
来自日本:食用塑料的酵素:大阪伊德氏菌
预计将应用于回收:
美国和英国的研究小组:
宣布它已经成功“创造了一种酶,可以分解塑料的速度比以前快六倍”。
京都工艺纺织大学发现:
日本研究人员,例如京都小金纺织大学,发现食用PET后几天内就会分解的细菌。
这项研究的基础是日本研究小组在2016年报告的发现。
它是在大阪府坂井市的一家宠物瓶加工厂发现的。
研究人员将这种细菌命名为“ Sakaiensis Ideonella”。
PET =聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯
PET =聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯,是一种广泛用作PET瓶材料的塑料,被认为在自然界中不会分解。
美英研究小组:
这次,美国和英国的研究小组
两步分解two酒中发现的PET的两种酶是人工结合的。
我做了一个“超级酶”。
“据此证实,PET的分解速度比以前快6倍。”
东方电视台新闻
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/articles/4d5794f45c4eb6f44da83a9f35b15a3259de8342
(PNAS) Brandon C. Knott et al.(2020)Characterization and engineering of a two-enzyme system for plastics depolymerization
Abstract
Plastics pollution
represents a global environmental crisis. In response, microbes are evolving the capacity to utilize synthetic polymers as carbon and energy sources.
Recently, Ideonella sakaiensis
was reported to secrete a two-enzyme system to deconstruct polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to its constituent monomers.
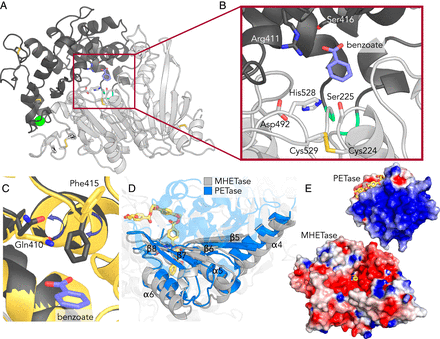
Specifically, the I. sakaiensis PETase depolymerizes PET, liberating soluble products, including mono(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (MHET), which is cleaved to terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol by MHETase.
Here, we report a 1.6 Å resolution MHETase structure, illustrating that the MHETase core domain is similar to PETase, capped by a lid domain.
Simulations of the catalytic itinerary predict that MHETase follows the canonical two-step serine hydrolase mechanism.
https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/09/23/2006753117
EurekAlert! Plastic-eating enzyme ‘cocktail’ heralds new hope for plastic waste
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2020-09/uop-pe092520.php