
COVID-19: Elucidation of the mechanism of intravascular invasion!
– Elucidation of aggravation of corona with iPS chip –
Kyoto University:
The iPS cell research institute has clarified “the mechanism by which the new coronavirus invades blood vessels”.
In the future, it will lead to the prevention of aggravation of the new coronavirus.
novel coronavirus
Infection route/mechanism
The new coronavirus first infects respiratory cells such as the respiratory tract.
It then spreads to other organs via blood vessels.
However, the mechanism by which it penetrates blood vessels has not been elucidated.
Mechanism of entry into blood vessels:
When infected with the new coronavirus, the “function of proteins that connect cells” is suppressed.
We clarified that “gaps are formed” in “cell walls that prevent virus invasion”.
Enters blood vessels through gaps:
The new coronavirus invades blood vessels through this gap.
The results of this study:
The results of this research will lead to the development of therapeutic drugs that prevent the aggravation of the novel coronavirus.
(Yomiuri TV)-Yahoo! News
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/ba81a7f7819c1e9fb8377bf03f8bd0ee9cdc8686
Organ chip technology: Elucidation of the mechanism by which the new coronavirus invades blood vessels
~Destruction of the respiratory vascular endothelial barrier by inhibiting Claudin-5 expression~
CiRA
Research results:
• COVID-19 suppresses Claudin-5 expression and disrupts the respiratory vascular endothelial barrier.
• Elucidated the “mechanism of respiratory vascular endothelial barrier disruption” using airway chips.
• Fluvastatin can treat respiratory endothelial barrier disruption caused by COVID-19.
iPS Cell Research Institute, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/j/pressrelease/news/220922-030000.html
COVID-19 : Élucidation du mécanisme de l’invasion intravasculaire !
– Élucidation de l’aggravation du corona avec la puce iPS –
Université de Kyôto :
L’institut de recherche sur les cellules iPS a précisé “le mécanisme par lequel le nouveau coronavirus envahit les vaisseaux sanguins”.
À l’avenir, cela conduira à la prévention de l’aggravation du nouveau coronavirus.
coronavirus nouveau
Voie/mécanisme d’infection
Le nouveau coronavirus infecte d’abord les cellules respiratoires telles que les voies respiratoires.
Il se propage ensuite à d’autres organes via les vaisseaux sanguins.
Cependant, le mécanisme par lequel il pénètre dans les vaisseaux sanguins n’a pas été élucidé.
Mécanisme d’entrée dans les vaisseaux sanguins :
Lorsqu’ils sont infectés par le nouveau coronavirus, la “fonction des protéines qui relient les cellules” est supprimée.
Nous avons précisé que “des lacunes sont formées” dans “les parois cellulaires qui empêchent l’invasion du virus”.
Pénètre dans les vaisseaux sanguins par les interstices :
Le nouveau coronavirus envahit les vaisseaux sanguins par cette lacune.
Les résultats de cette étude :
Les résultats de cette recherche conduiront au développement de médicaments thérapeutiques qui préviendront l’aggravation du nouveau coronavirus.
(Yomiuri TV) – Yahoo Actualités
Technologie des puces d’organes : élucidation du mécanisme par lequel le nouveau coronavirus envahit les vaisseaux sanguins
~Destruction de la barrière endothéliale vasculaire respiratoire par inhibition de l’expression de Claudin-5~
CiRA
Résultats de recherche:
• Le COVID-19 supprime l’expression de Claudin-5 et perturbe la barrière endothéliale vasculaire respiratoire.
• Élucidation du « mécanisme de perturbation de la barrière endothéliale vasculaire respiratoire » à l’aide de puces pour voies respiratoires.
• La fluvastatine peut traiter la perturbation de la barrière endothéliale respiratoire causée par la COVID-19.
Institut de recherche sur les cellules iPS, Université de Kyoto
COVID-19: Aufklärung des Mechanismus der intravaskulären Invasion!
– Aufklärung der Corona-Verschlimmerung mit iPS-Chip –
Universität Kyoto:
Das iPS-Zellforschungsinstitut hat „den Mechanismus aufgeklärt, durch den das neue Coronavirus in Blutgefäße eindringt“.
In Zukunft wird es dazu führen, dass eine Verschlimmerung des neuen Coronavirus verhindert wird.
neuartiges Coronavirus
Infektionsweg/-mechanismus
Das neue Coronavirus infiziert zunächst Atemwegszellen wie die Atemwege.
Es breitet sich dann über Blutgefäße auf andere Organe aus.
Der Mechanismus, durch den es in Blutgefäße eindringt, wurde jedoch nicht aufgeklärt.
Eintrittsmechanismus in Blutgefäße:
Bei einer Infektion mit dem neuen Coronavirus werde die „Funktion von Proteinen, die Zellen verbinden“ unterdrückt.
Wir haben klargestellt, dass in „Zellwänden, die das Eindringen von Viren verhindern“, „Lücken gebildet werden“.
Dringt durch Lücken in Blutgefäße ein:
Das neue Coronavirus dringt durch diese Lücke in die Blutgefäße ein.
Die Ergebnisse dieser Studie:
Die Ergebnisse dieser Forschung werden zur Entwicklung von Therapeutika führen, die die Verschlimmerung des neuartigen Coronavirus verhindern.
(Yomiuri TV) – Yahoo!-Nachrichten
Organchip-Technologie: Aufklärung des Mechanismus, mit dem das neue Coronavirus in Blutgefäße eindringt
~Zerstörung der respiratorischen vaskulären endothelialen Barriere durch Hemmung der Claudin-5-Expression~
CiRA
Forschungsergebnisse:
• COVID-19 unterdrückt die Claudin-5-Expression und unterbricht die respiratorische vaskuläre endotheliale Barriere.
• Aufklärung des „Mechanismus der Störung der respiratorischen vaskulären endothelialen Barriere“ unter Verwendung von Atemwegs-Chips.
• Fluvastatin kann die durch COVID-19 verursachte Störung der respiratorischen endothelialen Barriere behandeln.
iPS-Zellforschungsinstitut, Universität Kyoto
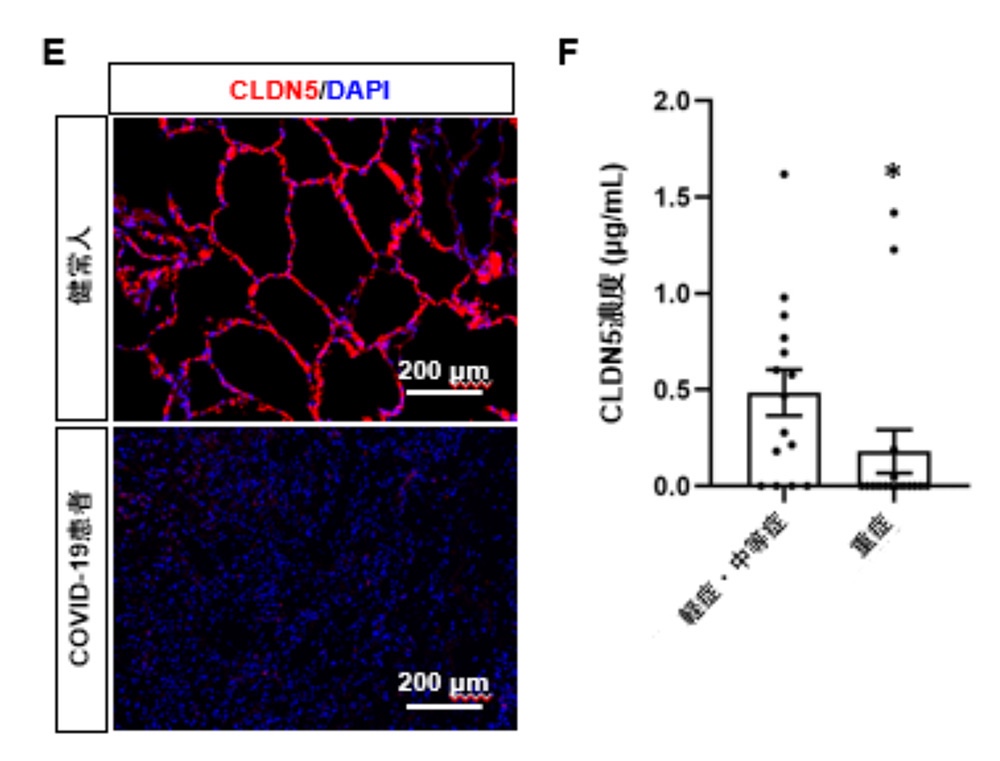
SARS-CoV-2 disrupts respiratory vascular barriers by suppressing Claudin-5 expression
Science Advances
Abstract
In the initial process of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19),
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
infects respiratory epithelial cells and then transfers to other organs the blood vessels.
It is believed that SARS-CoV-2
can pass the vascular wall by altering the endothelial barrier using an unknown mechanism.
In this study,
we investigated the effect of SARS-CoV-2 on the endothelial barrier using an airway-on-a-chip that mimics respiratory organs and found that
SARS-CoV-2 produced from infected epithelial cells disrupts the barrier
by decreasing Claudin-5 (CLDN5),
a tight junction protein, and disrupting vascular endothelial cadherin–mediated adherens junctions.
Consistently,
the gene and protein expression levels of CLDN5 in the lungs of a patient with COVID-19 were decreased.
CLDN5 overexpression or Fluvastatin treatment
rescued the SARS-CoV-2–induced respiratory endothelial barrier disruption.
We concluded that
the down-regulation of CLDN5 expression is a pivotal mechanism for SARS-CoV-2–induced endothelial barrier disruption in respiratory organs
and that inducing CLDN5 expression is a therapeutic strategy against COVID-19.