「零功率損耗」:列車採用超導輸電運行
・利用特殊材料的電纜實現超導電力傳輸
・使用液態氮作為高溫超導線材
我們為您帶來朝日電視台(ANN)發表的文章摘要。
Japanese Railway Research Institute: (RTRI)
Verification of the superconducting power transmission system began on March 13th at Izu-Hakone Railway.
Superconducting power transmission uses cables made of special materials to eliminate power loss.
Superconducting power transmission with zero power loss: Cooling special material cables reduces voltage drops and power transmission losses.
This time, we will first use a 100m cable. Next, test with a cable of several kilometers

Advantages of superconducting power transmission:
1. The number of ‘substations that require huge operating costs’ will be reduced.
2. Substation maintenance costs will be significantly reduced by half.
We are currently inundated with inquiries from about 10 railway operators.
If there are no problems with verification, we will commercialize the product as soon as possible.
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/7e7a2ca4e2d545170d71dbb314f9b8ad7cda26c7

Railway Research Institute: Establishes superconducting power transmission system technology
We will provide you with a summary of articles published in the Tekko Shimbun.
RTTI: Director of Superconductivity/Low Temperature Laboratory
Establish power transmission system technology using superconducting cables within the next five years.

Procurement of high temperature superconducting wire:
High-temperature superconducting wire was procured from a major Japanese wire manufacturer.
This superconducting cable is used as an electrical conductor.
Japan’s high temperature superconducting technology:
1. Major electric wire companies are positioning high-temperature superconducting wire materials as one of their focus areas.
2. We have currently completed basic technology development and are planning investment to increase production.
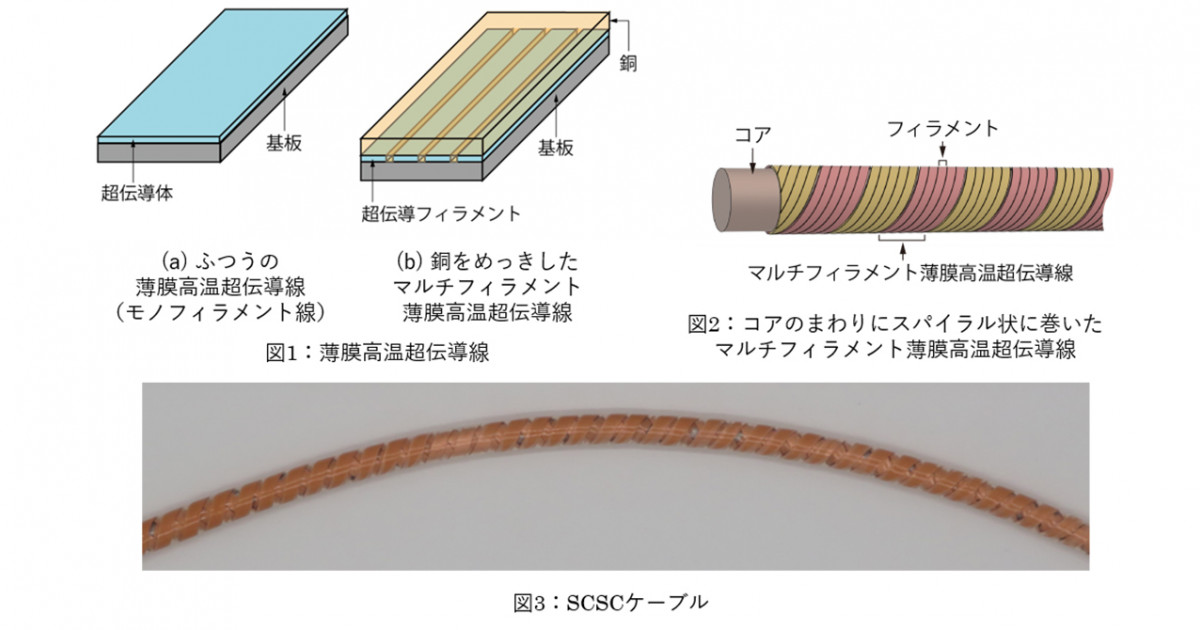
What is high temperature/superconducting wire:
Superconductor material eliminates electrical resistance.
1. Liquid nitrogen at a relatively high temperature is used for high-temperature superconducting wire.
2. When used in power transmission cables, it reduces voltage drops and power transmission losses.
mechano-electrical systems of Railway Research Institute:
1. A mechano-electrical system is used to send power from the substation to the vehicle.
2. The cable uses superconducting wire as the electrical conductor.
Verification of superconducting power transmission system:
This time, we will use a 102m superconducting cable. The electricity supplied will then be used to actually operate the train.
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/18b3783700a9816e9c798fa7171c06a24d76fe7f

Superconducting power transmission:
Sakura Internet introduced at data center in Hokkaido
Ishikari City, Hokkaido, where data centers (DCs) gather
Demonstrating ‘superconducting power transmission’ at a data center.
Practical application of superconducting power transmission:
Harnessing the potential of renewable energy. Using cutting-edge technology, we aim to achieve zero power loss.
https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXZQOFC06DAD0W3A201C2000000/

Japan’s next-gen electricity cable :promises zero transmission loss
Nikkei Asia TOKYO
Superconducting power transmission:
technology has entered the practical stage in Japan,offering a potentially less costly way to operate trainsand a possible countermeasure to global warming.

A Japan Railway Technical research institute(RTRI)
It has laid a 1.5-km superconducting transmission line
— the world’s longest practical-use cable —
at a facility in Miyazaki Prefecture, where it is holding demonstration tests.
Transmission loss mainly caused when electricity turns into heat due to the electrical resistance of electric wires.

The technology’s cost :
When a transmission line is cooled to minus 269 C with liquid helium and put into a superconducting state,
the electrical resistance becomes zero, and power loss can be all but eliminated.
Thanks to the development of materials that can be superconducting at minus 196 C,liquid nitrogen can be used as a coolant, which is 10% cheaper than the standard liquid helium.

The test cable:the RTRI says.
The test cable can carry the railway-required 1,500 volts and several hundred amperes.
if we can make the distance of one power line more than 1 km, we can reduce the cost by utilizing existing power transmission facilities,
To reduce the number of substations :
Substations are located every 3 km, the annual maintenance cost is estimated to be 20 million yen ($173,000) per substation.
The RTRI is already working on the development of a power transmission line longer than 1.5 km.
According to the Institute of Energy Economics, Japan
the country loses 4% of its electricity as it is being delivered.
The country’s railways use about 17 billion kilowatt-hours a year,
4% of that is about 700 million kilowatt-hours, equivalent to what 160,000 ordinary households require.

Transmission loss:
Transmission loss is a serious issue in many countries.
Lines in India:
Lines in India leak about 17% of the electricity they carry.
Lines in China:
China’s state-owned transmission company
in November installed a 1.2-km superconducting line in Shanghai.
Lines in Germany:
In Germany, the Ministry of Economy and Energy
leads a project that in 2020 began laying a 12-km superconducting transmission line under Munich.

Materials for power lines in Japan:
Japan has strengths in materials for power lines,
as companies like SWCC Showa Holdings manufacture power lines used for superconducting power transmission.
The Linear Chuo Shinkansen,
a high-speed maglev train line between Tokyo and Nagoya,
that Central Japan Railway is working on also uses superconductivity, and the know-how cultivated there has become the technological foundation for the power transmission field.