NICT:每秒成功傳輸 1 拍比特:
-世界上第一根4芯光纖
2022 年 5 月 19 日
NICT:
“4芯光纖每秒超過1PB的大容量傳輸實驗”取得成功。
實現了“通過擴展波段實現了總共801個波長的寬帶波長復用”。
基於現有的發送/接收技術實現了大容量。
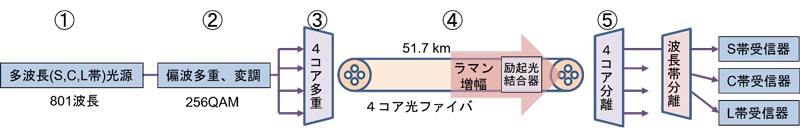
NICT傳輸系統:
採用NICT標準外徑4芯光纖,
我們充分利用波分複用技術和多種光放大方式構建了傳輸系統。
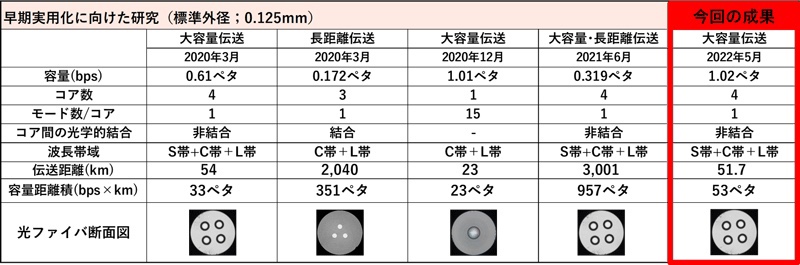
每秒 1.02 拍比特:
成功傳輸實驗,每秒 1.02 拍比特,51.7 公里。
本實驗:
通過加寬 S 波段的拉曼放大,
20 tera Hz 頻段可用,
共復用了801個波長。
而且,
在所有頻段
採用信息密度高的256QAM調製方式,
實現了每秒 1.02 petabit 的傳輸。
2022 | NICT-國家信息與通信技術研究所
https://www.nict.go.jp/press/2022/05/19-1.html
NTIC : Transmission réussie de 1 pétabit par seconde :
-La première fibre optique à 4 cœurs au monde
19 mai 2022
NTIC :
Réussite dans “Expérience de transmission à grande capacité dépassant 1 pétabit par seconde avec fibre optique à 4 cœurs”.
Réalise un “multiplexage de longueur d’onde à large bande avec un total de 801 longueurs d’onde en élargissant la bande de longueur d’onde”.
Atteint une grande capacité basée sur la technologie de transmission / réception existante.
Système de transmission NTIC :
Utilisant une fibre optique 4 cœurs de diamètre extérieur standard NICT,
Nous avons construit un système de transmission en utilisant pleinement la technologie de multiplexage par répartition en longueur d’onde et de multiples méthodes d’amplification optique.
1,02 pétabits par seconde :
Expérience de transmission réussie à 1,02 pétabits par seconde, 51,7 km.
Cette expérience :
En élargissant l’amplification Raman pour la bande S,
une bande de fréquence de 20 tera Hz est disponible,
Au total, 801 longueurs d’onde ont été multiplexées.
en outre,
Dans toutes les bandes de fréquences
En utilisant la méthode de modulation 256QAM avec une densité d’informations élevée,
Atteint 1,02 pétabit de transmission par seconde.
2022 | NTIC-Institut National des Technologies de l’Information et de la Communication
NICT: Erfolgreiche Übertragung von 1 Petabit pro Sekunde:
-Die weltweit erste 4-adrige Glasfaser
19. Mai 2022
NICT:
Erfolgreiches „Übertragungsexperiment mit hoher Kapazität von mehr als 1 Petabit pro Sekunde mit 4-Kern-Glasfaser“.
Erreicht „Breitband-Wellenlängen-Multiplexing mit insgesamt 801 Wellenlängen durch Erweiterung des Wellenlängenbands“.
Erreicht eine große Kapazität basierend auf der bestehenden Sende-/Empfangstechnik.
NICT-Übertragungssystem:
Unter Verwendung einer 4-adrigen optischen Faser mit NICT-Standardaußendurchmesser,
Wir haben ein Übertragungssystem aufgebaut, indem wir die Technologie des Wellenlängenmultiplexings und mehrere optische Verstärkungsmethoden voll ausgenutzt haben.
1,02 Petabit pro Sekunde:
Erfolgreiches Übertragungsexperiment bei 1,02 Petabit pro Sekunde, 51,7 km.
Dieses Experiment:
Durch Verbreitern der Raman-Verstärkung für das S-Band,
20-Tera-Hz-Frequenzband ist verfügbar,
Insgesamt wurden 801 Wellenlängen gemultiplext.
Außerdem,
In allen Frequenzbändern
Unter Verwendung des 256QAM-Modulationsverfahrens mit hoher Informationsdichte,
1,02 Petabit Übertragung pro Sekunde erreicht.
2022 | NICT-Nationales Institut für Informations- und Kommunikationstechnologie
0.61 Pb/s S, C, and L-Band Transmission in a 125μm Diameter 4-Core Fiber Using a Single Wideband Comb Source
IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore
Abstract:
We investigate
high-throughput,
multi-band transmission in a 4-core multi-core fiber (MCF) with the same 125 μm cladding diameter of standard single-mode fiber (SMF).
A single wideband comb source
is used to transmit up to 561 wavelength channels with 25 GHz spacing over a 120 nm bandwidth in S, C, and L bands.
We demonstrate
a maximum decoded throughput of 610 Tb/s in PDM-256QAM and PDM-64QAM signals over a 54 km fiber,
transmitting more than 155 Tb/s in a single core and measuring a per-core average throughput exceeding record transmission demonstrations in SMF.
In addition,
we use noise loading measurements
to characterize the achievable signal quality across the wideband transmitter.
These results show that
a single comb source can enable high-spectral efficiency modulation over wide bandwidths
and further that low-core count homogeneous MCF technology can
offer the same transmission performance as single-mode fibers without sacrificing mechanical reliability,
and still offering the benefits of shared resources and greater efficiency that drives SDM technologies.
IEEE Xplore