COVID-19: Waseda Univ., Ultrasensitive Antigen Test: Virus detection in 30 minutes
COVID-19:
Waseda University: Professor Ito. Research group
Significantly simplifies the conventional PCR test method,
High virus detection sensitivity,
We have succeeded in developing an ultrasensitive antigen test method (new test method).
A quick and easy “antigen test”:
For new coronavirus infectious diseases, PCR tests are difficult to perform in general clinics.
There is a long-awaited demand for the spread of “antigen tests” that can replace these methods and can be tested quickly and easily.
Conventional problems:
Until now, antigen tests had problems such as “insufficient detection sensitivity and inability to distinguish detected viruses”.
This solution:
Use the microplate reader provided in many laboratories.
We have developed a cheaper and simpler method than the PCR test, which only measures the change in absorption of light of a specific wavelength.
In the future, we will carry out measurements on actual patient samples as soon as possible and aim to detect viruses in 30 minutes.
Utilize a microplate reader
“The ultra-sensitive quantitative measurement method of ultra-trace amount protein that we have been working on” was applied.
Using a microplate reader, you can “detect a virus simply by measuring the change in absorption of light of a specific wavelength”.
The reagents used are much cheaper than PCR tests and can detect new coronavirus with high sensitivity.
Results of this research:
It was published in the international scientific magazine “Diagnostics” on August 14, 2020 (Japan time).
https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20200819/index.html
Received: 17 July 2020; Accepted: 12 August 2020; Published: 14 August 2020
Abstract:
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based antigen tests are technically difficult,
time-consuming, and expensive, and may produce false negative results requiring follow-up confirmation with computed tomography.
The global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
has increased the demand for accurate, easy-to-use, rapid, and cost-effective antigen tests for clinical application.
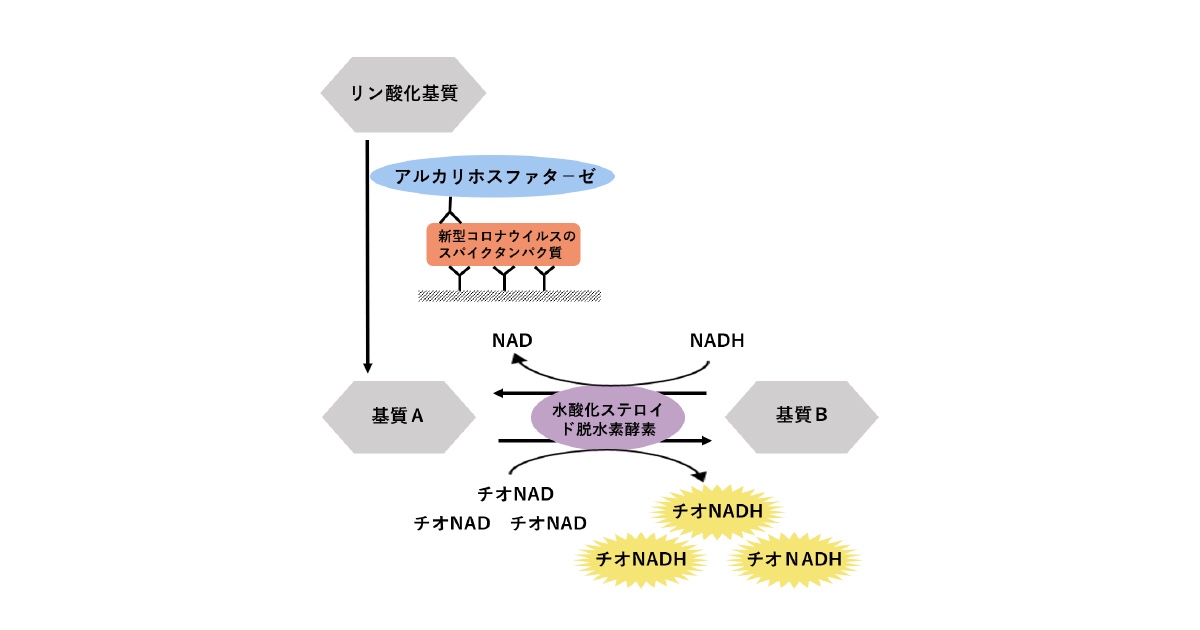
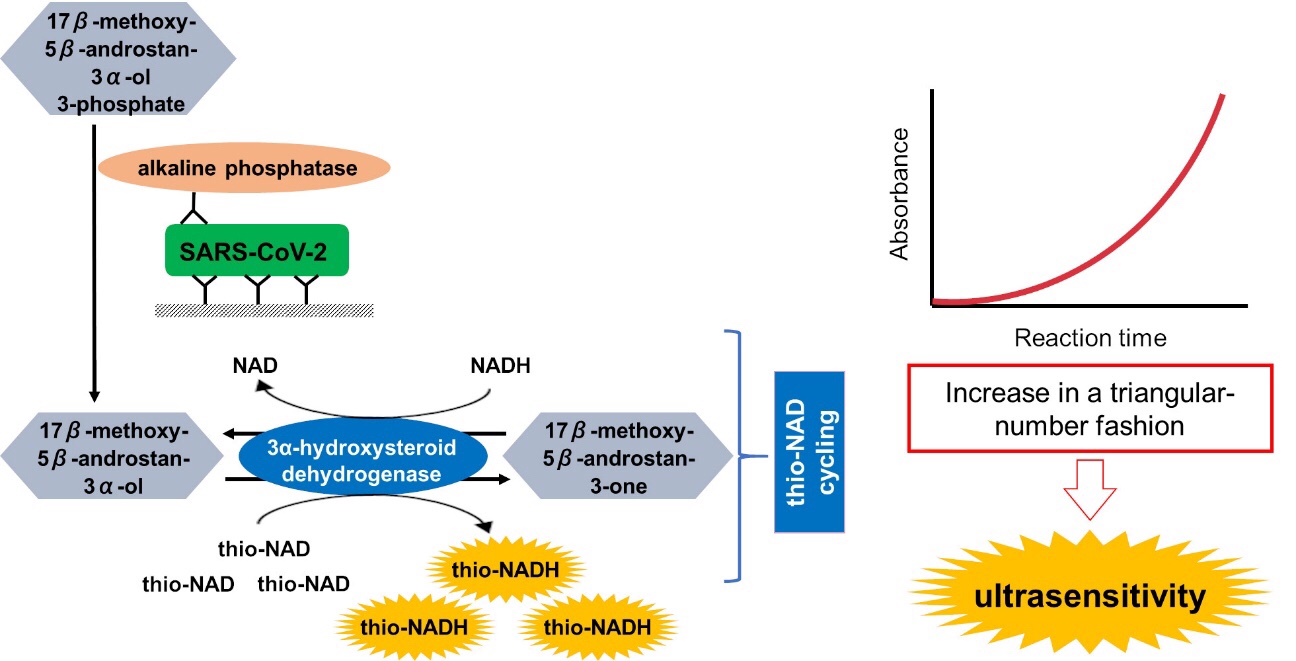
We propose a de novo antigen test for diagnosing COVID-19 using the combination of sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and thio-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (thio-NAD) cycling.
Our test
takes advantage of the spike proteins specific to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus.
The limit of detection of our test was 2.3 × 10−18 moles/assay.
If the virus has ~25 spike proteins on its surface, our method should detect on the order of 10−20 moles of virus/assay, corresponding to ~104 copies of the virus RNA/assay.
The detection sensitivity
approaches that of PCR-based assays because the average virus RNA load used for PCR-based assays is ~105 copies per oro- or naso-pharyngeal swab specimen.
To our knowledge, this is the first ultrasensitive antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins that can be performed with an easy-to-use microplate reader.
Sufficient sensitivity can be achieved within 10 min of thio-NAD cycling.
Our antigen test allows for rapid, cost-effective, specific, ultrasensitive, and simultaneous multiple measurements of SARS-CoV-2, and has broad application for the diagnosis for COVID-19.