All-solid-state battery: understanding the movement of Li-ions!
-Energy spectrum corresponding to charge curve and Li ion distribution-
RIKEN
Optical Quantum Engineering Research Center
Japan Atomic Energy Agency
Neutron Materials Analysis Research Division
International joint research group:
We succeeded in capturing the movement of Li ions in an all-solid-state battery [1] during charging.
so far,
It was not possible to “capture the movement of Li ions in real time.”
“Methods for quantitative analysis during operation of all-solid-state devices” have been limited.
Research results:
In this research, a thin-film all-solid-state battery is used to capture the movement of Li ions.
This method also enables the analysis of relatively thick samples up to 30 μm.
Since the incident beam is a thermal neutron,
In the case of a sample that has a front side and a back side, “it can be measured without a big difference”.
Analysis of commercially available and all-solid-state batteries:
for example,
A solid electrolyte with a thickness of 150 μm and positive and negative electrodes with a thickness of 20 μm,
All-solid battery samples can also be analyzed.
In the future, we will develop the analysis of all-solid-state batteries that are close to commercially available products.
International joint research group:
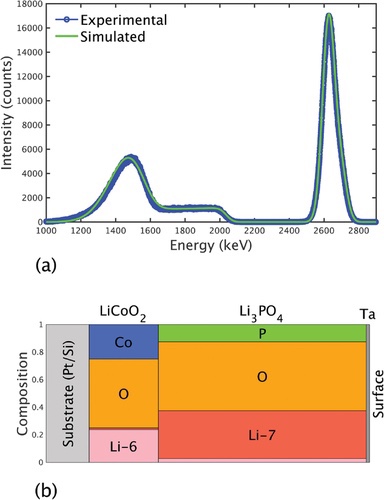
An all-solid-state battery sample was fabricated using the [3] positive electrode enriched with lithium-6 (6Li).
Injecting thermal neutrons into the sample,
6Li(n,α)3H thermal neutron-induced nuclear reaction, time-resolved analysis of emitted particle energies.
Succeeded in capturing the movement of Li ions in an all-solid-state battery.
Inside all-solid-state battery
movement of lithium ion
Analysis of its behavior:
We have identified the “movement mechanism and movement region of Li ions in solid electrolytes”.
These results:
The development of all-solid-state batteries
While obtaining knowledge of the movement of Li ions during charging and discharging,
It indicates that it has entered the development stage.
This research was published in the online edition of the scientific journal Small (September 30).
https://www.riken.jp/press/2022/20221025_2/index.html
Batterie tout solide : comprendre le mouvement des Li-ions !
-Spectre d’énergie correspondant à la courbe de charge et à la distribution des ions Li-
RIKEN
Centre de recherche en ingénierie quantique optique
Agence japonaise de l’énergie atomique
Division de la recherche sur l’analyse des matériaux neutroniques
Groupe de recherche mixte international :
Nous avons réussi à capturer le mouvement des ions Li dans une batterie tout solide [1] pendant la charge.
jusqu’à présent,
Il n’était pas possible de “capturer le mouvement des ions Li en temps réel”.
Les « méthodes d’analyse quantitative pendant le fonctionnement des dispositifs entièrement à semi-conducteurs » ont été limitées.
Résultats de recherche:
Dans cette recherche, une batterie à semi-conducteurs à couche mince est utilisée pour capturer le mouvement des ions Li.
Cette méthode permet également l’analyse d’échantillons relativement épais jusqu’à 30 μm.
Le faisceau incident étant un neutron thermique,
Dans le cas d’un échantillon qui a un recto et un verso, “il peut être mesuré sans grande différence”.
Analyse des batteries disponibles dans le commerce et entièrement à l’état solide :
par exemple,
Un électrolyte solide d’une épaisseur de 150 μm et des électrodes positive et négative d’une épaisseur de 20 μm,
Des échantillons de batterie entièrement solides peuvent également être analysés.
Dans le futur, nous développerons l’analyse des batteries tout solide proches des produits disponibles dans le commerce.
Groupe de recherche mixte international :
Un échantillon de batterie entièrement à l’état solide a été fabriqué à l’aide de l’électrode positive [3] enrichie en lithium-6 (6Li).
Injecter des neutrons thermiques dans l’échantillon,
Réaction nucléaire induite par les neutrons thermiques 6Li(n,α)3H, analyse résolue en temps des énergies des particules émises.
A réussi à capturer le mouvement des ions Li dans une batterie entièrement à l’état solide.
À l’intérieur de la batterie à semi-conducteurs
mouvement du lithium-ion
Analyse de son comportement :
Nous avons identifié le “mécanisme de mouvement et la région de mouvement des ions Li dans les électrolytes solides”.
Ces résultats :
Le développement des batteries tout solide
Tout en obtenant des connaissances sur le mouvement des ions Li pendant la charge et la décharge,
Cela indique qu’il est entré dans la phase de développement.
Cette recherche a été publiée dans l’édition en ligne de la revue scientifique Small (30 septembre).
All-Solid-State-Batterie: Die Bewegung von Li-Ionen verstehen!
-Energiespektrum entsprechend Ladungskurve und Li-Ionenverteilung-
RIKEN
Forschungszentrum für optische Quantentechnik
Japanische Atomenergiebehörde
Forschungsabteilung für Neutronenmaterialanalyse
Internationale gemeinsame Forschungsgruppe:
Es ist uns gelungen, die Bewegung von Li-Ionen in einer All-Solid-State-Batterie [1] während des Ladevorgangs zu erfassen.
bis jetzt,
Es sei nicht möglich, “die Bewegung von Li-Ionen in Echtzeit zu erfassen”.
„Methoden zur quantitativen Analyse während des Betriebs von All-Solid-State-Geräten“ waren begrenzt.
Forschungsergebnisse:
In dieser Forschung wird eine Dünnfilm-Solid-State-Batterie verwendet, um die Bewegung von Li-Ionen zu erfassen.
Dieses Verfahren ermöglicht auch die Analyse relativ dicker Proben bis 30 μm.
Da der einfallende Strahl ein thermisches Neutron ist,
Bei einer Probe, die eine Vorder- und eine Rückseite hat, „kann man ohne großen Unterschied messen“.
Analyse von handelsüblichen und All-Solid-State-Batterien:
zum Beispiel,
Ein Festelektrolyt mit einer Dicke von 150 μm und positive und negative Elektroden mit einer Dicke von 20 μm,
Auch Feststoffbatterieproben können analysiert werden.
In Zukunft werden wir die Analyse von All-Solid-State-Batterien entwickeln, die nahe an kommerziell erhältlichen Produkten liegen.
Internationale gemeinsame Forschungsgruppe:
Eine Festkörperbatterieprobe wurde unter Verwendung der mit Lithium-6 (6Li) angereicherten positiven Elektrode [3] hergestellt.
Injizieren thermischer Neutronen in die Probe,
6Li(n,α)3H thermische Neutronen-induzierte Kernreaktion, zeitaufgelöste Analyse der emittierten Teilchenenergien.
Es gelang, die Bewegung von Li-Ionen in einer Festkörperbatterie zu erfassen.
Im Inneren einer All-Solid-State-Batterie
Bewegung von Lithium-Ionen
Analyse seines Verhaltens:
Wir haben den „Bewegungsmechanismus und Bewegungsbereich von Li-Ionen in Festelektrolyten“ identifiziert.
Diese Ergebnisse:
Die Entwicklung von All-Solid-State-Batterien
Beim Gewinnen von Kenntnissen über die Bewegung von Li-Ionen während des Ladens und Entladens,
Es zeigt an, dass es in die Entwicklungsphase eingetreten ist.
Diese Forschung wurde in der Online-Ausgabe der wissenschaftlichen Zeitschrift Small (30. September) veröffentlicht.
In‐Operando Lithium‐Ion Transport Tracking in an All‐Solid‐State Battery
– Kobayashi – Small – Wiley Online Library
Abstract
An all-solid-state battery
is a secondary battery that is charged and discharged by the transport of lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes.
To fully realize the significant benefits of this battery technology,
for example,
higher energy densities, faster charging times, and safer operation,
it is essential to understand how lithium ions are transported and distributed in the battery during operation.
However,
as the third lightest element,
methods for quantitatively analyzing lithium during operation of an all-solid-state device are limited such that real-time tracking of lithium transport has not yet been demonstrated.
Here,
the authors report that
the transport of lithium ions in an all-solid-state battery is quantitatively tracked in near real time
by utilizing a high-intensity thermal neutron source and lithium-6 as a tracer in a thermal neutron-induced nuclear reaction.
Furthermore,
the authors show that
the lithium-ion migration mechanism and pathway through the solid electrolyte can be determined by in-operando tracking.
From these results,
the authors suggest that
the development of all-solid-state batteries has entered a phase where further advances can be carried out while understanding the transport of lithium ions in the batteries.