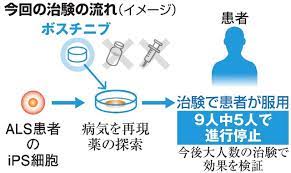
Kyoto University: Reproduce intractable disease ALS with iPS cells: Therapeutic drug “Bosutinib”
-Hope for therapeutic drug, Kyoto University to clinical trial-
Kyoto University Team:
Using iPS cells, the condition of the intractable disease “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)” was reproduced.
Discovery of an effective treatment for leukemia:
As a result of research looking for candidates for ALS treatment, we have found an effective treatment for leukemia.
Kyoto University announced on September 26th.
A team from Kyoto University begins a clinical trial of ALS.
ALS clinical trial started:
A clinical trial is a necessary procedure to receive public medical insurance coverage.
Aiming for the practical application of a therapeutic drug for ALS, we have begun to move.
Therapeutic drug “bosutinib”:
The drug is “Bosutinib”, a treatment for chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Drink by mouth once daily for 12 weeks.
It will be implemented for 24 people at 4 medical institutions such as Kyoto University Hospital.
Administered to 24 ALS patients:
It is intended for patients aged 20 to 79 years within 2 years after onset.
ALS symptoms are progressing,
On the other hand, I can still work
This applies to people who can do household chores.
Japanese ALS patients:
There are about 9,000 ALS patients in Japan.
Muscle strength weakens and it becomes increasingly difficult to move.
There are drugs that slow the progression, but there is no established cure.
Asahi Shimbun Digital
https://www.asahi.com/articles/ASM3V3S6PM3VPLBJ001.html
Announcement of a clinical trial for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University,
has announced a new Phase 1*1) clinical trial for the drug bosutinib to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the Kyoto University Hospital (KUH).
Leading the project from CiRA is Professor Haruhisa Inoueand from KUH is Professor Ryosuke Takahashi.
This trial has received approval from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA).
News and Events | CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/pressrelease/news/190403-110000.html
Deep learning amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by taking pictures
A team of scientists led by CiRA Professor Haruhisa Inoue
reports the combination of deep learning and iPS cell technology for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Recently, researchers have reported that
deep learning could potentially identify individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease (https://www.nytimes.com/2021/02/01/health/alzheimers-prediction-speech.html).
In the new study on ALS seen in Annals of Neurology,
Inoue and colleagues show how deep learning can be used to identify indications of ALS,
a relentless motor neuron disease, by using iPS cell technology to reprogram patient blood cells into motor neurons, the cells most afflicted by the disease.
Convolutional neural networks
were trained using images of motor neurons prepared from the iPS cells of 15 healthy donors and 15 ALS patients.
Based on just images of motor neurons,
the network could predict with over 0.97 of area under curve (AUC) whether other donors were healthy or ALS patients.
On the other hand,
conventional machine learning with the same images,focusing on soma size, neurite length, and cell number, presented approximately 0.97 of AUC (see figure).
News and Events | CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/pressrelease/news/210224-100000.html