
Carbon dioxide and hydrogen: Concentration measurement in real time!
– Highly efficient CO2 resource recovery and highly reliable carbon footprint –
Summary Report from Toshiba Timely Disclosure Information

Operating principle of a thermal conductivity sensor using MEMS technology (source: Toshiba)
Toshiba’s compact sensing technology:
Monitors multiple gas concentrations at 1/200 the size and 150 times faster than conventional models.
We have achieved highly efficient CO2 recycling technology and a highly reliable carbon footprint.

Toshiba R&D Center:
Developed “compact sensing technology that can measure concentration in real time” from mixed gases containing carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Even with a mixed gas containing three or more types of CO2, H2, and CO gases, the concentration of each gas can be measured simultaneously and at high speed in a real environment.

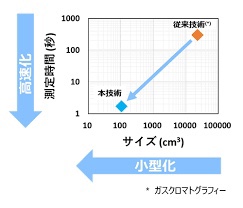
Comparison with gas chromatography:
Gas chromatography has traditionally been used to measure gas concentrations.
Toshiba was able to measure gas concentrations 150 times faster with a size less than 1/200.
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) Downsizing technology:
Using proprietary MEMS technology, ultra-small sensors with different sensitivities are collectively formed on a single substrate.
Simultaneous concentration measurement of multiple gases is realized by algorithm processing of sensor detection values.
It uses Micro Electro Mechanical Systems integrated on one substrate.
Real-time gas concentration monitoring:
Promote the development of methanation technology that converts CO2 into gas resources, and further improve the CO2 conversion efficiency.
A reliable “carbon footprint”:
Currently, greenhouse gas emissions are calculated using CO2 equivalent values. Direct measurement of each greenhouse gas provides a “reliable carbon footprint”. eachgreenhousegasprovides a “reliable carbon footprint”. 
“TRANSDUCERS 2023”:
Our company announced this technology on June 28 at TRANSDUCERS 2023 to be held in Kyoto.
https://www.global.toshiba/jp/technology/corporate/rdc/rd/topics/23/2306-02.html