COVID-19: Fujifilm, AI to support corona diagnosis: CT image automatic analysis
COVID-19:
May 19, 2020 17:45
FUJIFILM Holdings:
May 19th, announced that it will develop technology to support the diagnosis of new coronavirus pneumonia using artificial intelligence (AI).
It assists doctors in deciding the progress and treatment effect of patients by digitizing medical conditions from images taken by CT.
We have started joint research in Japan and are aiming for commercialization by the end of FY2020.
Nihon Keizai Shimbun
https://r.nikkei.com/article/DGXMZO59295700Z10C20A5XB0000?s=4
FUJIFILM: AI support for diagnosis of new corona pneumonia: Automatic analysis of CT images
May 19, 2020
FUJIFILM:
May 19, announced that it will jointly develop a technology to support the follow-up of patients and the judgment of therapeutic effects by using AI in collaboration with a medical institution accepting patients with pneumonia due to a novel coronavirus infection.
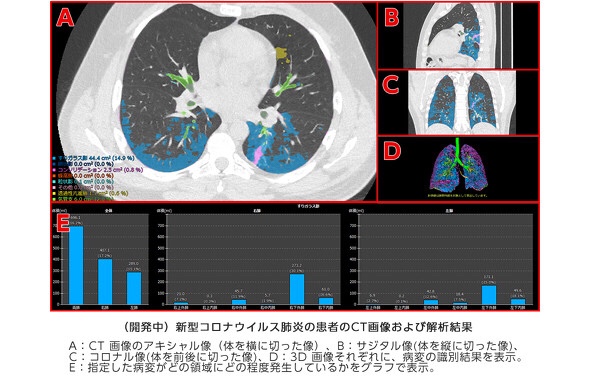
It is said that CT images of the chest will be automatically analyzed to identify abnormalities due to pneumonia.
Apply the technology that the company has been conducting joint research with Kyoto University since 2018.
Divide the lungs into 12 areas,
For bronchi and blood vessels of the lungs
Determine the size and proportion of abnormal parts.
Based on the information, the doctor confirms the medical condition and determines the effect of treatment.
Kyoto University: Joint research
When treating a patient with pneumonia due to a novel coronavirus infection, the doctor visually confirms the ever-changing medical condition from CT images.
However, there are hundreds of CT images per patient, which puts a burden on doctors.
The company hopes to contribute to the development and evaluation of therapeutic agents for new coronavirus infections, saying that it can be used to measure the effects of drugs.
ITmedia NEWS
https://www.itmedia.co.jp/news/spv/2005/19/news105.html
Fujifilm to develop AI-based technology to aid COVID-19-
induced pneumonia diagnosis and assess the effectiveness of treatments | Fujifilm Global
TOKYO, May 19, 2020 —
FUJIFILM Corporation (President: Kenji Sukeno) is commencing a research study to develop Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based technology to aid in the diagnosis and treatment assessment of patients with COVID-19-induced pneumonia.
The technology for quantifying the lesions of interstitial pneumonia*, co-developed with Kyoto University (the Department of Respiratory Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Professor Toyohiro Hirai), will be applied to the project.
The company will now embark on a joint research study with local medical institutions treating COVID-19 patients, starting with the Kanagawa Cardiovascular and Respiratory Center (Yokohama, Japan).
The spread of the novel coronavirus, which causes COVID-19, has emerged as a serious issue around the world.
The world has yet to see clear judging criteria for determining the effectiveness of various treatment options, currently explored by doctors. In order to confirm the progression of pneumonia and the effectiveness of treatments,
doctors need to examine hundreds of chest CT images for each patient to visually check the characteristics of ever-changing lesions and it puts a serious strain on specialists.
There are expert opinions that COVID-19-induced pneumonia presents similarly to interstitial pneumonia in diagnostic images and has diverse variations in lesion patterns.
Fujifilm’s CT quantification technology for interstitial pneumonia is powered by an AI-based software
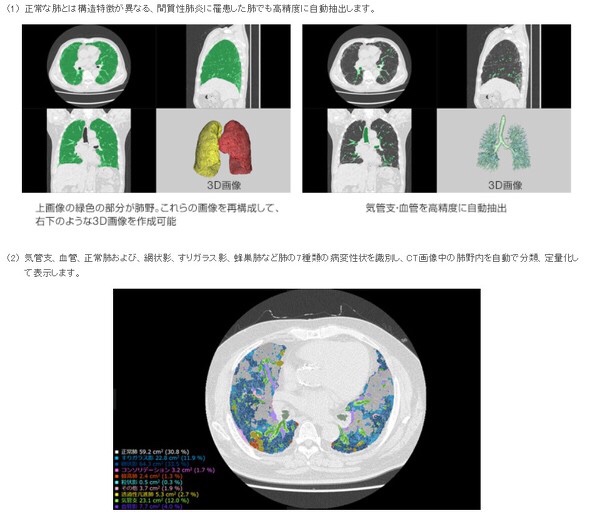
that examines CT images to identify
- bronchi,
- blood vessels and
- normal lungs in lung field**
as well as seven types of lesions such as
- reticular opacities,
- ground-glass opacities and
- honeycomb lungs***,
and automatically carries out categorization and measurement to quantify lesions of interstitial pneumonia.
It also divides the lung field into 12 zones*4
and shows the volume and ratio of lesions for each of the zones so that clinicians can examine the distribution and progression of lesions within the lung field in details.