

ソニー:宇宙と地上間、双方向光通信に成功:小型光通信実験装置「SOLISS」(動画):
Sony:Small Optical Link for International Space Station (SOLISS):
索尼:国际空间站的小型光学链路(SOLISS)
ソニー:
~国際宇宙ステーションからEthernet経由で光地上局が高精細度画像を受信~
JAXA/NICT/ソニーCSL:
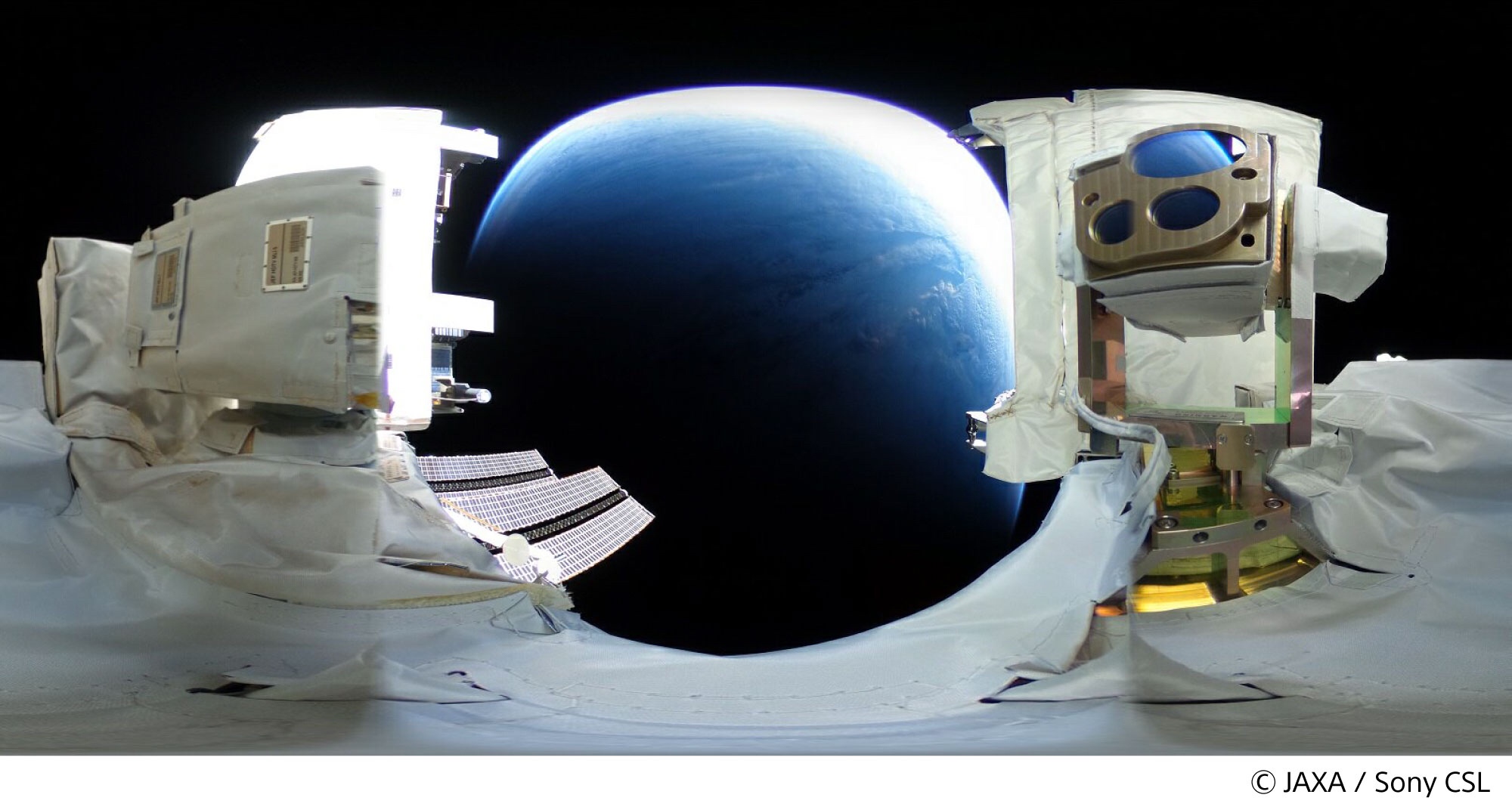
ISSの「きぼう」日本実験棟に設置した小型光通信実験装置「SOLISS」(Small Optical Link for International Space Station)、
- NICTの光地上局との間で、
- 双方向光通信リンクを確立し、
- Ethernet経由での、
高精細度(HD)画像伝送に成功しました。
これは、小型衛星搭載用/光通信機器として、Ethernetによる通信を実現した世界初の事例となります。
port32946-1:
「SOLISS」からHD画像が、光通信で伝送されました。
「SOLISS」は、2019年9月、ISSの「きぼう」船外実験プラットフォームに設置。
その後、軌道上と光地上局との間で双方向光通信リンクを確立すべく、各種パラメータを調整。
毎週一回程度の頻度で通信試験を行ってきました。
2019年10月25日:
光地上局への光ダウンリンク指向制御を確立。
2020年3月5日:
「SOLISS」と光地上局との間で波長1.5µmレーザ光による双方向光通信リンクの確立に成功しました。
2020年3月11日:
「SOLISS」から 100 MbpsのEthernetによる通信を用いてHD画像を光地上局で受信することに成功しました。
JAXA/ソニー株式会社:
2016年より共同で研究を行ってきました。
JAXA宇宙探査イノベーションハブの研究提案の枠組みを利用しています。、
衛星間や地上との大容量リアルタイムデータ通信の実現を目指します。
2017年から:
ソニーCSL、JAXAの基盤研究を、引き継ぎました。
JAXA/ソニーCSLが、長距離空間大容量データ通信を目的とする「SOLISS」を共同開発。
「光通信部にはソニーが長年培ってきた光ディスク技術」が、使用されています。
JAXA:
「きぼう」日本実験棟を通じて、
2019年9月、宇宙ステーション補給機「こうのとり」8号機で、「SOLISS」をISSへ送り届けました。
「きぼう」日本実験棟の船外実験プラットフォーム/中型曝露実験アダプター(i-SEEP)に設置。
NICT/ソニーCSL:
「SOLISS」と光地上局との間の双方向通信実証に向けて2018年より共同で研究を実施してきました。
NICT:
「SOLISS」の開発、NICTが保有している衛星搭載用光通信ターミナルの開発技術を基にした知見を提供。
「SOLISS」軌道上実証試験に必要な計測や実験を共同で行ってきました。
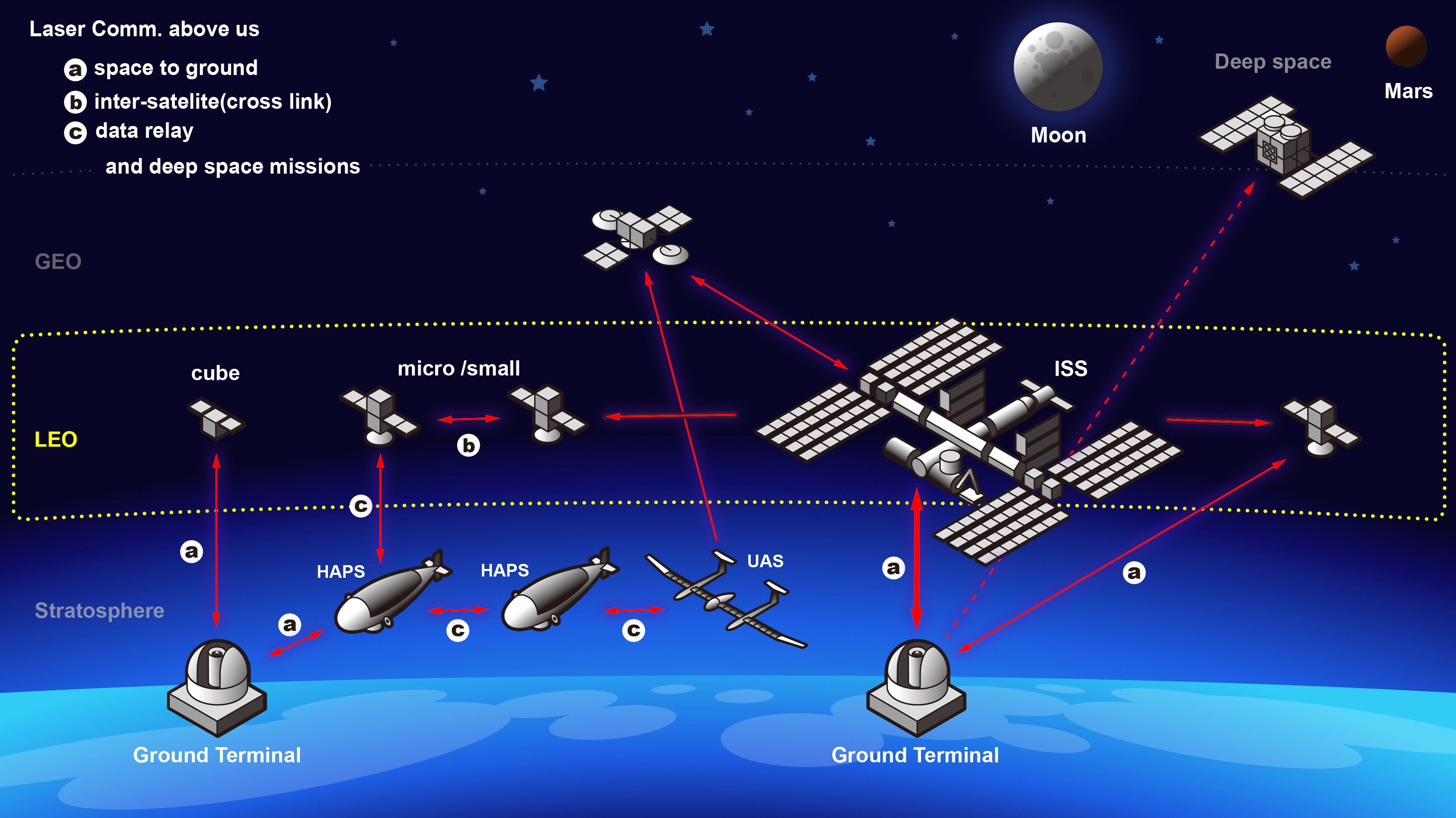
光には電波と比べて高速大容量の通信を可能とする特長があります。
光双方向通信実験:
今回、「既に確立された光ディスク技術と標準規格であるEthernetによる光双方向通信実験が成功したこと」によって、
今後、
- 宇宙空間における地球周回軌道を起点に、
- 衛星間/地上との超高速(低遅延)データ通信や、
- 大容量リアルタイムデータ通信、
- の実現や汎用化などが期待されます。
今後、通信の安定性の向上などを目指した実験運用は2020年6月初旬頃まで継続する予定です。
Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc.
https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/press/prs20200423/
Sony:Small Optical Link for International Space Station (SOLISS)
Succeeds in Bidirectional Laser Communication Between Space and Ground Station
JAXA,NICT,Sony CSL
announced today that they were successful in establishing a bidirectional laser communication link
between
SOLISS (Small Optical Link for International Space Station), installed in the Exposed Facility of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) “Kibo” of the International Space Station (ISS)
and
the optical ground station for satellite communications (hereinafter, optical ground station) *1 of NICT,
and in transmitting high-definition (HD) image data via Ethernet.
This marks the first time in the world that bidirectional symmetric Ethernet links have been established by using laser communication devices designed for small satellites.
The SOLISS system
was installed on the Kibo’s exposed facility on the ISS in September 2019.
Since then, in order to establish a bidirectional laser communication link between the on-board system and the optical ground station, communication tests have been conducted about once a week, weather permitting, while making adjustments to various parameters.
As a result,
on October 25, 2019,
an optical downlink (orientation control),
a fine pointing control from SOLISS to the optical ground station was successfully established,
on March 5, 2020,
bidirectional laser communication link with the optical ground station using a laser beam (with a wavelength of 1.5 µm) was successfully established.
on March 11,
HD images were successfully received at the optical ground station from SOLISS via 100 Mbps Ethernet.
JAXA and Sony Corporation have been conducting joint research since 2016 with the aim of establishing real-time, mass-data communication system for future inter-satellite communications and communications with ground stations under the Request for Proposal (RFP) joint study framework of the JAXA Space Exploration Innovation Hub Center.*2 Starting in 2017,
Sony CSL undertook the task of basic research, and JAXA and Sony CSL jointly developed SOLISS for the purpose of realizing mass-data communication over long distances.
The optical communication unit employs the optical disc technology that Sony Corporation has cultivated over many years.
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology