Kyoto Univ:ALS治療薬候補を発見:bosutinib:de médicaments candidats pour la SLA:ALS-Medikamentenkandidaten :Discovered ALS drug candidates:發現ALS候選藥物:
ーALS患者からiPS細胞を作製ー
京都大学:
難病・ALSの患者のiPS細胞を使った治療薬の開発へさらなる治験をはじめます。
ALSとは:
筋肉の運動を司る神経細胞に、異常タンパク質が蓄積し、
細胞死を起こして、全身や呼吸器を麻痺させる難病です。
京都大学iPS細胞研究所
井上治久教授研究グループ:
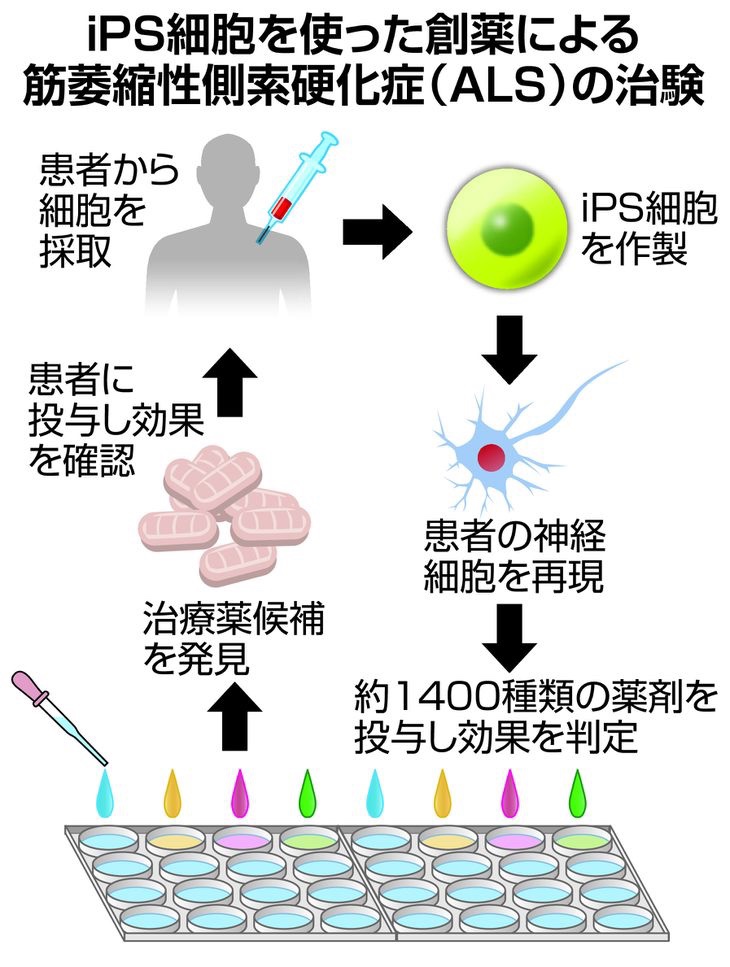
ALS患者の細胞からiPS細胞を作製しました。
それを用いて異常たんぱく質の蓄積を防ぐ、治療薬の候補を発見。
効果と安全性を確認:
今回、これまでより治験者数を増やします。
投薬する期間を半年間に伸ばして、
病気の進行を止める効果と、安全性を確認します。
テレビ大阪ニュース
https://www.tv-osaka.co.jp/news/articles/20220415-00000005/
Université de Kyoto : découverte de médicaments candidats pour la SLA : le médicament bosutinib
-Créer des cellules iPS à partir de patients SLA-
Université de Kyôto :
Nous allons commencer d’autres essais cliniques pour développer des médicaments thérapeutiques utilisant des cellules iPS pour les patients atteints de maladies incurables et de la SLA.
Qu’est-ce que la SLA :
Des protéines anormales s’accumulent dans les cellules nerveuses qui contrôlent les mouvements musculaires,
C’est une maladie incurable qui provoque la mort cellulaire et paralyse tout le corps et les organes respiratoires.
Centre de recherche et d’application sur les cellules iPS, Université de Kyoto
Professeur Haruhisa InoueGroupe de recherche:
J’ai fabriqué des cellules iPS à partir de cellules de patients SLA.
En l’utilisant, nous avons trouvé un candidat pour un médicament thérapeutique qui empêche l’accumulation de protéines anormales.
Efficacité et sécurité confirmées :
Cette fois, nous allons augmenter le nombre d’enquêteurs.
Prolonger la période de dosage à six mois,
Confirmer l’effet et la sécurité de l’arrêt de la progression de la maladie.
Nouvelles de la télévision d’Osaka
Universität Kyoto: ALS-Medikamentenkandidaten entdeckt: das Medikament Bosutinib
-Herstellung von iPS-Zellen von ALS-Patienten-
Universität Kyoto:
Wir werden weitere klinische Studien starten, um therapeutische Medikamente unter Verwendung von iPS-Zellen für Patienten mit hartnäckigen Krankheiten und ALS zu entwickeln.
Was ist ALS:
Abnormale Proteine sammeln sich in Nervenzellen an, die die Muskelbewegung steuern,
Es ist eine hartnäckige Krankheit, die den Zelltod verursacht und den ganzen Körper und die Atmungsorgane lähmt.
Zentrum für iPS-Zellforschung und -anwendung, Universität Kyoto
Professor Haruhisa InoueForschungsgruppe:
Ich habe iPS-Zellen aus Zellen von ALS-Patienten hergestellt.
Damit haben wir einen Kandidaten für ein therapeutisches Medikament gefunden, das die Ansammlung abnormaler Proteine verhindert.
Bestätigte Wirksamkeit und Sicherheit:
Diesmal werden wir die Zahl der Ermittler erhöhen.
Verlängerung der Einnahmedauer auf ein halbes Jahr,
Bestätigen Sie die Wirkung und Sicherheit des Stoppens des Fortschreitens der Krankheit.
TV Osaka Nachrichten
Announcement of a clinical trial for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Kyoto University
April 03, 2019
1. Main Point The Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA),
Kyoto University, has announced a new Phase 1*1) clinical trial
for the drug bosutinib to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the Kyoto University Hospital (KUH).
Leading the project from CiRA
is Professor Haruhisa Inoueand from KUH is Professor Ryosuke Takahashi.This trial has received approval
from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA).2. Research Background ALS
is a disease in which motor neurons progressive die.Their death causes muscle atrophy and weakness, ultimately leading to patient death.
The only approved treatments are riluzole and edaravone,
which extend the patient’s life at best a few months and relieve patient symptoms.
Prof. Inoue has been researching ALS
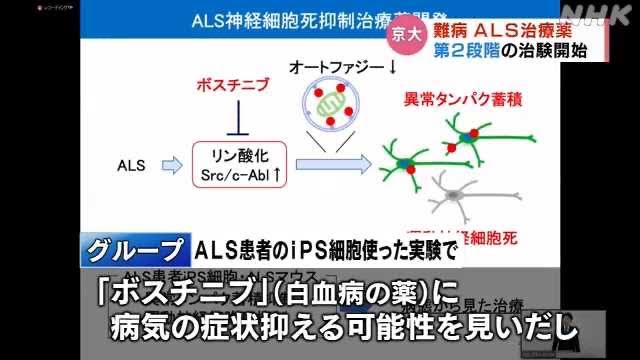
by generating induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells from ALS patients.Differentiating the iPS cells to motor neurons and testing a series of drug compounds led to the discovery
that bosutinib could have a substantial effect on preventing motor neuron death.
Bosutinib is currently used in the clinic to treat chronic myeloid leukemia.
However, in motor neurons,
Inoue foundthat it prevents the abnormal accumulation of proteins associated with ALS and improves cell survival.
News and Events | CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application,
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/pressrelease/news/190403-110000.html