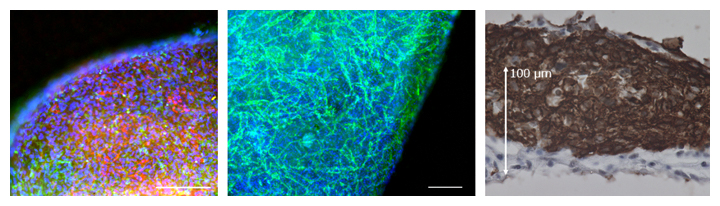
図1 動的トレーニング培養により得られたヒトiPS細胞からの三次元的なマイクロ心臓組織
(左)心筋細胞(赤)および血管壁細胞(血管内皮をとりまく細胞;緑)。スケールバーは200μm。
(中)血管内皮細胞(緑)。マイクロ心臓組織内に血管網が形成されている。スケールバーは200μm。
(右)心筋層(茶)。マイクロ心臓組織は150μmを超える厚みを持つ。
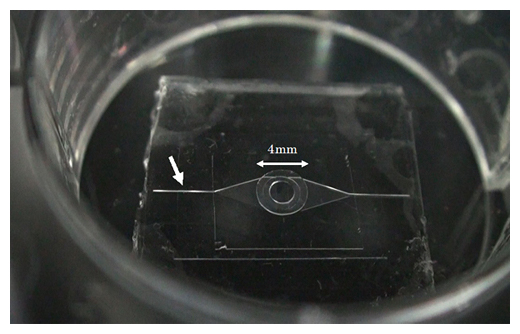
図2 MEMS技術により作製したマイクロ流体チップ
中央の円形(直径4mm)は下部に直径2mmの凸部を持ち、マイクロ心臓を上に載せると、その拍動が下のマイクロ流路に伝えられる仕組み。白矢印は、蛍光粒子を流すマイクロ流路の流入側幅100μmの溝。
理研:iPS細胞で「ハートオンチップ」:マイクロデバイスを開発(動画):
RIKEN: “Heart-on-chip” with iPS cells: Developed microdevices:
RIKEN:具有iPS单元的“芯片上心脏”:已开发的微型设备
理研:
共同研究グループ:
- ヒトiPS細胞技術と、
- マイクロデバイス技術を用いて、
「ハートオンチップ[4]型マイクロデバイス」を開発。
ハートオンチップ[4]型マイクロデバイスは、高感度にヒト心臓の機能を評価します。
本研究成果:
本研究成果は、iPS細胞を用いた心臓の再生医療や創薬研究に貢献します。
心臓病に対する再生医療:
心臓病に対する再生医療や創薬研究において、ヒトiPS細胞から人工的に作製された三次元的なヒト心臓組織の応用が、期待されています。
人工心臓組織の機能評価:
従来の問題:
再現された人工心臓組織の機能を高感度に評価できる系は、確立されていませんでした。
今回の開発:
今回、共同研究グループは、「ハートオンチップ型マイクロデバイス」を開発し、これまでにない高感度な人工心臓の機能評価系を確立しました。
細胞シート状の3Dマイクロ心臓組織:
ヒトiPS細胞から:
動的トレーニング培養[5]によって厚みを持たせた、細胞シート状の三次元的なマイクロ心臓組織を開発。
微細加工技術を用いて:
マイクロ流路による、流体的な心臓機能の評価系を、組み合わせました。
本研究は、科学雑誌『Scientific Reports』オンライン版(11月5日付)に掲載されます。
理化学研究所
https://www.riken.jp/press/2020/20201105_5/
Establishment of a heart-on-a-chip microdevice based on human iPS cells for the evaluation of human heart tissue function
Abstract
Human iPS cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (CMs) hold promise for drug discovery for heart diseases and cardiac toxicity tests.
To utilize human iPSC-derived CMs,
the establishment of three-dimensional (3D) heart tissues from iPSC-derived CMs and other heart cells,and a sensitive bioassay system to depict physiological heart function are anticipated.
We have developed a heart-on-a-chip microdevice (HMD)
as a novel system consisting of dynamic culture-based 3D cardiac microtissues
derived from human iPSCs and microelectromechanical system (MEMS)-based microfluidic chips.The HMDs
could visualize the kinetics of cardiac microtissue pulsations by monitoring particle displacement,which enabled us to quantify the physiological parameters, including fluidic output, pressure, and force.
The HMDs
demonstrated a strong correlation between particle displacement and the frequency of external electrical stimulation.The transition patterns
were validated by a previously reported versatile video-based system to evaluate contractile function.The patterns
are also consistent with oscillations of intracellular calcium ion concentration of CMs, which is a fundamental biological component of CM contraction.The HMDs showed a pharmacological response to isoproterenol,
a β-adrenoceptor agonist, that resulted in a strong correlation between beating rate and particle displacement.
Thus, we have validated the basic performance of HMDs as a resource for human iPSC-based pharmacological investigations.
Scientific Reports