Japan (NIPS): pH imaging tool development: CMOS sensor application
National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NIPS) / Toyohashi Univ of Technology
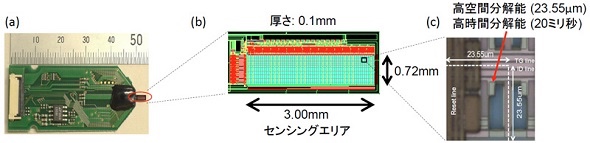
On February 5, 2020, we developed a high-definition pH imaging tool using a thin CMOS sensor.
High definition pH imaging tools:
This pH imaging tool can be applied to living organisms.
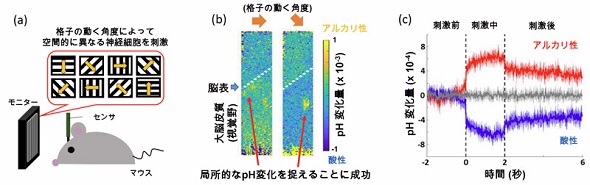
A mouse experiment was used to detect how pH in the brain dynamically changes with visual stimuli.
Sensor features:
Time resolution: 20 ms,
Spatial resolution: 23.55μm,
Sensor range: 0.72 × 3.00mm,
Thinner sensing area (also used for small brains such as mice)
Experimental result: mouse brain
“Measuring the activity of 50 μm microneural cells” and pH imaging can be performed in the mouse brain.
When showing various visual patterns to the mouse,
Imaging of pH changes in the primary visual field,
Observation of pH changes with different spatial patterns in the brain for each visual pattern.
The brain pH was found to change dynamically in milliseconds with neural activity.
Conventional sensors:
Conventional pH measurement methods have been limited to local measurement because they use a pH electrode.
However, diseases such as epilepsy and cerebral ischemia change the pH outside the brain cells beyond its range.
The sensor this time:
This high-resolution biological brain pH imaging enables spatial and temporal understanding.
Contribute to the elucidation and treatment of pathological mechanisms related to changes in pH, such as brain diseases and cancer.
MONOist
https://monoist.atmarkit.co.jp/mn/spv/2002/27/news010.html
Integrated Biosensor / MEMS Group BioGroup