岛津:实现细胞三维培养:简单安全
-在公司外提供3D纳米纤维“HYDROX”-
大阪大学药学研究科
岛津
在一项联合研究中,它被用于诱导人 iPS 细胞向肝细胞的分化。
实现细胞三维培养。
我们将从 2022 年 1 月起向研究机构和公司提供 3D 纳米纤维 HYDROX(图 1)。
实现细胞三维培养:
我们公司
支持参与细胞研究的研究机构
我们在细胞培养解决方案的研发方面促进了开放式创新。
提供的细胞质量样本:
在细胞研究、药物发现、再生医学等方面。
需要在体外构建接近活体功能的细胞群。
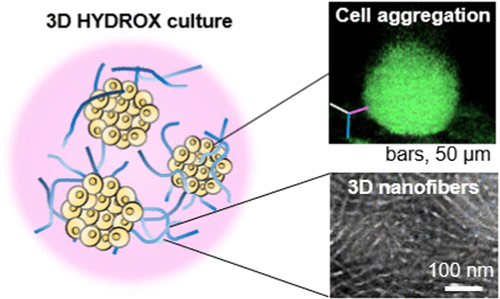
3D纳米纤维“HYDROX”:
它是我公司独创的一种辅助细胞团块形成的新材料。
大阪大学分子生物学系
水口博之教授,
鸟羽由纪子特聘助理教授
今年8月与课题组合作
我们成功地“诱导 HYDROX 从 iPS 细胞分化为肝细胞”。
阐明其高效分化为肝细胞(参考文献1)
在分子生物学学会上发表:
关于“HYDROX”
12月1日在日本分子生物学会宣布,
我们计划在 12 月 8 日举行的再生医学博览会(幕张展览馆)上展出它。
2021 | 新闻 | 岛津
https://www.shimadzu.co.jp/news/press/rwzo59_ut8znh8pf.html
Development of a 3D Cell Culture System Using Amphiphilic Polydepsipeptides and Its Application to Hepatic Differentiation
Abstract
Various three-dimensional (3D) culture systems
are available to provide more accurate in vivo mimicry than two-dimensional (2D) cultures.
Synthetic and/or xeno-free biomaterials are desired, as they would provide lower batch-to-batch variability and high repeatability.
Here,
we introduce a 3D culture system
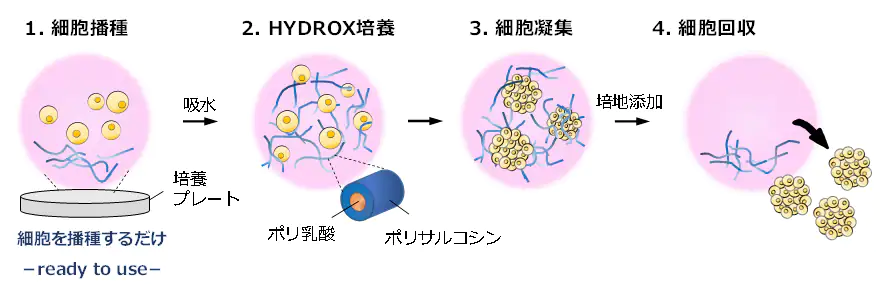
using nanofibers composed of an amphiphilic polydepsipeptide-based polymer named HYDROX, which turns into 3D nanofibers after hydration.Our system produces a large amount of cell aggregates and requires only the seeding of a cell mixture.
In addition,
cells cultured with HYDROX
can be collected with only a centrifugation procedure, and analytical assays can then be performed.Here,
we applied HYDROX to hepatic differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells.The cells cultured with HYDROX formed
aggregates and HYDROX strongly promoted hepatic differentiation and maturation in terms of functions
such as the positive ratio of
alpha-1 antitrypsin,
the production of albumin,
the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 activity, and the low-density-lipoprotein uptake ability.In addition,
primary human hepatocytes cultured with HYDROXshowed significantly improved CYP3A4 gene expression and activity.
The viscoelasticity and stiffness of HYDROX
can be modulated by varying the concentration of the synthetic polymer, thereby providing a suitable microenvironment for the differentiation of cells with various characteristics toward a target cell type.
Our findings demonstrated that
HYDROX is a promising biomaterial for 3D cultures in research fields ranging from basic cell research to drug discovery.ACS Applied Bio Materials