:quality(50)/cloudfront-ap-northeast-1.images.arcpublishing.com/sankei/5BOMXMOPUNKDZP26BZ2ARFMZKA.jpg)
滑翔階段攔截彈:日美聯合開始開發GPI飛彈
・日本負責GPI的火箭和彈頭推進系統
・宙斯盾艦Mk41VLS將配備GPI飛彈
我們將為您提供日經新聞發表的文章摘要。

Japan and the US jointly develop new interceptor missile:
Japan and the US will jointly develop a new type of GPI missile.
On May 15th, the Japanese and U.S. governments signed an agreement on a new anti-missile missile development project.
Responsible for developing new interceptor missiles:
This is equipment for intercepting hypersonic missiles.
1. Japan is responsible for the rocket part of the missile and the propulsion system for the warhead.
2. The United States is responsible for the interceptor warhead’s infrared sensor and guidance system.
Aiming for completion in the 2030s.

Companies in charge of development in Japan and the US:
On the US side, two companies are candidates.
They are Northrop Grumman and RTX (formerly Raytheon Technologies).
The Japanese side will make the selection through a public call for candidates in 2024.

Agreed at Japan-U.S. summit meeting:
In August 2023, an agreement was reached on joint development at the Japan-U.S. summit meeting.
The Japanese government has included 75.7 billion yen in development costs in its fiscal year 2024 budget.
US Department of Defense estimates:
The total cost for developing the new GPI missile will reach more than $3 billion (460 billion yen) in Japan and the United States.
Japan will contribute $1 billion (150 billion yen) of this amount.
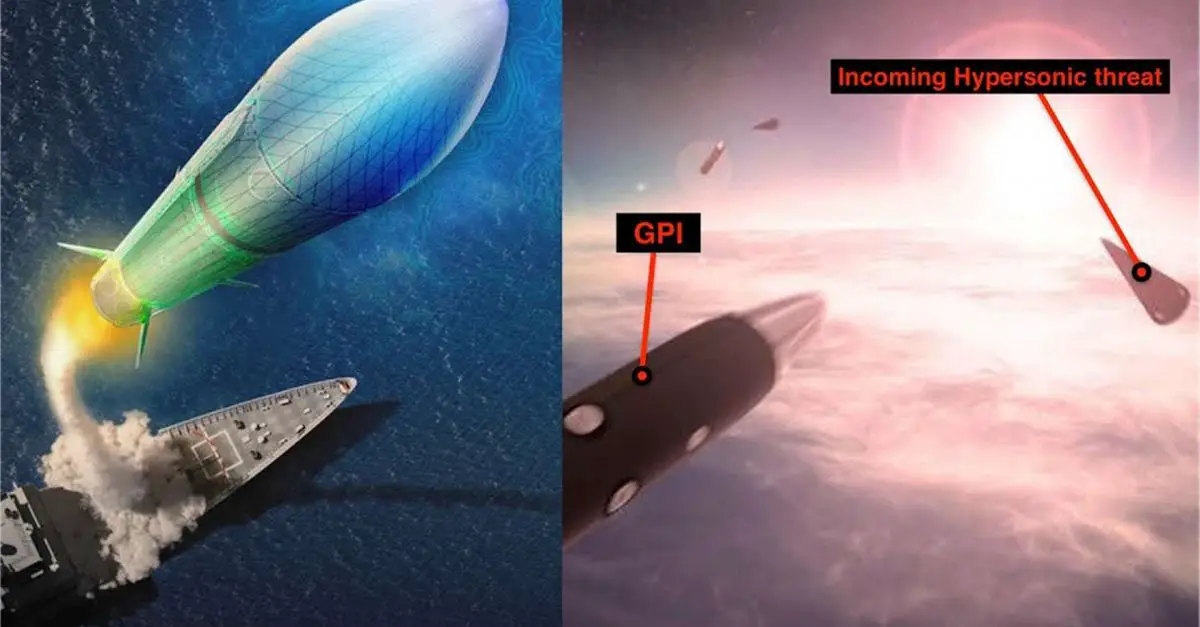

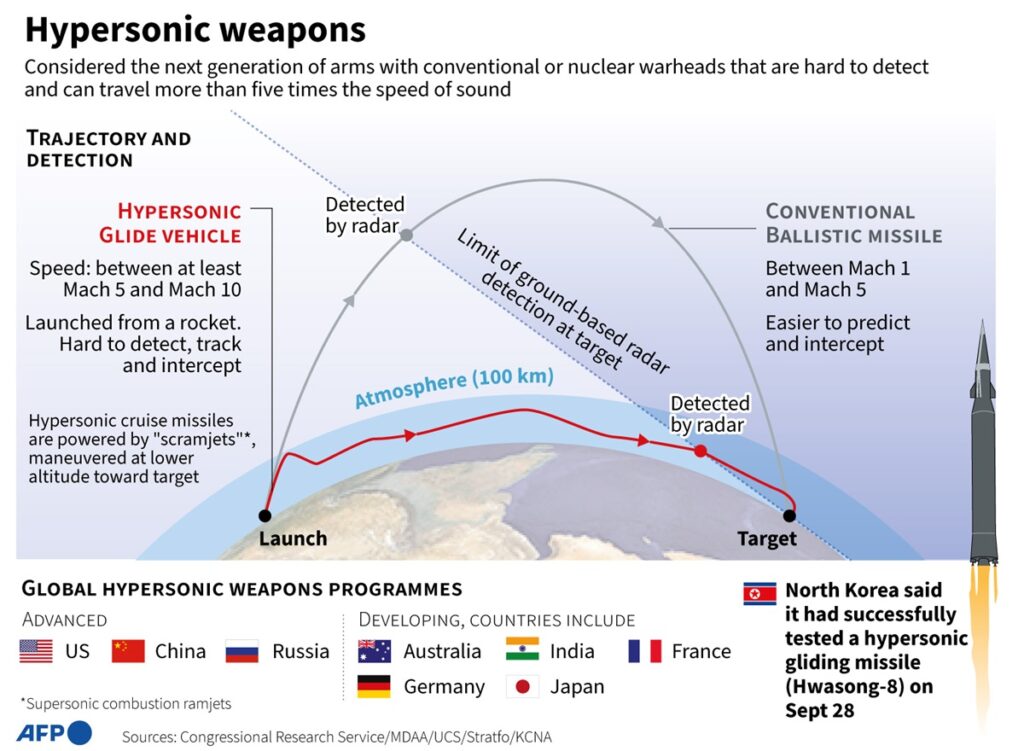
What is a hypersonic missile?
Currently, China, Russia, and North Korea are deploying hypersonic missiles.
It flies at more than five times the speed of sound and takes an irregular trajectory, making it difficult to intercept.
1. GPI missiles intercept enemy missiles while gliding.
2. Combined with conventional interception systems to increase response capabilities.
Traditional interceptor systems shoot down enemy missiles just before they hit the ground.
https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXZQOUA15AHG0V10C24A5000000/
GPI missile: Japan is responsible for rocket motor and propulsion system
We will provide you with a summary of articles published in JSF.
GPI missile jointly developed by Japan and the US:
On May 15th, regarding the interceptor missile GPI (guided missile for glide phase interception),
The areas of development responsibility for Japan and the US were announced.
U.S. Department of Defense:
Statement on the Signing of the Glide Phase Interceptor Cooperative Development
Japan will lead development of rocket motors and propulsion components of GPI.

Fields of development in Japan:
Japan will lead the development of GPI’s rocket motor and GPI’s propulsion system.

Areas of development responsibility in the United States:
The United States will lead the infrared sensor and guidance system for the interceptor warhead.

To be installed on Mk41VLS for Aegis ships:
1. The Aegis ship’s Mk41VLS (vertical missile launcher) is equipped with a GPI missile.
2. GPI missiles are scheduled to be launched from Aegis ships.
There is a possibility that the existing Mk72 booster will be used for the first stage rocket.
Expected components of GPI:
The detailed components of GPI have not yet been announced.
It will probably have two main propulsion rocket stages plus an interceptor warhead, making it three stages in total.
1. First stage rocket: Existing US-made Mk72 booster or a new model developed in Japan?
2. 2nd stage rocket: In charge of Japanese development
3. Interceptor warheads: US (sensors and guidance equipment) and Japan (propulsion equipment)?
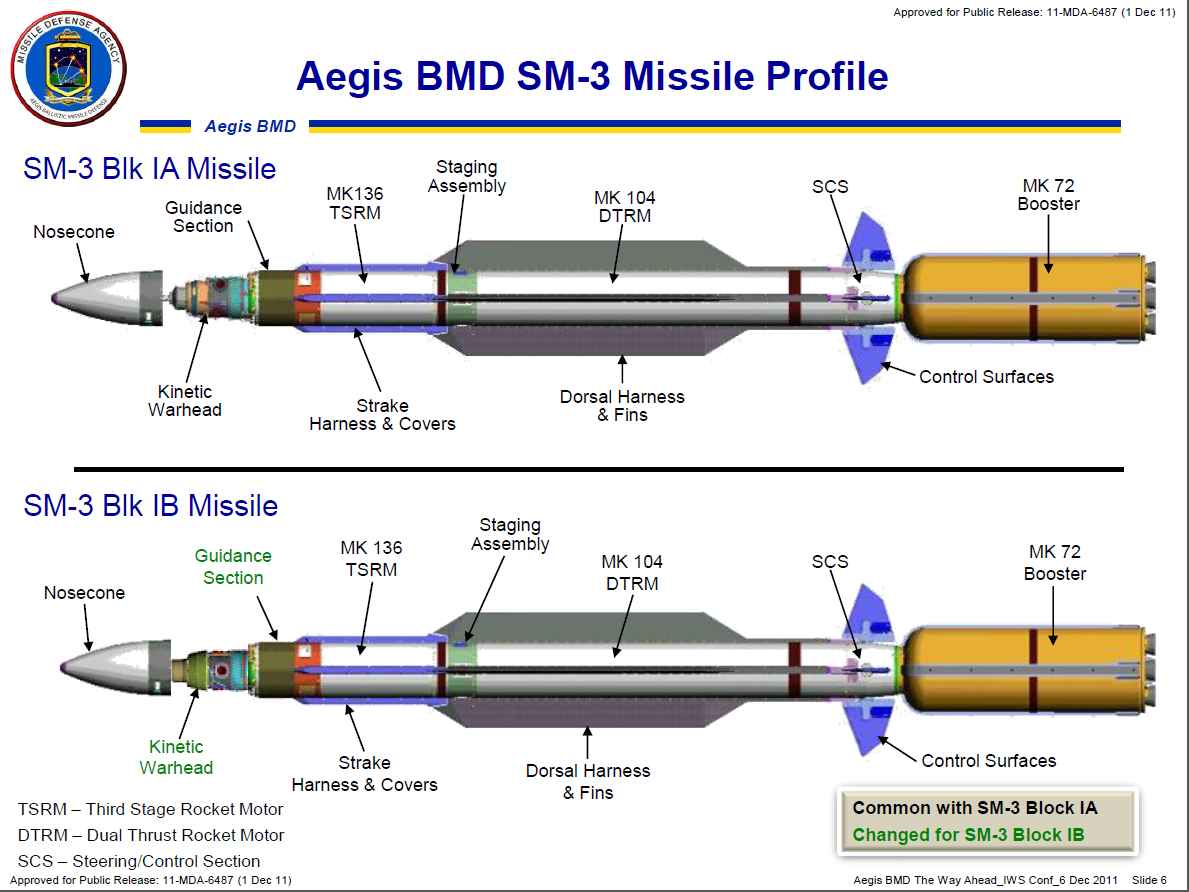
For the extraatmospheric interceptor missile SM-3:
The SM-3 is an extraatmospheric interceptor missile of the same size as the GPI.
It has a total of four stages, including three main propulsion rocket stages and an interceptor warhead.
Maneuverability required for GPI missiles:
GPI missile warheads require high maneuverability even with low air resistance.
Equipped with propulsion system on GPI missile warhead:
There is also the possibility that the interceptor warhead will be equipped with a propulsion system.
Case of Israeli missile “Arrow”:
The interceptor warhead of the Israeli ballistic missile “Arrow” has a propulsion system installed.
TVC (thrust vector control) ensures maneuverability without relying on aerodynamic steering.

Hypersonic weapon interceptor missiles of each country:
1. There are currently more than 10 types of hypersonic weapon interceptor missile programs in various countries.
2. However, the following five types of interceptor warhead components are known:
Components of the interceptor warhead:
1. Japan, Defense Equipment Agency: Guided missiles for dealing with HGV
Side thruster + aerodynamic steering system
There is a possibility that Japan’s plan will end with elemental research (and actual deployment if budget is available).
2. Germany, Diehl: IRIS-T HYDEF
Side thruster + TVC method
European plans are scheduled to be consolidated (unconfirmed)
3. France, MBDA: Aquila
Side thruster + TVC method
European plans are scheduled to be consolidated (unconfirmed)
4. Israel, IAI: Arrow 4
Aerodynamic steering + TVC method
Practical use of Arrow 4 is almost certain (as an improved version of Arrow 2, the risk of development failure is low)
5. Rafael, Israel: Skysonic
Aerodynamic steering + TVC method
It looks like Sky Sonic will end up with just a proposal.
https://news.yahoo.co.jp/expert/articles/9e1df2ef6373738ed7b1bf4b89e6641455d86f2a
