Sony: In-vehicle stacked TOF sensor development: LiDAR with SPAD Pixels,
-Measurement of 300m ahead at 15cm intervals-
Sony:
On February 18, 2021, it announced that it had developed a stacked direct Time of Flight (dToF) method and rangefinder sensor for in-vehicle LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging).
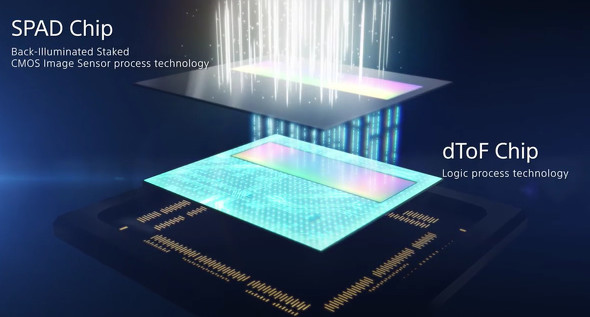
It uses SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) pixels.
“Industry’s first” to use SPAD pixels as a stacked ranging sensor for in-vehicle LiDAR (Sony)
Embedded Development News-MONOist
https://monoist.atmarkit.co.jp/mn/articles/2102/19/news040.html
Sony Develops a Stacked Direct Time of Flight Depth Sensor for Automotive LiDAR with SPAD Pixels, an Industry First
SPAD is a pixel structure
that uses avalanche multiplication to amplify electrons from a single incident photon, causing a cascade like an avalanche, and it can detect even weak light.
It is possible to accomplish long-distance, high-precision distance measuring by employing SPAD
as the detector in a dToF sensor, which measures the distance to an object based on the time of flight (time difference) of a light emitted from a light source until it returns to the sensor, after being reflected by the object.
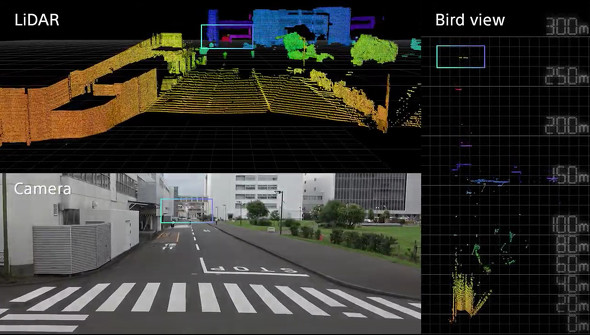
Sony has succeeded in developing a compact yet high-resolution sensor.
This enables high-precision, high-speed measurement at 15-centimeter range resolutions up to a distance of 300 meters*3.
The new development
will also help enable detection and recognition under severe conditions such as various temperature and weather as required for automotive equipment, thereby contributing to greater reliability for LiDAR.
Achieving a single chip also helps lower the cost of LiDAR.
Sony has also developed a MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System)LiDAR system
equipped with this new technology for evaluation purposes, which is now being offered to customers and partners.