Tokyo Univ : 38MHz Transistor: Organic Semiconductor / Single Crystal Thin Film
The University of Tokyo / AIST / National Institute for Materials Science
Organic semiconductor: single crystal thin film
We have newly developed a 1μm channel length microfabrication method on organic semiconductors / single crystal thin films.
A flexible device is manufactured using “ink and printing process dissolved in organic solvent”.
Research group:
We have developed a printing method that can apply a 10 nm thick / organic semiconductor / single crystal ultra-thin film over a large area.
High quality / organic single crystal thin film realizes “high mobility exceeding 10cm2 / Vs”.
This is an extremely promising method for speeding up organic transistors.
Semiconductor integrated devices: response frequency
The response frequency of a semiconductor integrated device depends on “transistor mobility and its channel length”, which performs logical operations.
Traditional approach:
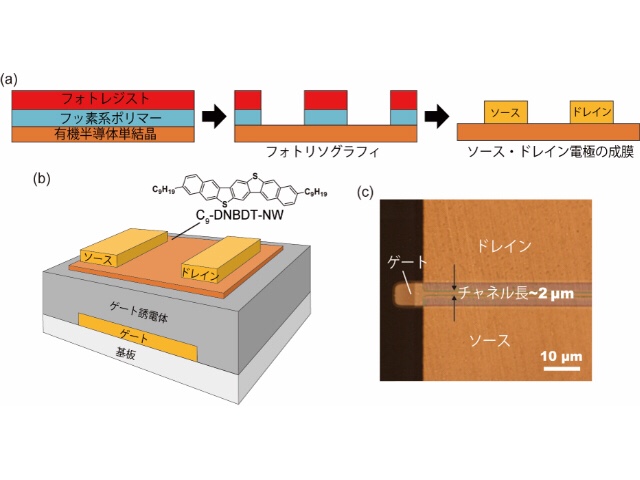
Conventionally, lithography using photoresist has been widely used as a fine processing technique.
However, many photoresists damage organic semiconductor films.
For organic transistors, it was difficult to achieve both high mobility and short channel by lithography.
This time:
This time, the research group applied a thin fluoropolymer film on an organic semiconductor single crystal thin film.
Newly developed damage free / lithography method for organic semiconductors.
Successful 1μm scale fine processing,
High mobility of 10cm2 / Vs and short channel at the same time,
Double the world record of cutoff frequency,
Achieved the world’s fastest 38MHz.
Organic transistors: rectification
In addition, as a result of examining the rectification of this organic transistor, which converts an AC signal into a DC signal, it was demonstrated that the rectification was not lost even at 100 MHz.
Organic transistors: fields of application
The research group succeeded in developing the world’s first organic transistor operating in the ultrahigh frequency range.
Wireless tag power supply:
With a value higher than the RFID tag communication frequency of 13.56 MHz, the device fabricated this time is at a level that can be sufficiently applied to wireless tag power supply.
FM radio broadcast:
The ultra high frequency band is used as radio waves for FM radio broadcasting and amateur radio.
The response frequency is further increased to produce organic integrated circuits for long-range wireless communication in the ultra-high frequency band.
IoT logistics management:
Mass production is possible with a simple printing process. In the future, low cost wireless tags for IoT logistics management.
It can be used for a wide range of applications, such as wireless power supply systems that supply power from electromagnetic waves.
OPTRONICS ONLINE