
The University of Tokyo: A tube that turns seawater into drinking water:
-Extra-fine tube that allows only water to pass at high speed-
The University of Tokyo:
The research team has developed an “ultra-fine tube that allows only water to pass through at high speed without passing salt.”
Features of extra-fine tube:
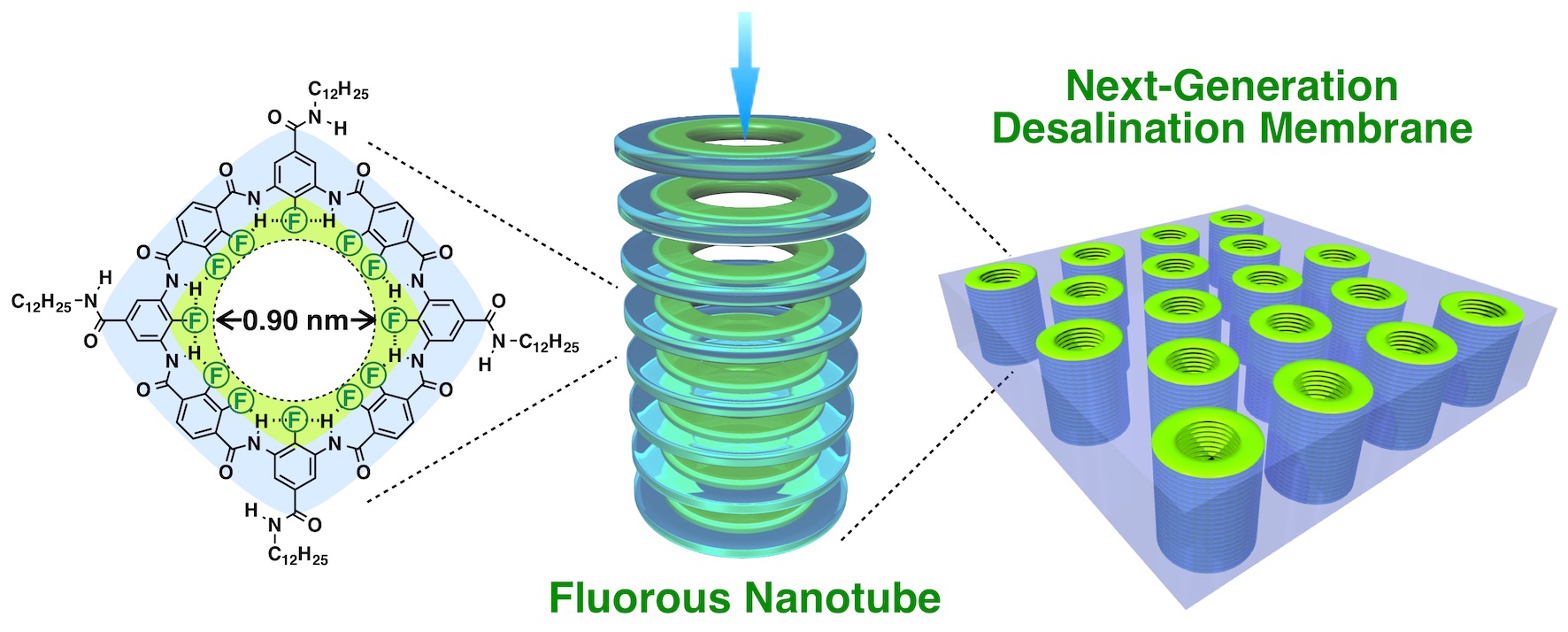
The feature is that the inside is covered with fluorine like a frying pan.
It is a next-generation water treatment technology that desalinates seawater and turns it into drinking water.
Published in the US scientific journal Science on May 13.
University of Tokyo
Professor Takuzo Aida
Associate Professor Yoshimitsu Ito
Small ring-shaped molecules were synthesized from organic compounds containing fluorine.
By stacking this ring many times,
The hole diameter is only 0.9 nanometers,
I made an extra-fine tube.
Extra-fine tube:
The inside of the tube is covered with fluorine.
“Fluorine is negatively charged”, so
Repulsion with “Chloride ion in seawater with the same negative electricity”,
Since “salt cannot pass through”, seawater can be desalinated.
High efficiency by desalination of seawater:
For human cells
There is “aquaporin, a protein that allows only water to pass through efficiently”.
It was also found that “tubes pass water 4500 times faster than aquaporins.”
Apply to seawater desalination equipment to improve efficiency.
Asahi Shimbun Digital
https://www.asahi.com/articles/ASQ5C7FQGQ5CULBH00R.html
L’Université de Tokyo : Un tube qui transforme l’eau de mer en eau potable :
-Tube extra-fin qui ne laisse passer que l’eau à grande vitesse-
L’Université de Tokyo :
L’équipe de recherche a mis au point un “tube ultra-fin qui ne laisse passer que l’eau à grande vitesse sans laisser passer le sel”.
Caractéristiques du tube extra-fin :
La particularité est que l’intérieur est recouvert de fluor comme une poêle à frire.
Il s’agit d’une technologie de traitement de l’eau de nouvelle génération qui dessale l’eau de mer et la transforme en eau potable.
Publié dans la revue scientifique américaine Science le 13 mai.
Université de Tokyo
Professeur Takuzo Aïda
Professeur associé Yoshimitsu ItoDe petites molécules en forme d’anneaux ont été synthétisées à partir de composés organiques contenant du fluor.
En empilant cet anneau plusieurs fois,
Le diamètre du trou n’est que de 0,9 nanomètre,
J’ai fait un tube extra-fin.Tube extra-fin :
L’intérieur du tube est recouvert de fluor.
“Le fluor est chargé négativement”, donc
Répulsion avec “Ion chlorure dans l’eau de mer avec la même électricité négative”,
Puisque “le sel ne peut pas passer”, l’eau de mer peut être dessalée.Haut rendement par dessalement de l’eau de mer :
Pour les cellules humaines
Il y a “l’aquaporine, une protéine qui ne laisse passer efficacement que l’eau”.
Il a également été constaté que “les tubes laissent passer l’eau 4500 fois plus vite que les aquaporines”.
Appliquer à l’équipement de dessalement d’eau de mer pour améliorer l’efficacité.
Asahi Shimbun Numérique
Die Universität Tokio: Eine Röhre, die Meerwasser in Trinkwasser verwandelt:
-Extrafeiner Schlauch, der nur Wasser mit hoher Geschwindigkeit passieren lässt-
Die Universität Tokio:
Das Forschungsteam hat ein “ultrafeines Rohr entwickelt, das nur Wasser mit hoher Geschwindigkeit passieren lässt, ohne Salz durchzulassen”.
Eigenschaften des extrafeinen Rohrs:
Das Merkmal ist, dass das Innere wie eine Bratpfanne mit Fluor bedeckt ist.
Es handelt sich um eine Wasseraufbereitungstechnologie der nächsten Generation, die Meerwasser entsalzt und in Trinkwasser umwandelt.
Veröffentlicht in der US-amerikanischen Fachzeitschrift Science am 13. Mai.
Universität Tokio
Professor Takuzo Aida
Außerordentlicher Professor Yoshimitsu ItoAus fluorhaltigen organischen Verbindungen wurden kleine ringförmige Moleküle synthetisiert.
Indem Sie diesen Ring viele Male stapeln,
Der Lochdurchmesser beträgt nur 0,9 Nanometer,
Ich habe ein extra feines Rohr gemacht.Extrafeines Rohr:
Die Innenseite des Röhrchens ist mit Fluor bedeckt.
“Fluor ist negativ geladen”, also
Abstoßung mit “Chloridion in Meerwasser mit gleicher negativer Elektrizität”,
Da “Salz nicht passieren kann”, kann Meerwasser entsalzt werden.Hohe Effizienz durch Meerwasserentsalzung:
Für menschliche Zellen
Es gibt “Aquaporin, ein Protein, das nur Wasser effizient passieren lässt”.
Es wurde auch festgestellt, dass “Röhren Wasser 4500-mal schneller passieren als Aquaporine”.
Auf Meerwasserentsalzungsanlagen auftragen, um die Effizienz zu verbessern.
Asahi Shimbun Digital
AbstractUltrafast water permeation in aquaporins is promoted by their hydrophobic interior surface.Polytetrafluoroethylenehas a dense fluorine surface, leading to its strong water repellence.We reporta series of fluorous oligoamide nanorings with interior diameters ranging from 0.9 to 1.9 nanometers.These nanorings undergo supramolecular polymerization in phospholipid bilayer membranes to form fluorous nanochannels,the interior walls of which are densely covered with fluorine atoms.The nanochannel with the smallest diameterexhibits a water permeation flux that is two orders of magnitude greater than those of aquaporins and carbon nanotubes.The proposed nanochannelexhibits negligible chloride ion (Cl–) permeability caused by a powerful electrostatic barrier provided by the electrostatically negative fluorous interior surface.Thus, this nanochannel is expectedto show nearly perfect salt reflectance for desalination.