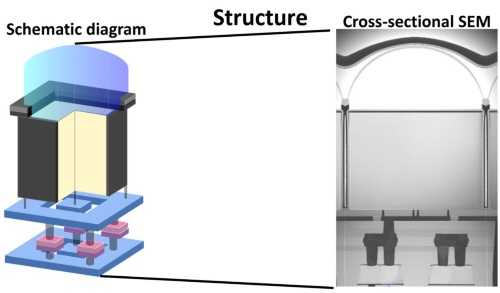
Cross section of the prototype SPAD
(Source: Research groups of Sony companies and IEDM)
Sony: Entered autonomous driving LiDAR element: SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode)
-Achieving the highest level of efficiency in the industry-
2020.12.25
Sony:
Enter the development of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) parts, which are the core of autonomous driving.
Society of Semiconductor Devices:
Sony announced a light receiving element for near-infrared laser light.
In addition to image sensors, he also handles LiDAR parts.
Take a further offensive in the automobile business.
It is likely to play a role in improving the performance of self-driving cars under development in-house.
Announced at IEDM 2020:
Sony Semiconductor Solutions:
Sony Semiconductor Manufacturing:
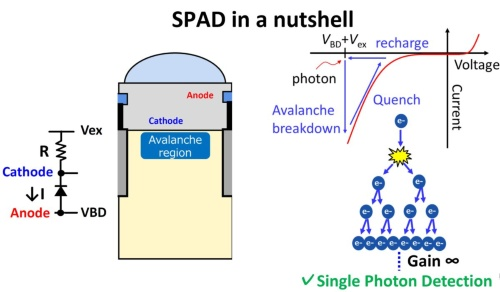
SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode)
SPAD as a light receiving element: A single photon avalanche diode was prototyped.
It was announced at the “66th International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM 2020)” held from December 12 to 18, 2020.
3D sensor and LiDAR:
Three-dimensional (3D) sensors for smartphones and long-range LiDAR for automobiles.
It is common to measure the distance by the ToF (Time of Flight) method.
Irradiate a near-infrared laser beam, calculate the time it takes for the object to reflect and return, and measure the distance.
ToF (Time of Flight) method:
The ToF method depends on the measurement method.
With indirect method (indirect ToF, iToF)
It can be roughly divided into two types: direct method (direct ToF, dToF).
Of these, direct ToF is often used in long-distance LiDAR for automobiles.
Sony has prototyped a highly sensitive SPAD as a light receiving element for direct ToF.
Light receiving element for ToF SPAD:
A distance image is acquired by arranging SPADs in a two-dimensional array.
SPAD operates APD (Avalanche Photodiode) in “Geiger mode” and counts the number of incident photons (photons).
Used as a photon counter.
With a large amount of electrons from one incident photon
Generates a large number of hole pairs like an avalanche
The avalanche phenomenon is used to increase the light-receiving sensitivity, making it suitable for long-distance distance measurement.
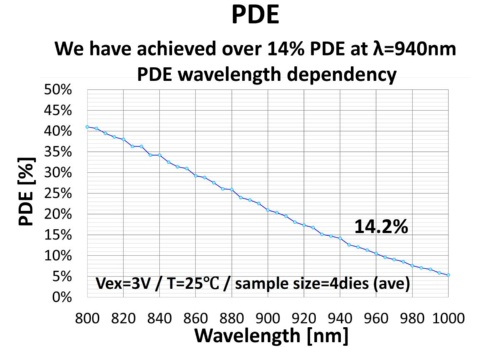
SPAD efficiency index PDE:
Sony has improved efficiency by devising the structure of SPAD.
For near-infrared light of 940 nm, “PDE (Photon Detection Efficiency)”, which is an index of SPAD efficiency, has been increased to 14.2%.
It is 3 to 4 times larger than the conventional SPAD.
Nikkei Cross Tech (xTECH)