Fujitsu: GaN HEMT, simplification and downsizing of cooling system: downsizing of radar system
Fujitsu / Fujitsu Laboratories:
Developed the world’s first “technology to form a highly heat-dissipating diamond film” on the surface of a gallium nitride (GaN) high electron mobility transistor (HEMT).
GaN HEMT: Conventional problems
GaN HEMT is used in power amplifiers such as weather radar.
Transistors used in radar systems generate more heat because of the higher output associated with longer distances.
Because the performance deteriorates due to the heat generation, a cooling device is required.
Since the entire system including the air conditioning equipment is expensive and the installation location is limited, the simplification and downsizing of the cooling device has been an issue.
GaN HEMT: This development
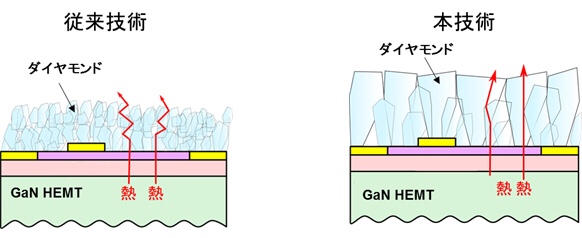
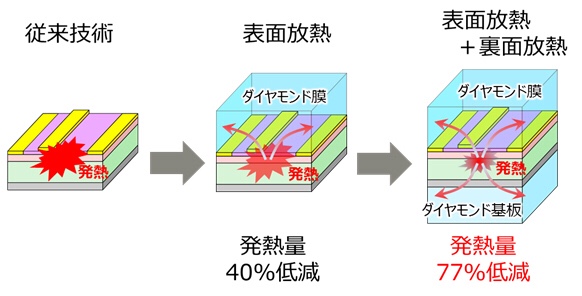
Fujitsu has succeeded in efficiently dissipating heat from the back side of GaN HEMT using “GaN HEMT substrate and single crystal diamond bonding technology (* 4)” at room temperature.
However, in order to obtain a higher heat dissipation effect, a technology to form a diamond film with excellent heat dissipation on the surface side is also required.
The general diamond film formation temperature is “very high, about 900 ° C.”, so there was a problem of “destructing the GaN HEMT”.
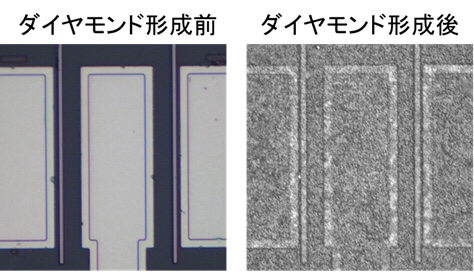
This time, we developed a technology to form a diamond film with high heat dissipation on the surface of GaN HEMT at a low temperature (about 650 ° C where GaN HEMT is not destroyed), and to reduce the amount of heat generated during operation by 40%. Succeeded.
This makes it possible to simplify the cooling system and reduce the size of the radar system using GaN HEMT.
Details of this technology will be announced at the 2019 MRS FALL MEETING & EXHIBIT conference on materials science held in Boston, USA, from December 1 (Sunday) to December 6 (Friday).
Fujitsu