Verification of inhibitory effect of hydroxyl radicals contained in water (nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particle) on novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
Osaka, Japan –
Panasonic Corporation today
announced that, in collaboration with Mayo Yasugi, Associate Professor, Department of Veterinary Science, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University,
it has verified the inhibitory effect of the hydroxyl radicals contained in water (nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particle) on the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
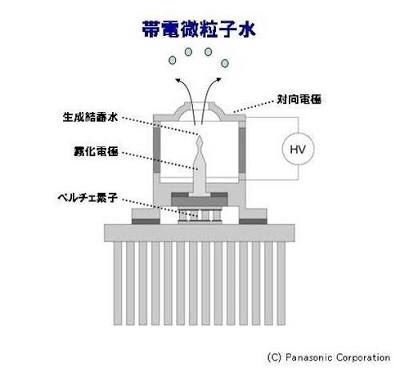
Hydroxyl radicals contained in water
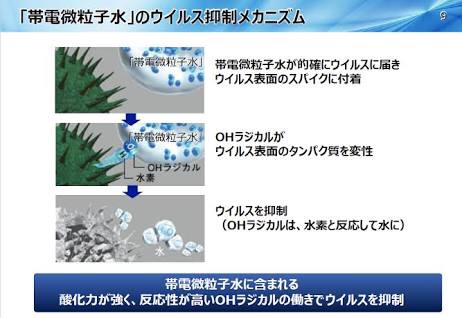
are particulate ions containing hydroxyl radicals that are generated by applying a high voltage to moisture in the air.
They are characterized by being strongly oxidative and highly reactive.
Panasonic
has been conducting research on this technology over the past 20 years since 1997,
and has verified its effectiveness in a variety of areas, including inhibiting pathogenic microorganism (bacteria, fungi, and viruses) and allergens, breaking down PM 2.5 components that have adverse effects on the human body*1.
In 2012, Panasonic
conducted a virus clearance test with a third-party organization and confirmed the effectiveness of each of the 4 categories in terms of biological characteristics.
Based on this result,
Panasonic announced that “hydroxyl radicals contained in water” technology could be expected to have a inhibitory effect on new viruses*2.
The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) of the current global pandemic is one such new type of virus,
and testing with Osaka Prefecture University
has now confirmed that the hydroxyl radicals contained in water does have an inhibitory effect on this virus.
This testing was carried out in a closed laboratory environment, and was not designed to assess its efficacy in uncontrolled living spaces.
Panasonic will continue to pursue the potential of “hydroxyl radicals contained in water” technology to address possible risks associated with air pollution such as new pathogenic microorganisms, with the aim of creating healthy environments for people around the world.
For reference :
Testing of inhibitory effect of hydroxyl radicals contained in water (nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particle) on the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
・Overview
A comparative verification was conducted in a 45L test space containing the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) with and without exposure to hydroxyl radicals contained in water.
・Results
Over 99% of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) activity was inhibited within 3 hours.
Note: This verification was designed to generate basic research data on the effects of hydroxyl radicals contained in water on the novel coronavirus in laboratory conditions different from those found in living spaces. It was not designed to evaluate product performance.
・Methodology and data
Organization:Osaka Prefecture University
Period:July, 2020
Subject:Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
Device:”Hydroxyl radicals contained in water” generator
Method:
– “Hydroxyl radicals contained in water” generator is installed at 15cm from the floor in the 45L test space.
– A piece of gauze inoculated with the virus solution was placed in a petri dish and exposed to ”hydroxyl radicals contained in water ” for a predetermined time.
– The virus infectious titer was measured and used to calculate the inhibition rate.
– The same test was performed 3 times to confirm reproducibility.
・Results data
Test subject Hours Inhibition rate*
SARS-CoV-2 First time 3 hours 99.7%
Second time 3 hours 99.9%
Third time 3 hours 99.9%
*Panasonic’s calculation
Headquarters News | Panasonic Newsroom Global
https://news.panasonic.com/global/press/data/2020/07/en200731-5/en200731-5.html