COVID-19: Tokyo Medical University predicts aggravation of blood particles: “exosomes”
Tokyo Medical University:
Professor Takahiro Ochiya:
found “COVID-19, a protein that can be used to identify people who are prone to severe illness.”
People who have this protein in their blood remain mild when it develops.
Only those who are at serious risk can be identified and treated.
“Exosomes” in the blood:Research group:
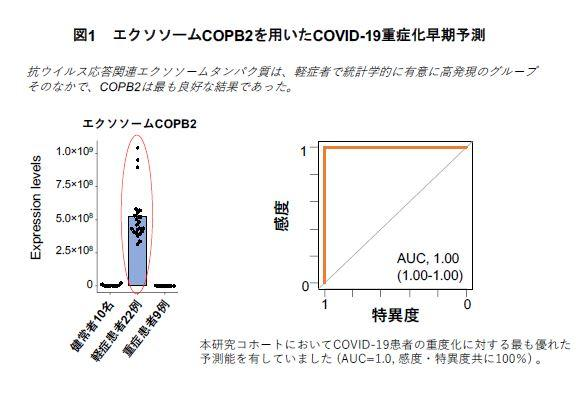
Blood was collected from 31 mildly ill patients with the new corona.
Investigate proteins containing fine particles called “exosomes” in the blood.
Results of patient comparison:
Nine people who became severely ill after hospitalization and
As a result of comparing 22 people who were discharged with mild illness
Everyone who was discharged had a protein called “COPB2”.
This protein appears to be involved in immunity.Development of inspection technology:
The research group has also developed inspection technology and is expected to be able to identify it in a few hours.
By examining the protein in the blood of an infected person, it is possible to determine whether it will be severe or mild.
This protein is involved in immunity and may be useful in the development of therapeutic agents.
Nihon Keizai Shimbun
https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXMZO64895490S0A011C2I00000/
Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science: Professor Takahiro Ochida Research Team
Identification of aggravation predictors in COVID-19 using liquid biopsy
-Expectations not only for prediction but also for new treatment methods and elucidation of pathological conditions-
Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science
Jikei University School of Medicine
University of California, San Francisco, USA
International Space Medical
Collaborative research team:
Conducted “analysis of exosomes and nucleic acids in blood,” which is a liquid biopsy method used for cancer diagnosis.
We have identified a new predictor of aggravation in COVID-19.
Exosomes and nucleic acids in blood:
We have identified exosomes and nucleic acids in the blood.
In addition to its role as a predictive biomarker, it is expected to develop new therapies and elucidate the pathophysiology.
[Background of research]
By analyzing the exosomes and nucleic acids of COVID-19-infected patients, it is possible to quickly find out the response of the human body involved in aggravation.
In this study, we aimed to analyze the blood of COVID-19-infected patients at admission and identify new predictors of COVID-19 aggravation using liquid biopsy.
Results and findings of this study:
From March to May 2020, 42 patients were admitted to the Jikei University School of Medicine Hospital.
WHO severity classification excludes 11 severely ill patients at admission,
The remaining 31 patients with mild illness at admission were analyzed.
A total of 41 samples were analyzed using control samples and sera of 10 healthy subjects.
Progress after admission:
Of 31 COVID-19 patients with mild on admission
Nine confirmed severe events requiring mechanical ventilation in intensive care.
The remaining 22 were discharged with mild illness.
“Blood samples of these 31 (22 mild + 9 severe) COVID-19 patients at admission”
Analysis of RNA and exosome protein in blood using “serum of 10 healthy subjects”.
Next-generation sequencer * 1)
And mass spectrometry (LC-MS) * 2)
Comprehensive analysis was performed.
From these analysis results, as an early prediction biomarker of severity in COVID-19 patients
Identify 3 different groups:
(1) Antiviral response Exosome proteins: exosomes, COPB2, PRKCB, etc.
(2) Coagulation exosome protein and RNA:
Exosomes: MFAP4, ECM1, CAPN, FGG, CD147
RNA: CDKN2B.AS1 (long-non coding RNA)
(3) Liver disorder related
RNA: microRNA-122-5p (microRNA), SNORD33 (small nucleolar RNA), etc.
Tokyo Medical University
https://www.tokyo-med.ac.jp/news/2020/1012_175135002503.html