JST: Successfully developed new device combining IGZO and next-generation functional material
Low Power Consumption, High Speed, Large Capacity of Memory Devices Expected
Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST),
Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
June 10, 2019
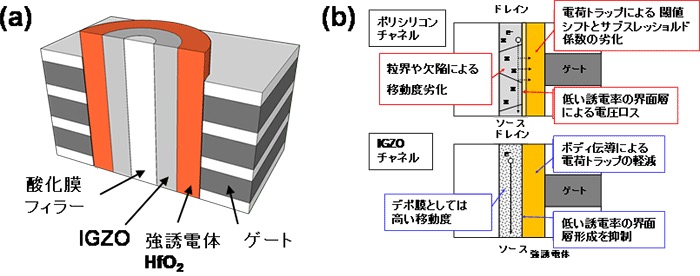
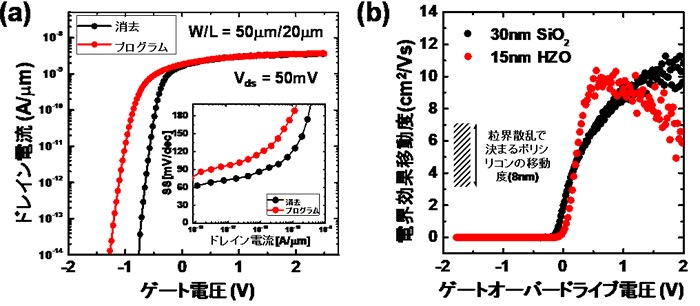
We succeeded in developing a transistor type ferroelectric memory (FeFET) Note 2) with a channel of 8 nanometer (nm) metal oxide semiconductor IGZO Note 1).
By this technology,
The subthreshold coefficient is an ideal 60 millivolts per deck (mV / dec),
Memory window is 0.5 volts (V) or more
We achieved excellent memory characteristics that can operate at low voltage with high mobility.
main research
In order to suppress the formation of the interface layer and the influence of the charge trap, and obtain a high read current even in the three-dimensional laminated structure,
We have proposed a ferroelectric HfO2 gate insulator FeFET whose channel is metal oxide semiconductor IGZO.
Using this device structure, the formation of a low dielectric constant interface layer can be suppressed between IGZO and ferroelectric HfO2.
point
In the silicon channel, an interface layer having a low dielectric constant is formed, which makes it difficult to operate at low voltage and has low reliability.
We have succeeded in developing a high mobility transistor type ferroelectric memory with excellent switching characteristics, using a very thin metal oxide semiconductor IGZO as a channel.
This technology will dramatically improve the energy efficiency of IoT devices, and is expected to develop more advanced and complete networks and services.