
Kinki University’s Liquid Fertilizer: Sweet Potato Production Increases 10 Times!
ー Turning treated sewage water into liquid fertilizer for sweet potato cultivation
Report from the latest article of KYODONEWS!
Sweet potato cultivation at Kinki University:
Professor Takahiro Suzuki’s team made a presentation on May 22nd.
We made a liquid fertilizer for sweet potato cultivation from sewage treatment water, and increased the production volume by 10 times.

Turn sewage water into liquid fertilizer:
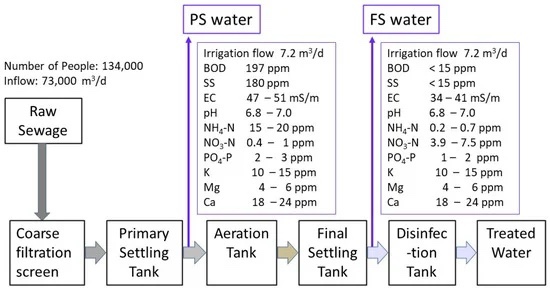
Sewage contains an excess of “nitrogen and phosphorus contained in fertilizers.”
Microorganisms increase when oxygen is dissolved in sewage.
Microorganisms absorb nitrogen, etc., and the concentration becomes appropriate for cultivation.
Growing sweet potatoes with liquid fertilizer:
The team conducted a cultivation experiment at a sewage treatment plant in Iwata City, Shizuoka Prefecture.
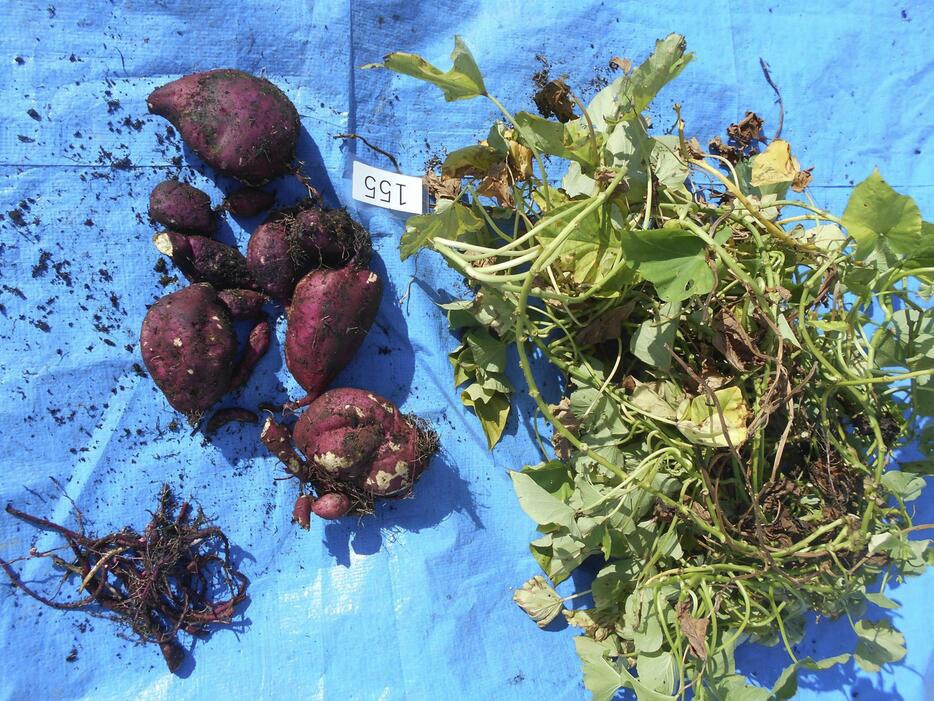
The pots in which the seedlings were planted were arranged in three tiers, and “25.3 kg of sweet potatoes per square meter per year” were harvested.
The national average yield of sweet potatoes is 2.4 kg per year.
Professor Suzuki will become a game changer in global warming countermeasures and increase energy self-sufficiency.
(Kyodo News) – Yahoo! News
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/b3188435de76c27c8eef67b7ffb2c6ef4abf4565

Growing sweet potatoes (left: liquid fertilizer, center: untreated sewage, right: treated sewage)
NEWS RELEASE:
Aiming to replace fossil fuels with biofuels |
Kindai University paper:
It was published in the international magazine “Horiculturae” on February 24, 2023 (Friday).
Succeeded in mass production of sweet potatoes using a cultivation system that uses treated sewage water as fertilizer
● Solar energy utilization efficiency achieved 3.6%, the highest in the world for biomass resources
●Fuel cell power generation using sweet potatoes is expected to replace fossil fuels and contribute to a significant reduction in greenhouse gases.
https://www.kindai.ac.jp/news-pr/news-release/2023/03/038368.html
Effects of Sewage Treatment Water Supply on Leaf Development and Yield of Tuberous Roots in Multilayered Sweet Potato Cultivation
Abstract
To develop a way to mass-produce sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) as an energy crop to replace fossil fuels,
the effects of using a sewage supply as a fertilizer and heat source were investigated.
When 25 pots planted with sweet potato vine seedlings were arranged in three layers and cultivated for 160 days from June to November by supplying treated sewage to the root zone,
the yield of tuberous roots reached 19.5 kg m−2 due to the massive growth of leaves.