Osaka Univ: Making eye conjunctival cells with iPS: Expectations for drug discovery of dry eye
Research team at Osaka University:
“We have succeeded in producing eye conjunctival cells from iPS cells,” a research team at Osaka University announced.
Making eye conjunctival cells from iPS:
It is expected to be used for drug discovery for dry eyes with dry eyes.
The conjunctiva covers the back of the eyelids and the white of the eye.
It secretes the tear component “mucin” that protects the surface of the eyes.
The treatise was published in the electronic version of the American scientific journal Cell Reports by the 6th.
Research team:
For the cells that are the source of the eyes, made from iPS
By adding proteins that promote growth
Conjunctival epithelial cells and mucin-secreting cells were created.
Research using iPS cells
At present, “in research using iPS cells, the production of retinal and black eye corneas” is ahead.
In the production of conjunctival cells of the eye, it is extremely difficult to obtain the necessary cells.
Professor Ryuhei Hayashi:
This time, a method for culturing conjunctival cells using iPS cells has been established.
He said it would be available in large quantities and would be useful in investigating therapeutic effects.
Current affairs dot com
https://www.jiji.com/jc/article?k=2021020600176&g=soc
Established a method for producing conjunctival epithelium from iPS cells
Points of research results
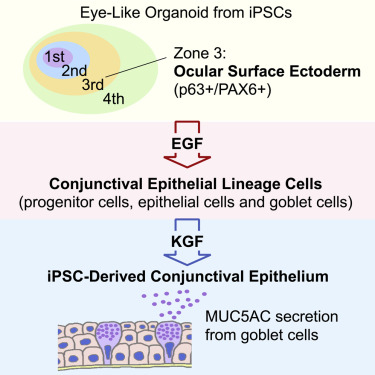
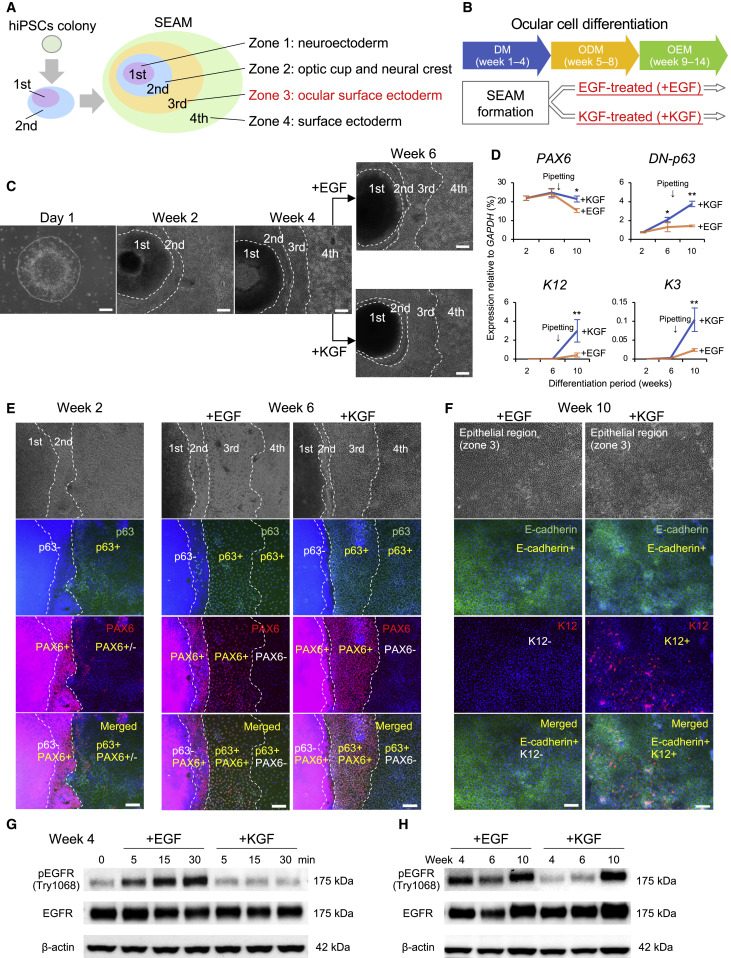
Utilizing eye organoid technology:
Established a method for inducing differentiation of human iPS cells into conjunctival epithelial lineage cells using ocular organoid technology.
Conjunctival epithelium derived from human iPS cells:
The prepared human iPS cell-derived conjunctival epithelium was a functional epithelial tissue that holds conjunctival goblet cells responsible for mucin secretion.
EGF and KGF:
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is used for differentiation into conjunctival epithelial progenitor cells.
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is used for maturation and differentiation from progenitor cells to conjunctival epithelium.
We have found that it is extremely important in maturation and differentiation.
Create conjunctival epithelium:
Previous studies have succeeded in producing corneal epithelium from human iPS cells.
However, it was difficult to prepare the conjunctival epithelium, which is the surface epithelium of the eye.
Drug discovery for eye diseases:
Basic research on human conjunctival epithelium, which was difficult to obtain, has become possible, and it is expected to be applied to drug discovery and regenerative medicine research for eye diseases such as dry eye.
Resou
https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/research/2021/20210203_1
Generation of functional conjunctival epithelium, including goblet cells, from human iPSCs Highlights
• Human iPSCs can give rise to cells of a conjunctival epithelial lineage
• EGF signaling is required for conjunctival cells to develop from iPSCs
• KGF is needed for the maturation of the iPSC-derived conjunctival epithelium
• The iPSC-derived conjunctival epithelium contains mucin-producing goblet cells
Summary
The conjunctival epithelium, which covers the sclera (the white of the eye) and lines the inside of the eyelids,
is essential for mucin secretion and the establishment of a healthy tear film.
Here, we describe human conjunctival development in a self-formed ectodermal autonomous multi-zone (SEAM) of cells
that were derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and mimic whole-eye development.
ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124721000280