
Tokyo Tech: Ammonia synthesis from hydrogen and nitrogen at 50 ° C: Revolution for the first time in 100 years
-Japan develops new manufacturing method-
Tsubame BHB (Chuo-ku, Tokyo)
A new method for producing ammonia is about to emerge from Japan.
Worked on “plant development that can produce ammonia on a small scale”.
Problems with the Haber-Bosch process:
The Haber-Bosch process was born in Germany in the early 20th century.
This method contributed to a dramatic improvement in agricultural production.
However,
Using nitrogen and hydrogen in the air as raw materials
200 to 350 bar,
A reaction condition of 500 degrees is required.
It has a high energy load and requires a large-scale plant.New method for producing ammonia:
Tsubame BHB is working on a new manufacturing method that is different from the past.
It is a plant that produces ammonia at “low temperature and low pressure”.
The key to this is the “C12A7 electride catalyst.”
Discovered by “Professor Hideo Hosono of Tokyo Institute of Technology”.
C12A7 electride catalyst:
Incorporates electrons into the constituent structure of cement.
Ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on electride.
It has 10 times more catalytic effect than before.
Reduce the energy required for the ammonia production reaction.
Ammonia production at low temperature and low pressure:With this catalyst, ammonia can be produced at a lower temperature and lower pressure than before.
You don’t need a large plant.
Tsubame BHB:
Transform the distribution of ammonia by providing small-scale facilities that can produce ammonia on-site (locally).
Regional decentralization of ammonia production:
In fact, ammonia production is concentrated in ammonia consuming countries and natural gas producing areas.
From now on, Tsubame BHB will
It plans to install small-scale equipment in areas with low ammonia production, such as Africa, to decentralize ammonia production.
Ammonia price cuts:
By enabling production in the area of use, CO2 required for transportation will be reduced.
Most of the ammonia prices are spent on transportation and storage.
Kawasaki City Pilot Plant:
We have already demonstrated an annual production capacity of 20 tons at a pilot plant in Kawasaki City.
We will start accepting orders from companies in 2009.
Aim for delivery within 23 years.
Manufacture of clean ammonia:Ammonia is produced from electricity generated from renewable energy.
It becomes “clean ammonia” that does not emit CO2 during manufacturing and use.
New switch
Fuelling the World Sustainably: Synthesizing Ammonia using Less Energy
Research Published: April 27, 2020
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology
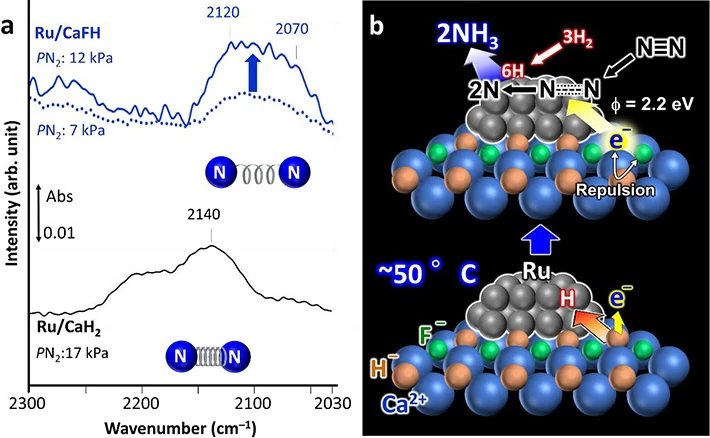
have developed an improved catalyst by taking the common dehydrating agent calcium hydride and adding fluoride to it.
The catalyst
facilitates the synthesis of ammonia at merely 50 °C, by using only half the energy that existing techniques require.
This opens doors to ammonia production with low energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emission.
Their catalyst
comprises a solid solution of CaFH, with ruthenium (Ru) nanoparticles deposited on its surface.The addition of fluoride (F-) to calcium hydride (CaH2),
a common dehydrating agent, is what makes the catalyst effective at lower temperatures and pressures.
After conducting spectroscopic and computational analyses,
the scientists propose a possible mechanism by which the catalyst facilitates ammonia production.
Tokyo Tech News | Tokyo Institute of Technology