Axelspace: 100kgでGbps衛星間通信!
Communication inter-satellites en Gbps avec 100kg !
Gbps Inter-Satelliten-Kommunikation mit 100kg!
Gbps inter-satellite communication with 100kg !
Axelspace:100公斤Gbps星間通信!
ーradiation-resistant Ka-band radio for LEO communication satellite constellationー
アクセルスペース
東京工業大学2月20日、
東京工業大学とともに、「放射線耐性の高い無線機の開発」に成功した。
Beyond 5G:
地上通信インフラに加えて、宇宙通信ネット(Non-Terrestrial Network:NTN)を利用。
地球低軌道・光通信ネットワーク:
ー高度2000km以下の地球低軌道(LEO)ー
「衛星同士が光通信するネットワークの構築」が、次世代キーテクノロジーだ。
低軌道衛星コンステレーション:
低軌道衛星コンステレーション研究やサービス化が、急速に進んでいる。
- 人工衛星に搭載する無線機についても、
- 高速通信で、宇宙環境に耐えられる、
- 衛星搭載用・無線機の需要が進む。
NICT受託研究:
ー「Beyond 5G次世代小型衛星コンステレーション」、「電波・光ハイブリッド通信技術」の開発ー
- 100kg衛星で、Gbps衛星間通信を行い、
- 地上との通信が可能な、小型衛星を用いて、
- 「電波・光ハイブリッド通信衛星ネットワーク」を構築する。
電波・光ハイブリッド通信:
ー光通信リンク確立のため、精密な衛星姿勢制御が必須ー
「光通信は電波に比べて高速に通信できるが、雲があると通信不能になる」という欠点がある。
高速通信帯域(27~40GHz、Ka帯)の使用:
そのため、「電波通信のなかで高速化が期待できる通信帯域(27~40GHz、Ka帯)」を使用する。
「Ka帯で電波・光ハイブリッドな通信システム」を構築する。
放射線が厳しい宇宙空間:
ー地上の電子部品は、宇宙放射線により劣化ー
人工衛星の内側と外側では、放射線を受ける量が大きく異なる。
外側に配置された電子部品は、
- 内側に配置された電子部品よりも、劣化度が高い。
- そのため、人工衛星の内側に電子部品を配置する。
放射線を減らす目的で、シールドで覆い保護するのだ。
電子部品劣化を防止:
宇宙空間に打ち上げた後、
- 「最新の劣化状況を、的確に把握すること」は難しい。
- 「設計段階で、軌道寿命から計算した電子部品の劣化量」を考慮する。
「劣化が最大でも、システムとして機能喪失しないように設計すること」が求められる。
フェーズドアレイIC:
ー新開発したフェーズドアレイICー
IC自体に、劣化量を測定する放射線センサーを内蔵した。
- このICを利用した無線機を使うことで、
- フェーズドアレイ上のあらゆる位置で、
- 放射線劣化量を検出できるようになる。
無線機の性能劣化を補正:
パラメータ再調整で、フェーズドアレイ無線機の性能悪化を防止する。
Kaバンド通信搭載:
数年以内に、
- 受信系フェーズドアレイ無線機、
- 送信系フェーズドアレイ無線機、
- 広帯域Ka帯送受信機を統合する。
「高放射線耐性で省電力な、Kaバンド通信搭載の実証小型衛星」を打ち上げる。
今回の成果:
半導体関連の国際学会「ISSCC 2023」で、発表する。
3月米国で開催される「Satellite 2023」で展示予定。
(UchuBiz) – Yahoo!ニュース
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/ad1e5386b310cb06b88d8c96a0e6b8f2ce16123c
衛星用の光通信技術のイノベーション:アクセルスペース ーTHE SPACE INDUSTRY IN 2023 | WIRED.jp
https://wired.jp/article/the-space-industry-in-2023-axelspace/
Axelspace : Communication inter-satellites en Gbps avec un satellite de 100kg !
ーRadio en bande Ka résistante aux radiations pour la constellation de satellites de communication LEOー
espace axel
Institut de technologie de Tokyo
20 février,
En collaboration avec l’Institut de technologie de Tokyo, nous avons réussi à “développer des équipements radio à haute résistance aux radiations”.
Au-delà de la 5G :
En plus de l’infrastructure de communication terrestre, un réseau de communication spatiale (Non-Terrestrial Network : NTN) est utilisé.
Orbite terrestre basse et réseau de communication optique :
– Orbite terrestre basse (LEO) en dessous de 2000 km d’altitude –
“Construire un réseau dans lequel les satellites communiquent optiquement” est la technologie clé de la prochaine génération.
Constellation de satellites en orbite terrestre basse :
La recherche et la commercialisation des constellations de satellites en orbite terrestre basse progressent rapidement.
Quant aux radios installées sur les satellites,
communication à grande vitesse, peut résister à l’environnement spatial,
La demande d’équipements sans fil montés sur satellite augmente.
Recherche commandée par les NTIC :
ーDéveloppement de la “constellation de petits satellites de nouvelle génération au-delà de la 5G” et de la “technologie de communication hybride radio/optique”ー
Satellite 100kg, communication inter-satellite Gbps,
À l’aide de petits satellites capables de communiquer avec le sol,
Construire un réseau satellitaire de communication hybride radio/optique.
Communication hybride radio/optique :
-Le contrôle précis de l’attitude du satellite est essentiel pour établir une liaison de communication optique-
“La communication optique peut communiquer à grande vitesse par rapport aux ondes radio, mais il y a un inconvénient qu’il devient impossible de communiquer en présence de nuages.”
Utilisation de la bande de communication haut débit (27-40 GHz, bande Ka) :
Par conséquent, nous utiliserons la “bande de communication (27 à 40 GHz, bande Ka) où le haut débit peut être attendu en communication radio”.
Construire un système de communication hybride radio/optique dans la bande Ka.
Espace extra-atmosphérique où le rayonnement est sévère :
-Les pièces électroniques au sol se détériorent à cause du rayonnement cosmique-
La quantité de rayonnement reçu diffère considérablement entre l’intérieur et l’extérieur du satellite.
Composants électroniques placés à l’extérieur
Le degré de détérioration est supérieur à celui des composants électroniques placés à l’intérieur.
Par conséquent, des composants électroniques sont placés à l’intérieur du satellite.
Il est recouvert d’un écran dans le but de réduire le rayonnement.
Empêche la détérioration des composants électroniques :
Après le lancement dans l’espace,
Il est difficile de “saisir avec précision la dernière situation de détérioration”.
Considérez la “quantité de dégradation des pièces électroniques calculée à partir de la durée de vie orbitale au stade de la conception”.
Il est demandé de « concevoir de manière à ce que le système ne perde pas sa fonction même si la détérioration est maximale ».
Circuit intégré à réseau phasé :
ー Circuit intégré à réseau phasé nouvellement développé ー
Le circuit intégré lui-même possède un capteur de rayonnement intégré qui mesure la quantité de détérioration.
En utilisant un appareil sans fil qui utilise ce CI,
à n’importe quelle position sur le réseau phasé,
Il devient possible de détecter la quantité de détérioration par rayonnement.
Compenser la dégradation des performances radio :
Le réajustement des paramètres empêche la détérioration des performances des radios multiéléments.
Équipé d’une communication en bande Ka :
Dans quelques années
Réception radio multiéléments,
radio à réseau phasé d’émetteur,
Intègre un émetteur-récepteur large bande Ka.
Nous lancerons un “petit satellite de démonstration équipé d’une communication en bande Ka hautement tolérante aux radiations et économe en énergie”.
Réalisations cette fois :
Présenté à ISSCC 2023, une conférence internationale liée aux semi-conducteurs.
Il sera exposé au “Satellite 2023” qui se tiendra aux Etats-Unis en mars.
(UchuBiz)-Yahoo Actualités
Innovation dans la technologie de communication optique pour les satellites : Axelspace – L’INDUSTRIE SPATIALE EN 2023 | WIRED.jp
Axelspace: Gbps Inter-Satelliten-Kommunikation mit 100kg-Satellit!
ーStrahlungsbeständiges Ka-Band-Funkgerät für LEO-Kommunikationssatellitenkonstellationー
Achsraum
Technisches Institut Tokio
20. Februar
Gemeinsam mit dem Tokyo Institute of Technology ist es uns gelungen, „Funkgeräte mit hoher Strahlungsfestigkeit zu entwickeln“.
Jenseits von 5G:
Zusätzlich zur terrestrischen Kommunikationsinfrastruktur wird ein Weltraumkommunikationsnetz (Non-Terrestrial Network: NTN) verwendet.
Niedrige Erdumlaufbahn und optisches Kommunikationsnetz:
– Low Earth Orbit (LEO) unter 2000 km Höhe –
„Der Aufbau eines Netzwerks, in dem Satelliten optisch kommunizieren“ ist die Schlüsseltechnologie der nächsten Generation.
Satellitenkonstellation im erdnahen Orbit:
Die Erforschung und Kommerzialisierung von Satellitenkonstellationen im erdnahen Orbit schreiten schnell voran.
Was die auf Satelliten installierten Radios betrifft, so
Hochgeschwindigkeitskommunikation, kann der Weltraumumgebung standhalten,
Die Nachfrage nach satellitengestützten drahtlosen Geräten wächst.
NICT-Auftragsforschung:
ーEntwicklung einer „Kleinsatellitenkonstellation der nächsten Generation jenseits von 5G“ und einer „funk/optischen Hybridkommunikationstechnologie“ー
100 kg Satellit, Gbps Inter-Satelliten-Kommunikation,
Mit kleinen Satelliten, die mit der Erde kommunizieren können,
Bauen Sie ein radio/optisches hybrides Kommunikationssatellitennetzwerk auf.
Funk/optische Hybridkommunikation:
-Präzise Satelliten-Lagekontrolle ist unerlässlich, um eine optische Kommunikationsverbindung herzustellen-
“Optische Kommunikation kann im Vergleich zu Funkwellen mit hoher Geschwindigkeit kommunizieren, hat aber den Nachteil, dass es unmöglich wird, in Gegenwart von Wolken zu kommunizieren.”
Nutzung des Hochgeschwindigkeits-Kommunikationsbands (27-40 GHz, Ka-Band):
Daher werden wir das “Kommunikationsband (27 bis 40 GHz, Ka-Band) verwenden, in dem bei der Funkkommunikation mit hoher Geschwindigkeit zu rechnen ist”.
Aufbau eines funk/optischen Hybrid-Kommunikationssystems im Ka-Band.
Weltraum, wo die Strahlung stark ist:
-Elektronische Teile am Boden verschlechtern sich durch kosmische Strahlung-
Die empfangene Strahlungsmenge ist innerhalb und außerhalb des Satelliten sehr unterschiedlich.
Außerhalb platzierte elektronische Komponenten
Der Grad der Verschlechterung ist höher als der von darin platzierten elektronischen Komponenten.
Daher werden elektronische Komponenten im Inneren des Satelliten platziert.
Es ist mit einer Abschirmung zur Reduzierung der Strahlung abgedeckt.
Verhindert die Verschlechterung elektronischer Komponenten:
Nach dem Start in den Weltraum,
Es sei schwierig, „die jüngste Verschlechterungssituation genau zu erfassen“.
Berücksichtigen Sie den „Abbaugrad elektronischer Bauteile, berechnet aus der Orbitallebensdauer in der Entwurfsphase“.
Es ist erforderlich, „das System so zu gestalten, dass es seine Funktion auch bei maximaler Verschlechterung nicht verliert“.
Phased-Array-IC:
ーNeu entwickelter Phased-Array-ICー
Der IC selbst hat einen eingebauten Strahlungssensor, der das Ausmaß der Verschlechterung misst.
Durch die Verwendung eines drahtlosen Geräts, das diesen IC verwendet,
an jeder Position auf dem Phased Array,
Es wird möglich, die Menge der Strahlungsverschlechterung zu erfassen.
Kompensieren Sie die Verschlechterung der Funkleistung:
Die Neueinstellung von Parametern verhindert eine Leistungsverschlechterung von Phased-Array-Funkgeräten.
Ausgestattet mit Ka-Band-Kommunikation:
Innerhalb einiger Jahre
Empfang von Phased-Array-Radio,
Sender Phased-Array-Radio,
Integriert einen Breitband-Ka-Band-Transceiver.
Wir werden einen „Demonstrations-Kleinsatelliten mit hochgradig strahlungstoleranter und energiesparender Ka-Band-Kommunikation“ starten.
Erfolge diesmal:
Präsentiert auf der ISSCC 2023, einer internationalen Konferenz zum Thema Halbleiter.
Es wird auf der „Satellite 2023“ ausgestellt, die im März in den Vereinigten Staaten stattfindet.
(UchuBiz)-Yahoo!-Nachrichten
Innovation in der optischen Kommunikationstechnologie für Satelliten: Axelspace – THE SPACE INDUSTRY IN 2023 | WIRED.jp
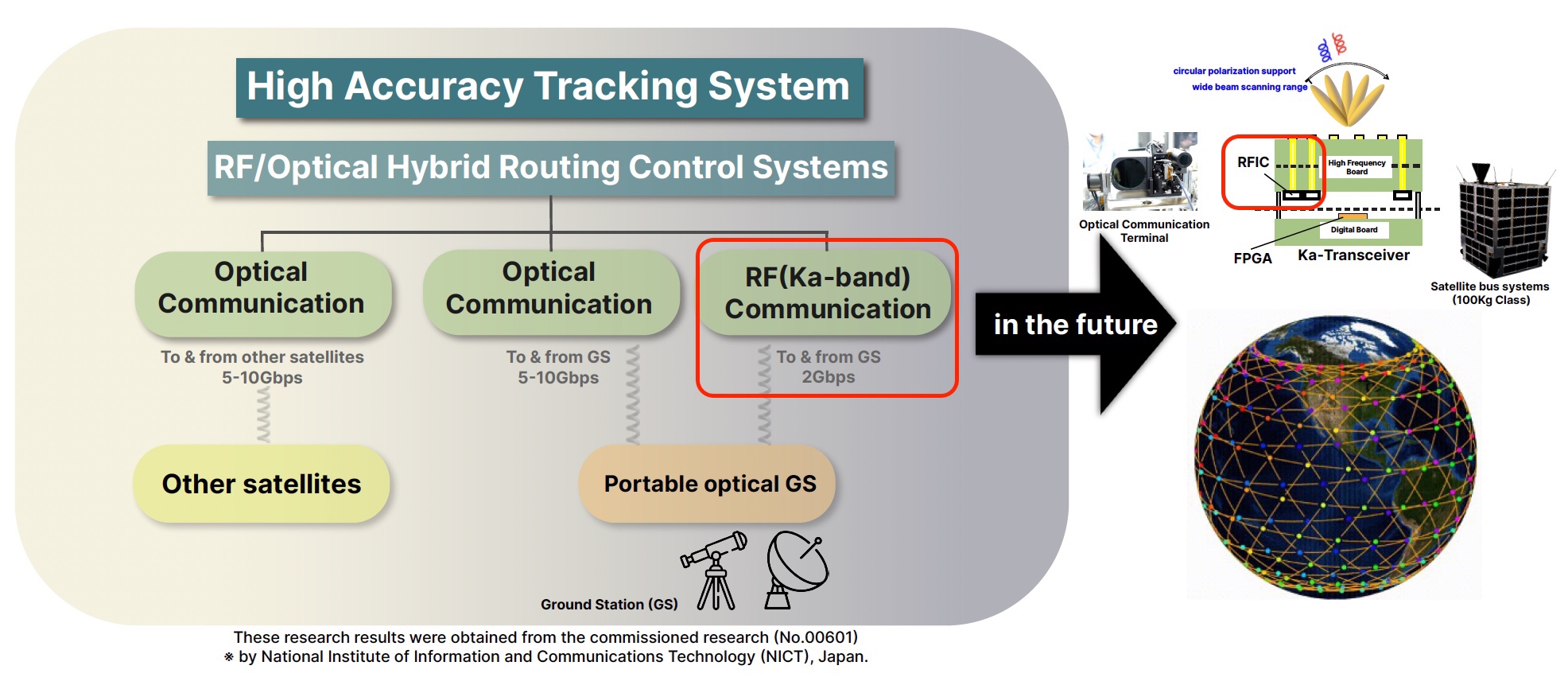
Successful collaborative development of radiation-resistant Ka-band radio for LEO communication satellite constellation
~Significant improvements in microsatellite communication speeds for Beyond 5G ~
Axelspace has been conducting the NICT-funded research project
“Research and Development of Radio-Optical Hybrid Communication Technology for B5G Next Generation Microsatellite Constellations”.
This R&D project
aims to construct a satellite constellation network of radio-optical hybrid communication using 100kg-class microsatellites.
With the goal that they can communicate with Gbps-class satellites and the ground.
Radio-optical hybrid communication requires precise satellite attitude control to establish optical communication links.
Optical communication is generally faster than radio communication.
Yet, it has the disadvantage of being completely disabled in clouds.
For that reason,
we aim to construct a hybrid radio-optical communication system.
This system will use
the Ka-band and is expected to be faster than radio communication.
In contrast,
the hybrid radio-optical communication system has a new difficult conflicting challenge.
The system must not interfere
with the precise attitude control while proving the high speed comparable to optical only.
The key technology to solve this
has been researching collaboratively with Tokyo Tech.
We have been jointly developing Ka-band phased-array radios and broadband Ka-band communicators together.
In space there is a high level of radiation and the environment is harsh.
Electronic components are subject to degradation due to this radiation.
The amount of radiation received differs between the inside and outside of a satellite.
Electronic components placed on the outside tend to deteriorate more than those placed on the inside.
Thus, normally electronic components are placeds on the inside of a satellite.
Often, they are also protected by shield to reduce radiation.
But this isn’t always the case.
After a satellite is launched into space measuring radiation exposure is possible.
But accurately getting the current degree and location of degradation is difficult.
The amount of degradation of electronic components calculated from the track life must be considered at the design stage.
The system must be designed so that
it does not lose functionality even under conditions of maximum degradation.
Many phased array radios for terrestrial applications have recently begun service.
Such as the millimeter wave band 5G communications.
These phased array radios integrated the antenna and phased array IC on the same substrate to reduce size, weight, and cost.
These Antenna and ICs can’t be mounted separately.
When mounted on a satellite, they are inevitably placed outside the satellite.
This means that the phased array IC is exposed to space and placed in a very harsh radiation environment.
Therefore, the challenge is to overcome the aging degradation of phased array ICs due to radiation.
There is a need to develop a phased array radio system that is robust against the radiation environment.
The newly developed phased array IC from this research incorporates a radiation sensor.
This sensor measures the amount of radiation degradation in the IC.
The amount of radiation degradation at any location on the array can be detected using this IC.
The radio equipment can then be reconfigured.
And by adjusting the parameters we can compensate for the degradation of radio performance.
Consequently, avoiding the degradation of the overall phased array radio performance.
And thus, a radio communication system that is more resistant to radiation has been developed.
Axelspace