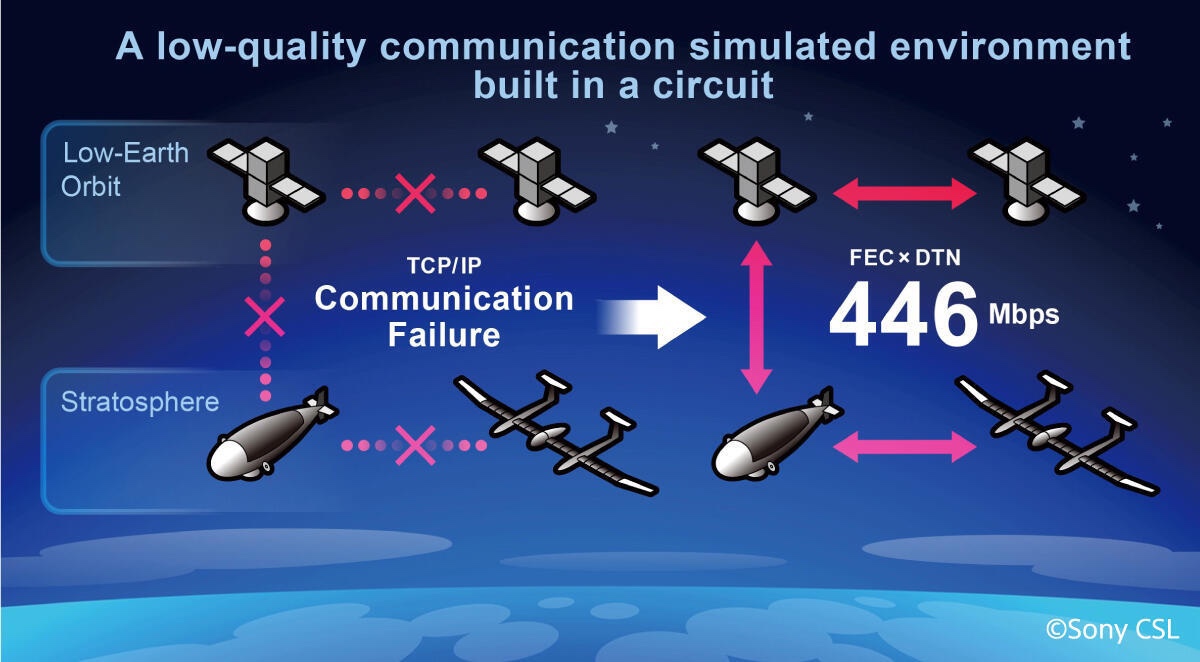
实验搭建千兆以太网线路,模拟自由空间光通信的误码率,
创造了一个低质量、没有互联网通信的通信环境。
446Mbps 完整文件传输:
索尼 CSL 和 JAXA:
它成功地以 446 Mbps 的通信速度无损地传输了完整的数据文件。
基于激光读取技术:
它基于索尼集团多年来为蓝光光盘和光学设备培育的激光读取技术。
索尼中超:
开发用于激光读取的纠错 (FEC) 技术。
日本宇宙航空研究开发机构:
结合 JAXA 的延迟容忍网络 (DTN) 技术。
它是通过使用两种信号处理技术来实现的。
实现高速/大容量/低功耗通信:
在低地球轨道和平流层
两点之间的光学互联网所必需的,
可实现高速/大容量/低功耗通信。
从现在开始,
低地球轨道卫星星座,
用于平流层无人机光学终端之间的通信服务
预计业务可以广泛扩展。
–PC 手表
https://pc.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/news/1383828.html
Sony CSL and JAXA Successfully Demonstrate Complete Data File Transfer in Error-Prone Environment, Forming Technical Foundations for Internet Service in Stratosphere & Outer Space
January 27, 2022
JAXA
Sony CSLas part of JAXA’s Space Innovation through Partnership and Co-creation (J-SPARC)1 program,
have successfully conducted an experiment to transfer a complete data file in a simulated low-quality and error-prone communications environment.
Accomplishing transfer data in a strict environment is key to future stratospheric and low-Earth orbit optical communications,
Sony CSL and JAXA have established the technical foundations for the commercialization of this technology.
For free-space optical communication to become practical in the extreme altitudes of the stratosphere and beyond,
communications equipment must be compact, energy-efficient, and capable of fast transmission speeds.
Additionally, the long distances between communications devices mean that
any changes to their orientation
can result in laser signals from the sending device not being stably received by the receiving device.Signal noise
could also occur in the environment and the receiving device causing signal errors.Because of these factors,
the standard internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) is unable to secure stable communications link between devices in such environments.The partnership between Sony CSL and JAXA
aims to establish an optical internet service between low orbit satellites and unmanned aircraft for stratospheric telecommunications.
An experimental environment with the bit error rate of free-space optical communication built on a Gigabit Ethernet line
was simulated in such a manner that communications through general Internet communication was impossible due to low quality.
The data file was successfully transferred, complete and uncorrupted, at a speed of 446 Mbps2 under such conditions.
This result indicates
the possibility for high-quality and high-speed communications similar to a terrestrial internet service, albeit free-space optical communication.The communication
was done using a signal processing method which combines Sony CSL’s Forward Error Correction (FEC),which is based on the Sony Group laser reading technology that has been refined through the development of optical technologies such as Blu-ray, and JAXA’s Delay/Disruption-Tolerant Networking (DTN).
With this successful demonstration,
a solution is in sight to the high speed, high bandwidth, and low energy consumption requirements of point-to-point optical internet service in the stratosphere or low-Earth orbit.We expect this to lead to future business development opportunities for communication services,
such as small optical communication terminals installed on low-Earth orbit satellite constellations,5 or unmanned aircraft for stratospheric telecommunications.