
Toshiba: Converting CO2 emitted from cleaning plants to CO: Power to Chemicals (P2C)
-CO is generated from CO2, Toshiba realizes industrialization-
Toshiba:
Electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO!
We have developed a technology to perform Power to Chemicals (P2C) on a large scale.
What is Power to Chemicals (P2C):
P2C can directly electrochemically convert CO2 into “CO, which is a raw material for fuels and chemicals.”
General cleaning plant:
“Approximately 70,000 tons of CO2 emitted annually by a general cleaning factory” can be converted into CO.
Coal-fired power plant:
It can also be applied to “coal-fired power plants that emit dozens of times more CO2 than incineration plants.”
New technology developed this time:
Uses electricity to generate CO from CO2,
Increase the area of P2C electrolytic cells,
We have developed a “stacking technology for stacking multiple electrolytic cells”.
Contents of new technology:
Developed an electrolytic cell with a 4-layer stack by expanding the area 100 times and 100 ㎠ compared to the conventional one.
When operated at a current density of 200mA / ㎠, Faraday efficiency of 94% is achieved.
Dramatically improved processing power:
Conventional electrolytic cell
CO2 processing capacity / ㎡ is only about 4 tons per year.
This electrolytic cell
The CO2 processing capacity / ㎡ can process about 35 tons per year.
Originally developed technology:
Toshiba has independently developed “a technology that can directly react with CO2 in the gas phase in March 2019”.
Uses reduction catalyst electrodes:
With an electrolytic cell using a reduction catalyst electrode
Compared to conventional electrolytic cells that react in the liquid phase
With a current density of 700mA / ㎠, which is 466 times higher
Achieved 92% Faraday efficiency.
Toshiba Transducer Technology Lab
Senior Researcher Ryota Kitagawa:
Faraday efficiency 92%: Achieves high performance
Three-phase interface control technology that efficiently reacts CO2 with the catalyst,
Realized by structural control technology that increases the catalytically active area with a porous structure.
Details of the catalyst material have not been disclosed.
General cleaning factory:
While the site area is 50,000 m2, the annual CO2 emissions will be 73,000 tons.
In the empty space of this incineration plant
If you install the newly developed P2C electrolytic cell electrolyzer,
Almost all of the emitted CO2 can be converted to CO.
Comparison with other technologies:
Compared with other technologies that convert CO2 into valuable resources such as CO.
Photocatalytic artificial photosynthesis: 195ha of site is required.
Algae Party Culture: 723ha of land required.
Future development plans:
This time, we succeeded in “larger area and stacking of electrolytic cells using original catalyst electrodes”.
From 2021, it will be demonstrated with “a system that processes CO2 of about 35 tons / ㎡ per year”.
Uses of Power to Chemicals (P2C):
Manufacture of gasoline, light oil and jet fuel
For example, by applying the Fischer-Tropsch method, gasoline, light oil, and jet fuel can be produced.
Manufacture of methanol and butane
In addition, methanol, butane, aldehyde, ethanol and the like, which are raw materials for acetic acid and dimethyl ether, can be produced from syngas.
Forefront of R & D –MONOist
https://monoist.atmarkit.co.jp/mn/articles/2103/22/news051.html
Toshiba: Developed CO2 resource recovery technology that can convert CO2 into valuable resources
-Convert at the highest speed in the world under normal temperature environment-
-Achieved processing capacity that contributes to decarbonization in a small space-
Toshiba Research and Development Center:
Toshiba has developed “Power to Chemicals”, a CO2 resource recovery technology.
It electrochemically converts CO2 into CO, which is a raw material for fuels and chemicals.
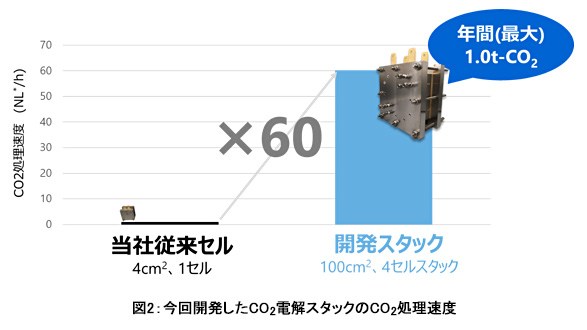
Electrolytic cell to convert
Stacked with our original technology
Increase the amount of processing per unit installation area,
With a postal envelope (length 3) size installation area,
Achieved a maximum annual processing amount of 1.0t-CO2.
World’s fastest processing speed:
This is the world’s fastest processing speed (* 1) for CO2 electrolysis stacks that operate in a room temperature environment.
Conventional:
There was a problem that the processing speed was reduced by stacking electrolytic cells.
this time:
We have succeeded in “preventing the speed reduction caused by stacking by using our unique technology”.
Convert CO2 to CO in a space-saving manner:
Since the amount of processing per unit installation area increases due to stacking, it is possible to convert CO2 into valuable resources with a practical level of space saving.
In the case of a cleaning plant (* 2) that emits 200 tons of CO2 per day.
Can be processed with an installation area of 2000 m2 (5 basket courts).
The 88th Annual Meeting of the Electrochemical Society:
Scale-up is possible by stacking cells further, making great progress toward early commercialization.
Details of this technology will be announced at the 88th Annual Meeting of the Electrochemical Society, which will be held online from March 22nd.
https://www.toshiba.co.jp/rdc/detail/2103_02.htm
Toshiba, ANA, Toyo and Idemitsu Kosan partner on power-to-chemicals strategy – Chemical Engineering | Page 1