NIFS: High performance plasma insulation layer with deuterium:
-First demonstration of plasma turbulence observation-
“Fusion power generation”:
In fusion power generation, it is necessary to raise the temperature of the central part of the plasma to 100 million degrees Celsius or higher.
If a heat insulating layer is formed in the plasma,
Less heat is transferred from the plasma to the outside,
The temperature in the center of the plasma rises,
It will be in a favorable state for fusion power generation.So far
“The effect of the difference in plasma mass on the formation of the heat insulating layer and performance” was unknown.
National Institute for Fusion Science, National Institute for Fusion Science
Assistant Professor Tatsuya Kobayashi,
Assistant Professor Akihiro ShimizuToward the realization of “fusion power generation”, we succeeded in “improving the performance of the plasma insulation layer using deuterium”.
Measure the flow inside the plasma and
Due to the strong flow generated by deuterium plasma
It was shown that a high-performance heat insulating layer is formed.
It leads to the generation of high temperature plasma, which is indispensable for fusion power generation.Superconducting fusion plasma experimental device
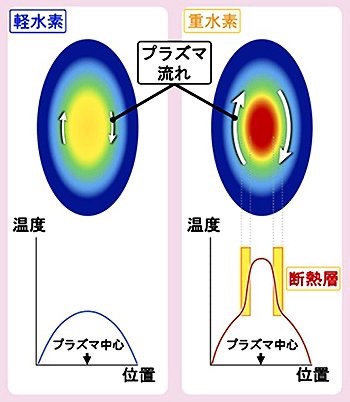
Large Helical Device (LHD)A comparative experiment between deuterium plasma and light hydrogen plasma was conducted.
Characteristics of deuterium plasma:
The deuterium plasma formed a heat insulating layer even at a density 1.5 times higher than that of the light hydrogen plasma.
Generally, the higher the plasma density, the less likely it is that the insulating layer will be formed.
Measuring the flow inside the plasma:
A “gold ion high-speed beam accelerated to 8 million km / h” was incident on the plasma.
Of the beam that passed through the plasma
Using the technique of obtaining an electric potential by changing energy,
The flow inside the plasma was measured.
as a result,Deuterium plasma has a stronger flow than light hydrogen plasma.
It turned out that “this leads to heat insulation performance”.
New switch
National Institute for Fusion Science
Fusion power generation:
In order to realize fusion power generation, it is necessary to stably confine high-temperature plasma with a magnetic field.
Plasma turbulence is a problem:
but,
Due to “turbulence generated in plasma * 1”
The problem is that the temperature of the plasma drops.
“Clarifying the characteristics of turbulence is an important research subject.”
Large Helical Device (LHD):
National Institute for Fusion Science (Toki City, Gifu Prefecture)
Assistant Professor Naoki Kamochi,
Professor Katsumi Ida,
Associate Professor Kihiko Tokuzawa
University of Wisconsin, USA
Professor Daniel J. Den HartggResearch group:
In the Large Helical Device (LHD) * 2
When heat escapes in the plasma
Turbulence that moves faster than heat,
I discovered it for the first time in the world.
Elucidating the characteristics of turbulence:The characteristic of this turbulence is “which makes it possible to predict changes in plasma temperature”.
from now on,
By observing turbulence,
We will develop a “method for controlling plasma temperature in real time”.
Research papers:
It was published in the online version of “Scientific Reports” in the UK on May 16th.
Research results:
By observing the predictive turbulence, it was possible to predict the change in plasma temperature.
In the future, it is expected to develop a method to control the plasma temperature in real time.
Research Results / News
https://www.nifs.ac.jp/news/researches/220519.html
NIFS : Couche d’isolation plasma haute performance au deutérium :
-Première démonstration d’observation de la turbulence du plasma-
“Production d’énergie par fusion”:
Dans la production d’énergie de fusion, il est nécessaire d’élever la température de la partie centrale du plasma à 100 millions de degrés Celsius ou plus.
Si une couche calorifuge se forme dans le plasma,
Moins de chaleur est transférée du plasma vers l’extérieur,
La température au centre du plasma augmente,
Il sera dans un état favorable pour la production d’énergie de fusion.Jusqu’à présent
“L’effet de la différence de masse de plasma sur la formation de la couche d’isolation thermique et les performances” était inconnu.
Institut national des sciences de la fusion, Institut national des sciences de la fusion
Professeur adjoint Tatsuya Kobayashi,
Professeur adjoint Akihiro ShimizuVers la réalisation de la “génération d’énergie de fusion”, nous avons réussi à “améliorer les performances de la couche d’isolation au plasma à l’aide de deutérium”.
Mesurer le débit à l’intérieur du plasma et
En raison du fort flux généré par le plasma de deutérium
Il a été montré qu’une couche d’isolation thermique à haute performance est formée.
Cela conduit à la génération de plasma à haute température, indispensable à la production d’énergie de fusion.Dispositif expérimental de plasma de fusion supraconducteur
Grand dispositif hélicoïdal (LHD)Une expérience comparative entre le plasma de deutérium et le plasma d’hydrogène léger a été menée.
Caractéristiques du plasma de deutérium :
Le plasma de deutérium a formé une couche d’isolation thermique même à une densité 1,5 fois supérieure à celle du plasma d’hydrogène léger.
Généralement, plus la densité du plasma est élevée, moins il est probable que la couche isolante se forme.
Mesure du débit à l’intérieur du plasma :
Un “faisceau d’ions d’or à grande vitesse accéléré à 8 millions de km/h” était incident sur le plasma.
Du faisceau qui a traversé le plasma
En utilisant la technique d’obtention d’un potentiel électrique par changement d’énergie,
Le débit à l’intérieur du plasma a été mesuré.
par conséquent,Le plasma de deutérium a un flux plus fort que le plasma d’hydrogène léger.
Il s’est avéré que “cela conduit à des performances d’isolation thermique”.
Nouvel interrupteur
Institut national des sciences de la fusion
Production d’énergie par fusion :
Afin de réaliser la production d’énergie de fusion, il est nécessaire de confiner de manière stable le plasma à haute température avec un champ magnétique.
La turbulence du plasma est un problème :
mais,
En raison de “la turbulence générée dans le plasma * 1”
Le problème est que la température du plasma chute.
“Clarifier les caractéristiques de la turbulence est un sujet de recherche important.”
Grand dispositif hélicoïdal (LHD):
Institut national des sciences de la fusion (ville de Toki, préfecture de Gifu)
Professeur adjoint Naoki Kamochi,
Professeur Katsumi Ida,
Professeur associé Kihiko Tokuzawa
Université du Wisconsin, États-Unis
Professeur Daniel J. Den HartggGroupe de recherche:
Dans le grand dispositif hélicoïdal (LHD) * 2
Quand la chaleur s’échappe dans le plasma
Turbulence qui se déplace plus vite que la chaleur,
Je l’ai découvert pour la première fois au monde.
Élucider les caractéristiques de la turbulence :La caractéristique de cette turbulence est “qui permet de prédire les changements de température du plasma”.
désormais,
En observant les turbulences,
Nous développerons une “méthode de contrôle de la température du plasma en temps réel”.
Documents de recherche:
Il a été publié dans la version en ligne de “Scientific Reports” au Royaume-Uni le 16 mai.
Résultats de recherche:
En observant la turbulence prédictive, il a été possible de prédire l’évolution de la température du plasma.
Dans le futur, il est prévu de développer une méthode pour contrôler la température du plasma en temps réel.
Résultats de recherche / Actualités
NIFS: Hochleistungs-Plasma-Isolationsschicht mit Deuterium:
-Erste Demonstration der Beobachtung von Plasmaturbulenzen-
“Fusionsstromerzeugung”:
Bei der Erzeugung von Fusionsenergie ist es notwendig, die Temperatur des zentralen Teils des Plasmas auf 100 Millionen Grad Celsius oder mehr zu erhöhen.
Bildet sich im Plasma eine wärmeisolierende Schicht,
Weniger Wärme wird vom Plasma nach außen übertragen,
Die Temperatur im Zentrum des Plasmas steigt,
Es wird sich in einem günstigen Zustand für die Erzeugung von Fusionsenergie befinden.Bisher
“Die Wirkung des Unterschieds in der Plasmamasse auf die Bildung der Wärmeisolierschicht und die Leistung” war unbekannt.
Nationales Institut für Fusionswissenschaft, Nationales Institut für Fusionswissenschaft
Assistenzprofessor Tatsuya Kobayashi,
Assistenzprofessor Akihiro ShimizuIm Hinblick auf die Realisierung der “Fusionsstromerzeugung” gelang es uns, “die Leistung der Plasmaisolationsschicht mit Deuterium zu verbessern”.
Messen Sie den Fluss innerhalb des Plasmas und
Aufgrund der starken Strömung, die durch Deuteriumplasma erzeugt wird
Es hat sich gezeigt, dass eine hochleistungsfähige Wärmedämmschicht entsteht.
Es führt zur Erzeugung von Hochtemperaturplasma, das für die Erzeugung von Fusionsstrom unverzichtbar ist.Supraleitendes Fusionsplasma-Experimentiergerät
Großes spiralförmiges Gerät (LHD)Es wurde ein Vergleichsexperiment zwischen Deuteriumplasma und leichtem Wasserstoffplasma durchgeführt.
Eigenschaften von Deuteriumplasma:
Das Deuteriumplasma bildete selbst bei einer 1,5-mal höheren Dichte als das leichte Wasserstoffplasma eine wärmeisolierende Schicht.
Im Allgemeinen ist es umso unwahrscheinlicher, dass die Isolierschicht gebildet wird, je höher die Plasmadichte ist.
Messung der Strömung im Plasma:
Ein „auf 8 Millionen km/h beschleunigter Goldionen-Hochgeschwindigkeitsstrahl“ traf auf das Plasma.
Von dem Strahl, der durch das Plasma ging
Mit der Technik, ein elektrisches Potential durch Energieänderung zu erhalten,
Der Fluss innerhalb des Plasmas wurde gemessen.
infolge,Deuteriumplasma hat eine stärkere Strömung als leichtes Wasserstoffplasma.
Es stellte sich heraus, dass „dies zu einer Wärmedämmleistung führt“.
Neuer Schalter
Nationales Institut für Fusionswissenschaft
Fusionsstromerzeugung:
Um eine Fusionsenergieerzeugung zu realisieren, ist es notwendig, ein Hochtemperaturplasma stabil mit einem Magnetfeld einzuschließen.
Plasmaturbulenz ist ein Problem:
sondern,
Aufgrund von “im Plasma erzeugter Turbulenz * 1”
Das Problem ist, dass die Temperatur des Plasmas sinkt.
„Die Aufklärung der Eigenschaften von Turbulenzen ist ein wichtiges Forschungsthema.“
Großes spiralförmiges Gerät (LHD):
Nationales Institut für Fusionswissenschaft (Stadt Toki, Präfektur Gifu)
Assistenzprofessor Naoki Kamochi,
Professor Katsumi Ida,
Außerordentlicher Professor Kihiko Tokuzawa
Universität von Wisconsin, USA
Professor Daniel J. Den HartggForschungsgruppe:
Im Large Helical Device (LHD) * 2
Wenn Wärme im Plasma entweicht
Turbulenzen, die sich schneller bewegen als Hitze,
Ich habe es zum ersten Mal auf der Welt entdeckt.
Erläuterung der Eigenschaften von Turbulenzen:Das Merkmal dieser Turbulenz ist, “das es ermöglicht, Änderungen der Plasmatemperatur vorherzusagen”.
von nun an,
Durch die Beobachtung von Turbulenzen
Wir werden ein “Verfahren zur Regelung der Plasmatemperatur in Echtzeit” entwickeln.
Forschungsunterlagen:
Es wurde am 16. Mai in der Online-Version von „Scientific Reports“ in Großbritannien veröffentlicht.
Forschungsergebnisse:
Durch Beobachtung der prädiktiven Turbulenz war es möglich, die Veränderung der Plasmatemperatur vorherzusagen.
Für die Zukunft soll ein Verfahren zur Steuerung der Plasmatemperatur in Echtzeit entwickelt werden.
Forschungsergebnisse / Neuigkeiten
Preceding propagation of turbulence pulses at avalanche events in a magnetically confined plasma
Abstract
The preceding propagation of turbulence pulses has been observed
for the first time in heat avalanche events during the collapse of the electron internal transport barrier (e-ITB) in the Large Helical Device.
The turbulence and heat pulses
are generated near the foot of the e-ITB and propagate to the peripheral region within a much shorter time than the diffusion timescale.
The propagation speed of the turbulence pulse
is approximately 10 km/s, which is faster than that of the heat pulse propagating at a speed of 1.5 km/s.
The heat pulse propagates at approximately the same speed as
that in the theoretical prediction, whereas the turbulence pulse propagates one order of magnitude faster than that in the prediction, thereby providing important insights into the physics of non-local transport.
Scientific Reports