
东京大学:提高太阳能电池的效率:近红外光/太阳能电池
-在氧化锡中加入钨-
-红外光没有被反射而变得透明的原因的阐明-
东京大学
名古屋工业大学
筑波大学
用作透明电极的氧化锡
随着钨的加入,
它变得透明而不反射红外光。
澄清了“不反射红外光而变得透明的原因”。
通过“混合晶体中氧和钨的电子轨道”来抑制散射。
这是“利用近红外光开发太阳能电池的基础知识”。
使用近红外光的太阳能电池:
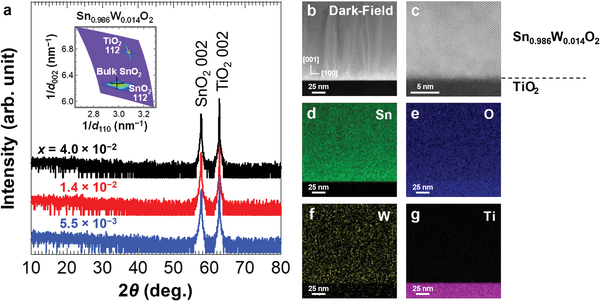
准备“在氧化锡中添加钨作为杂质的单晶薄膜”。
波长为2微米的红外线透过率约为80%,
它在传输红外光的同时起到电极的作用。
这种单晶:为什么它对红外光是透明的
调查了“这种单晶对红外光透明的原因”。
钨以“比四价锡离子多一价的五价离子”存在。
这抑制了电离杂质的散射。
用第一性原理计算考察:
“钨作为五价离子存在的原因”通过第一性原理计算进行了研究。
“周围的氧和电子形成混合轨道并且是稳定的。”
这抑制了电离杂质的散射。
红外透明电极的改进性能:
如果利用这个原理,红外透明电极的性能就会提高。
通过红外透明电极提高发电效率:
太阳能电池
通过“除了可见光之外,还使用红外线透明电极”,
可以进一步提高发电效率。
新开关
Ligand Field‐Induced Exotic Dopant for Infrared Transparent Electrode: W in Rutile SnO 2
Abstract and Figures
Transparent conductive oxides (TCOs) exhibiting high near-infrared (NIR) transmittance
are one of the key materials for highly efficient thin-film solar cells with widened spectral sensitivity.
To realize excellent NIR transparency in a TCO film,
developing a dopant providing high mobility (µ) carriers is quite important.
Herein,
it is demonstrated that
W is a high-μ dopant in rutile SnO2, which is unexpected from the conventional strategy.A combination of electrical transport property measurements and hybrid density functional theory calculations
reveals thatW behaves as a singly charged donor (W⁵⁺) showing minimized ionized impurity scattering.
This charge state is realized by the splitting of the W 5d t2g-states originating
not only from the octahedral crystal field
but also hybridization with the O 2p orbitals,
whose contribution has not been considered in transition metal-doped TCOs.
Hybridization between metal d orbital and O 2p orbitals
would provide a new guide for designing a novel dopant of NIR transparent conductors.