Toyohashi Univof Tech: realizing underwater wireless power transmission by electric field coupling – for underwater inspection robot
~ Underwater inspection robot catches deterioration of structure as soon as possible ~
<Overview>
Toyohashi Univ of Tech: Associate Professor Masaya Tamura’s research team
succeeded in wireless power transmission in freshwater using electric field coupling.
In the world of wireless power transmission, freshwater behaves as a very large loss dielectric.
Conventionally, it has been considered difficult to transmit wireless power in water by electric field coupling.
This time, we have clarified the high frequency characteristics of freshwater by experiment.
Even in the electric field
‘Frequency band that can be transmitted with high efficiency’
‘Electrode structure realizing high efficiency’
We discovered
<Details>
Wireless power transmission:
Until now, research on land-based environments has been mainly done, but underwater environments are expected as the next target.
Structural Health Monitoring System:
In structural health monitoring systems such as piping, cooling tower and dam wall surface, the development of an underwater inspection robot that can move freely and can investigate even in the event of a disaster is an urgent task.
However, since the robot is driven by a battery, it is necessary to repeat the task of pulling up the robot many times for charging and submerging again.
Technological development of wireless power information transmission (power supply station) underwater is essential in order to avoid lowering the operation efficiency due to this charging work.
Development of an electric field coupler capable of wireless power supply:
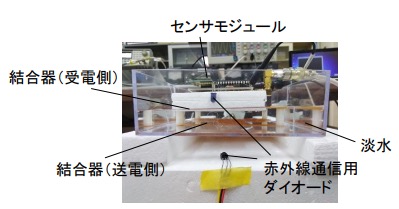
The research team developed an electric field coupler that can wirelessly feed even in freshwater.
As a result, power transmission efficiency of more than 90% at a power transmission distance of 2 cm and 80% or more at 5 cm is realized.
Actually driving the sensor module by wireless electric power transmission via freshwater, succeeded in infrared data communication.
Even when 400 W electric power is transmitted at a power transmission distance of 2 cm, the power transmission efficiency is maintained at 90% or more.
Considering putting it on the power supply station, it is considered to be efficient to withstand practical use.