Tokyo University of Science: Developed rare earth-free magnets:
-Making a magnetic film by stacking monatomic layers one by one-
Tokyo University of Science
National Institute for Materials Science
We have developed a rare earth-free magnet that surpasses iron meteorite magnets.
Using simulation and AI,
Identify the crystal structure of the substance,
A magnetic film was prepared by stacking monatomic layers one by one.
Development of rare earth free magnets:
In the future, it will lead to the development of magnetic materials with low resource risk.
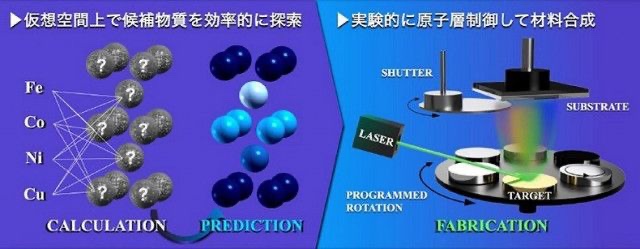
Search for candidate substances
First principle calculation
We searched for candidate substances in “first-principles calculations that predict physical properties based on quantum mechanics.”
Atomic arrangement of crystals
Bayesian optimization
The atomic arrangement of this crystal is narrowed down by “Bayesian optimization of AI technology”.
We proposed iron-copper alloys and iron-cobalt-nickel alloys.
“A substance that is difficult to come out from the experience and intuition of researchers” was found.
Synthesize candidate substances
Single atom alternating stacking method
Candidate materials were synthesized by the single-atomic alternating lamination method.
Iron Cobalt Nickel Alloy:
The iron-cobalt-nickel alloy showed a magnetic anisotropy of less than three times that of iron meteorite magnets.
It does not contain rare earths and is a candidate for magnetic materials with low resource risk.
New switch
Université des sciences de Tokyo : a développé des aimants sans terres rares :
-Fabriquer un film magnétique en empilant les couches monoatomiques une à une-
Université des sciences de Tokyo
Institut national des sciences des matériaux
Nous avons développé un aimant sans terre rare qui surpasse les aimants de météorite en fer.
En utilisant la simulation et l’IA,
Identifier la structure cristalline de la substance,
Un film magnétique a été préparé en empilant les couches monoatomiques une par une.
Développement d’aimants sans terre rare :
À l’avenir, cela conduira au développement de matériaux magnétiques à faible risque pour les ressources.
Recherche de substances candidates
Premier principe de calcul
Nous avons recherché des substances candidates dans des “calculs de premiers principes qui prédisent les propriétés physiques basées sur la mécanique quantique”.
Arrangement atomique des cristaux
Optimisation bayésienne
L’arrangement atomique de ce cristal est réduit par “l’optimisation bayésienne de la technologie AI”.
Nous avons proposé des alliages fer-cuivre et des alliages fer-cobalt-nickel.
“Une substance difficile à sortir de l’expérience et de l’intuition des chercheurs” a été trouvée.
Synthétiser des substances candidates
Méthode d’empilement alterné d’un seul atome
Les matériaux candidats ont été synthétisés par la méthode de stratification alternée à un seul atome.
Alliage fer-cobalt-nickel :
L’alliage fer-cobalt-nickel a montré une anisotropie magnétique inférieure à trois fois celle des aimants de météorite en fer.
Il ne contient pas de terres rares et est un candidat pour les matériaux magnétiques à faible risque pour les ressources.
Nouvel interrupteur
Tokyo University of Science: Seltenerdfreie Magnete entwickelt:
-Herstellen eines Magnetfilms durch Stapeln einatomiger Schichten nacheinander-
Wissenschaftliche Universität Tokio
Nationales Institut für Materialwissenschaft
Wir haben einen seltenerdfreien Magneten entwickelt, der Magnete aus Eisenmeteoriten übertrifft.
Mit Simulation und KI,
Identifizieren Sie die Kristallstruktur der Substanz,
Ein magnetischer Film wurde hergestellt, indem einatomige Schichten einzeln gestapelt wurden.
Entwicklung seltenerdfreier Magnete:
In Zukunft wird dies zur Entwicklung magnetischer Materialien mit geringem Ressourcenrisiko führen.
Suche nach Kandidatensubstanzen
Erste Prinziprechnung
Wir suchten nach Kandidatensubstanzen in “First-Principles-Berechnungen, die physikalische Eigenschaften auf der Grundlage der Quantenmechanik vorhersagen”.
Atomare Anordnung von Kristallen
Bayessche Optimierung
Die atomare Anordnung dieses Kristalls wird durch „Bayessche Optimierung der KI-Technologie“ eingegrenzt.
Wir haben Eisen-Kupfer-Legierungen und Eisen-Kobalt-Nickel-Legierungen vorgeschlagen.
„Eine Substanz, die aus der Erfahrung und Intuition von Forschern nur schwer herauszubekommen ist“, wurde gefunden.
Kandidatensubstanzen synthetisieren
Verfahren zum alternierenden Stapeln einzelner Atome
Kandidatenmaterialien wurden durch das Single-Atom-Wechsellaminierungsverfahren synthetisiert.
Eisen-Kobalt-Nickel-Legierung:
Die Eisen-Kobalt-Nickel-Legierung zeigte eine magnetische Anisotropie von weniger als dem Dreifachen von Eisenmeteoritenmagneten.
Es enthält keine Seltenen Erden und ist ein Kandidat für magnetische Materialien mit geringem Ressourcenrisiko.
Neuer Schalter