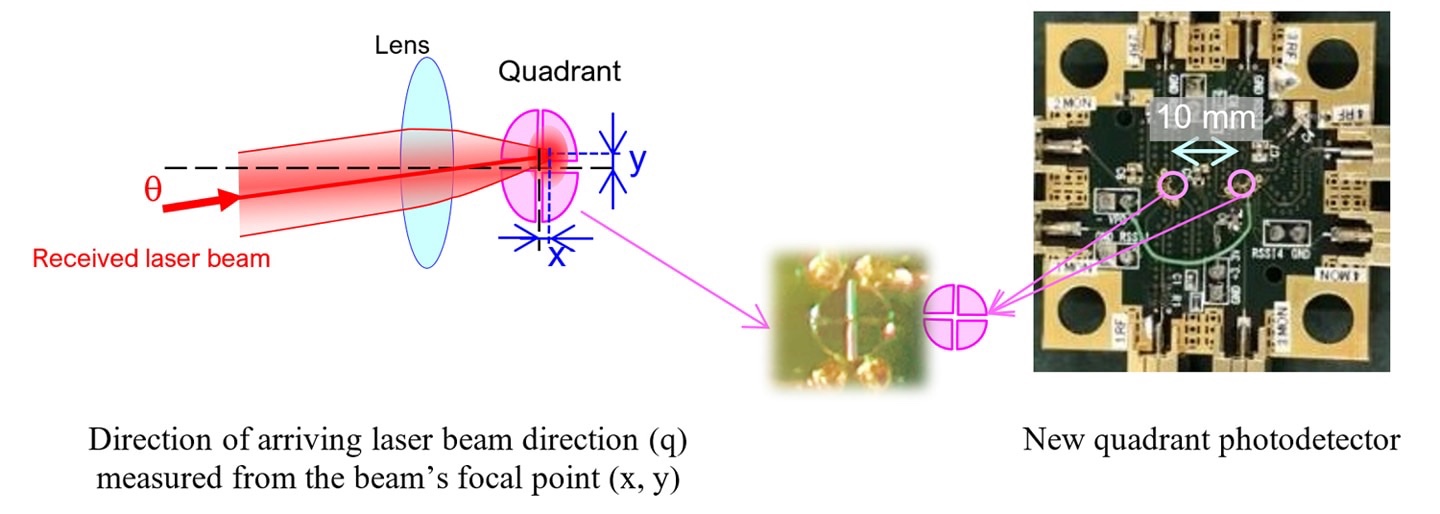
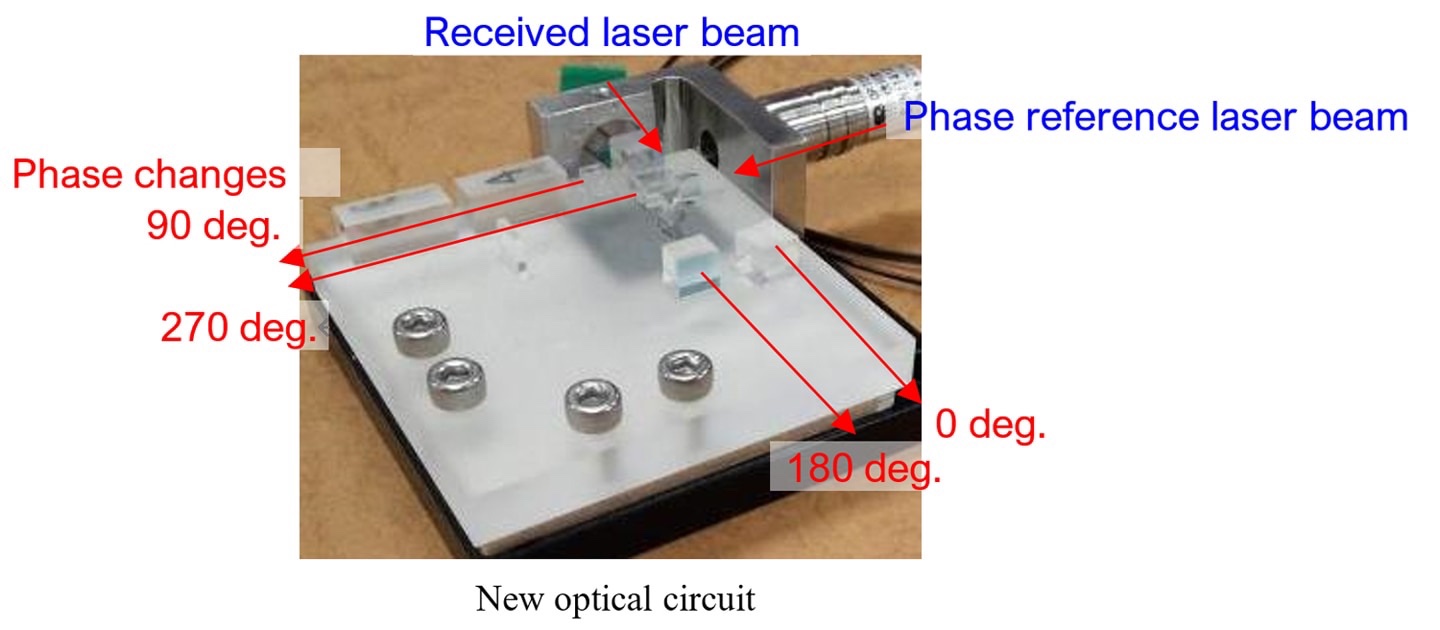
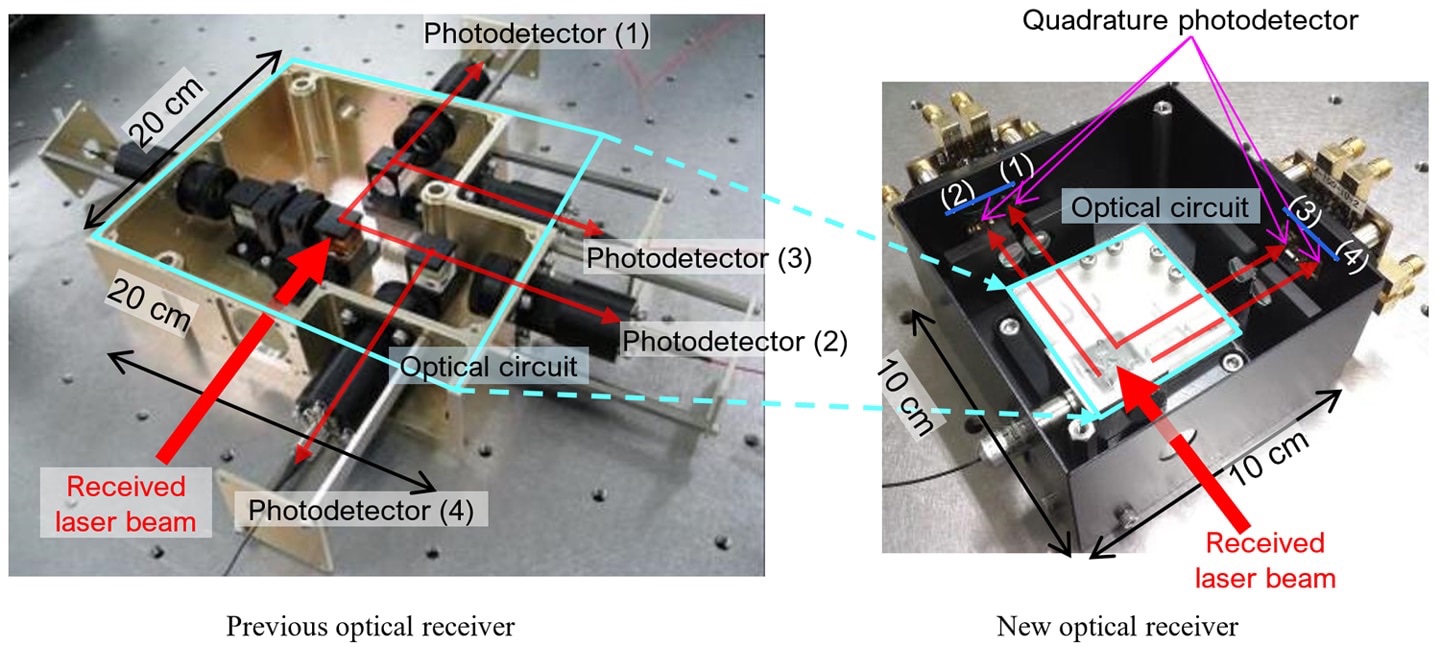
Mitsubishi: Developed a space optical communication receiver:
-Integrated space optical communication function and reception direction detection function-
Mitsubishi Electric:
Space optical communication function using laser beam and
Integrated laser beam reception direction detection function,
We have developed the world’s first optical receiver for space optical communication.
Image analysis by artificial satellite:
In recent years, images taken by artificial satellites have been widely used for grasping sediment-related disasters.
Currently, terrestrial fiber optic communication uses the general-purpose 1.5 μm band.
Terrestrial fiber optic communication:
Currently, when sending and receiving high-definition images in real time by radio satellite communication,
There were major restrictions on data capacity and antenna size.
Necessity of space optical communication:
In disaster prevention and mitigation, in order to grasp quickly and with high accuracy,
Large-capacity, high-speed space optical communication is required.
Challenges of space optical communication:
Space optical communication is
Compared to radio waves, it uses “a very narrow laser beam with a spread angle of 1/1000”.
Need for high precision sensor:
Between artificial satellites moving at high speed
The direction of travel of the laser beam to each other
Adjust to high accuracy.
There was a problem that a dedicated sensor was indispensable and the receiver size became large.
Achieve coherent optical communication:
This time, we have integrated the space optical communication function and the reception direction detection function.
Achieved “miniaturization of optical receiver”.
again,
We have developed “coherent optical communication using the phase of the laser beam”.
This will result in
In space optical communication
Compared to radio wave communication, it realizes “more than 10 times larger capacity, higher speed, and long-distance communication”.
Advantages of laser beam:
The wavelength of the laser beam is shorter than that of the radio wave.
Also, the antenna size can be reduced.
for that reason,
Places where it is difficult to lay optical fibers between buildings,
In the event of a disaster, etc .:
Situations where normal infrastructure is not functioning,
Desert etc .:
In developing countries and deserts where it is difficult to set up base stations
Moving objects, etc .:
It can be easily mounted on a moving body or installed in an existing facility.
Mitsubishi Electric News Release
https://www.mitsubishielectric.co.jp/news/2022/0531-b.html?cid=rss
Optical satellite communication system “LUCAS” -JAXA First Space Technology Division
https://www.satnavi.jaxa.jp/ja/project/lucas/index.html
Mitsubishi : a développé un récepteur de communication optique spatial :
-Fonction de communication optique spatiale intégrée et fonction de détection de direction de réception-
Mitsubishi électrique :
Fonction de communication optique spatiale utilisant un faisceau laser et
Fonction intégrée de détection de la direction de réception du faisceau laser,
Nous avons développé le premier récepteur optique au monde pour la communication optique spatiale.
Analyse d’image par satellite artificiel :
Ces dernières années, les images prises par des satellites artificiels ont été largement utilisées pour appréhender les catastrophes liées aux sédiments.
Actuellement, la communication terrestre par fibre optique utilise la bande à usage général de 1,5 μm.
Communication terrestre par fibre optique :
Actuellement, lors de l’envoi et de la réception d’images haute définition en temps réel par communication radio satellite,
Il y avait des restrictions majeures sur la capacité de données et la taille de l’antenne.
Nécessité de la communication optique spatiale :
Dans la prévention et l’atténuation des catastrophes, afin de saisir rapidement et avec une grande précision,
Une communication optique spatiale à grande capacité et à grande vitesse est requise.
Défis de la communication optique spatiale :
La communication optique spatiale est
Comparé aux ondes radio, il utilise “un faisceau laser très étroit avec un angle de propagation de 1/1000”.
Besoin d’un capteur de haute précision :
Entre satellites artificiels se déplaçant à grande vitesse
La direction de déplacement du faisceau laser l’un vers l’autre
Ajustez avec une grande précision.
Il y avait un problème qu’un capteur dédié était indispensable et la taille du récepteur est devenue grande.
Obtenez une communication optique cohérente :
Cette fois, nous avons intégré la fonction de communication optique spatiale et la fonction de détection du sens de réception.
Réalisé “miniaturisation du récepteur optique”.
encore,
Nous avons développé “une communication optique cohérente utilisant la phase du faisceau laser”.
Cela se traduira par
Dans la communication optique spatiale
Comparé à la communication par ondes radio, il réalise “plus de 10 fois plus de capacité, une vitesse plus élevée et une communication longue distance”.
Avantages du faisceau laser :
La longueur d’onde du faisceau laser est plus courte que celle de l’onde radio.
De plus, la taille de l’antenne peut être réduite.
pour cette raison,
Endroits où il est difficile de poser des fibres optiques entre les bâtiments,
En cas de sinistre, etc. :
Situations où l’infrastructure normale ne fonctionne pas,
Désert etc.:
Dans les pays en voie de développement et les déserts où il est difficile d’installer des stations de base
Objets en mouvement, etc. :
Il peut être facilement monté sur un corps mobile ou installé dans une installation existante.
Communiqué de presse de Mitsubishi Electric
Système de communication optique par satellite “LUCAS” – JAXA First Space Technology Division
Mitsubishi: Entwicklung eines optischen Kommunikationsempfängers für den Weltraum:
-Integrierte optische Weltraumkommunikationsfunktion und Empfangsrichtungserkennungsfunktion-
Mitsubishi Electric:
Weltraumoptische Kommunikationsfunktion unter Verwendung von Laserstrahl und
Integrierte Funktion zur Erkennung der Empfangsrichtung des Laserstrahls,
Wir haben den weltweit ersten optischen Empfänger für optische Weltraumkommunikation entwickelt.
Bildanalyse durch künstlichen Satelliten:
In den letzten Jahren wurden Bilder, die von künstlichen Satelliten aufgenommen wurden, weit verbreitet, um Sediment-bedingte Katastrophen zu erfassen.
Gegenwärtig verwendet die terrestrische Glasfaserkommunikation das universelle 1,5-μm-Band.
Terrestrische Glasfaserkommunikation:
Derzeit beim Senden und Empfangen von hochauflösenden Bildern in Echtzeit per Funksatellitenkommunikation,
Es gab große Einschränkungen bei der Datenkapazität und der Antennengröße.
Notwendigkeit der optischen Kommunikation im Weltraum:
In der Katastrophenvorsorge und -minderung, um schnell und mit hoher Genauigkeit zu erfassen,
Es ist eine optische Hochgeschwindigkeits-Weltraumkommunikation mit großer Kapazität erforderlich.
Herausforderungen der optischen Weltraumkommunikation:
Weltraumoptische Kommunikation ist
Im Vergleich zu Radiowellen verwendet es “einen sehr schmalen Laserstrahl mit einem Öffnungswinkel von 1/1000”.
Bedarf an hochpräzisen Sensoren:
Zwischen künstlichen Satelliten, die sich mit hoher Geschwindigkeit bewegen
Die Laufrichtung der Laserstrahlen zueinander
Auf hohe Genauigkeit einstellen.
Es gab ein Problem, dass ein dedizierter Sensor unverzichtbar war und die Empfängergröße groß wurde.
Erzielen Sie eine kohärente optische Kommunikation:
Dieses Mal haben wir die optische Weltraumkommunikationsfunktion und die Empfangsrichtungserkennungsfunktion integriert.
Erreichte “Miniaturisierung des optischen Empfängers”.
wieder,
Wir haben die „kohärente optische Kommunikation über die Phase des Laserstrahls“ entwickelt.
Dies wird dazu führen
Optische Kommunikation im Weltraum
Im Vergleich zur Funkwellenkommunikation realisiert es “eine mehr als 10-mal größere Kapazität, höhere Geschwindigkeit und Langstreckenkommunikation”.
Vorteile des Laserstrahls:
Die Wellenlänge des Laserstrahls ist kürzer als die der Radiowelle.
Außerdem kann die Antennengröße reduziert werden.
aus diesem Grund,
Orte, an denen es schwierig ist, Glasfasern zwischen Gebäuden zu verlegen,
Im Katastrophenfall etc.:
Situationen, in denen die normale Infrastruktur nicht funktioniert,
Wüste usw.:
In Entwicklungsländern und Wüsten, wo es schwierig ist, Basisstationen zu errichten
Bewegte Objekte usw.:
Es kann einfach an einem beweglichen Körper montiert oder in eine bestehende Anlage eingebaut werden.
Pressemitteilung von Mitsubishi Electric
Optisches Satellitenkommunikationssystem “LUCAS” – JAXA First Space Technology Division
Mitsubishi Electric Develops World’s First Laser Communication Terminal Integrating Space Optical Communication and Spatial Acquisition
Features
1)World’s first optical receiver that integrates spatial laser acquisition in the photodetector
2)Optical circuit detects four phase changes for high-speed, large-capacity communications
3)Optical receiver integrates photodetectors and optical circuit in one small (10cm3), lightweight module
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC News Releases