TDK: Heavy rare earth-free, hi heat-resistant rare earth magnet powder: Magnet for hybrid drive motor
-Promoting the development of magnets for motors for automobiles-
Features:
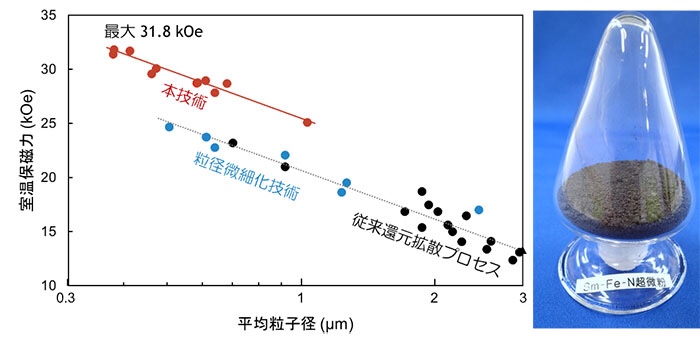
“Coercivity of samarium-iron-nitrogen magnet powder” is further improved by the magnet powder synthesis process
Realizes “Samarium-iron-nitrogen-based magnet powder” with “coercivity at room temperature of 30 kOe” and “coercivity at 200 ° C exceeds 10 kOe”
Expecting motor magnets “beyond neodymium-iron-boron magnets at high temperatures”
TDK: “AIST”
“AIST” Magnetic Powder Metallurgy Research Center, in collaboration with TDK,
Do not use heavy rare earth elements
Coercivity at room temperature exceeds 30 kOe
A technology that can produce samarium-iron-nitrogen (Sm2Fe17N3) magnet powder has been developed.
Sm2Fe17N3 magnet:
Expected to be a post-neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B) magnet.
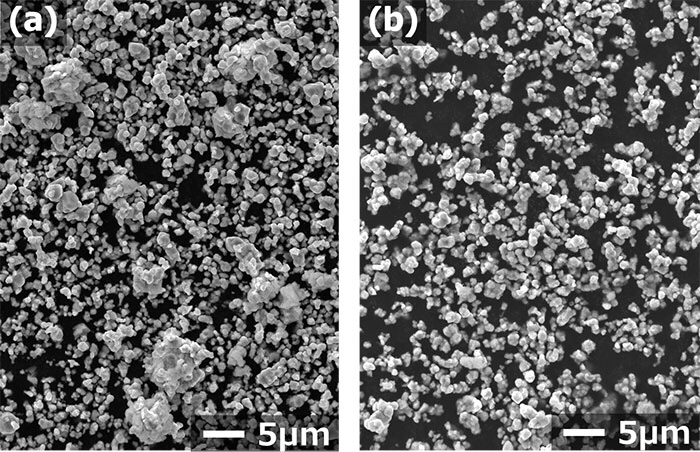
This time, we developed a rotary heat treatment technology specializing in the reduction diffusion method and improved the coercive force of Sm2Fe17N3 magnet powder.
Development of particle size refinement technology:
Furthermore, the particle size refinement technology developed so far is applied.
Room temperature: about 32 kOe,
Estimated application for motors for automobile drive: 11 kOe at 200 ºC
Realized high coercive force unprecedented in heavy rare earth-free rare earth-iron magnets.
Sm2Fe17N3 magnets have excellent heat resistance.
In the future, it is expected to realize magnets that exceed Nd-Fe-B magnets in high-temperature environments such as drive motors for hybrid vehicles.
-JETRO
https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2019/pr20191021/pr20191021.html