COVID-19:京都大学发现新的电晕候选药物:雷洛昔芬和吡格列酮
-通过iPS细胞研究发现新的电晕候选药物-
京都大学和长崎大学:
研究小组宣布,他们已经“开发了一种使用iPS细胞为新的冠状病毒感染寻找治疗候选者的方法”。
我们从“用于其他疾病的现有药物”缩小了范围。
骨质疏松药和
降低血糖的药物等
据说它可能会起作用。
新型电晕感染的治疗剂:
在每个国家中寻找有效的药物。
在日本:
Becklely(通用名称Remdesivir)和
地塞米松已被批准。
在世卫组织:
同时,世界卫生组织表示了“对伯克利的影响的负面看法”。
在世界范围内仍在寻找有效的药物。
利用人类iPS细胞:
该研究小组对人类iPS细胞进行了药物处理和研究。
我们着重研究了“具有相同基因类型的新型冠状病毒和仙台病毒”。
这次,我们调查了是否可以预防这种仙台病毒的入侵。
结果,阐明了确定药物作用的方法。
雷洛昔芬和吡格列酮:
我们调查了500种现有药物。
骨质疏松症药物Evista(通用名称雷洛昔芬)和
已经发现降血糖药物Actos(通用名称吡格列酮)是高度有效的。
确认的预防感染效果:
实际上,我们进行了一项实验,用新的冠状病毒感染细胞。
对于这些药物。证实具有预防感染的作用。
朝日新闻数码
https://www.asahi.com/articles/ASP464HD7P42PLBJ008.html
鉴定抑制RNA病毒感染的现有药物
-一种通过使宿主细胞对多种不同的RNA病毒脱敏来抑制感染的药物-
CiRA |京都大学iPS细胞研究与应用中心
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/j/pressrelease/news/210407-000000.html
CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/index.html
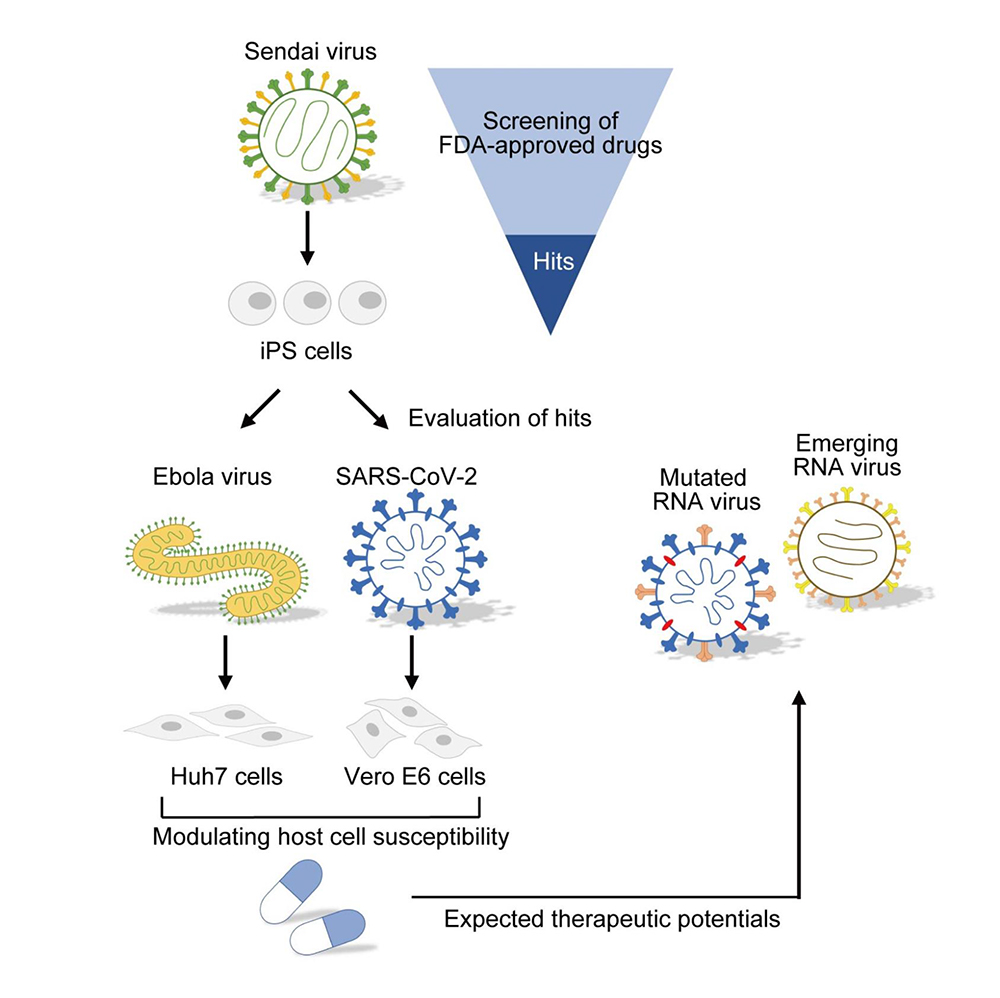
iPSC screening for drug repurposing identifies anti‐RNA virus agents modulating host cell susceptibility
iPSC screening for drug repurposing identifies anti‐RNA virus agents modulating host cell susceptibility
Keiko Imamura Yasuteru Sakurai Takako Enami Ran Shibukawa Yohei Nishi … See all authors First published: 06 April 2021
– FEBS Open Bio – Wiley Online Library
Abstract
Human pathogenic RNA viruses are threats to public health
because they are prone to escaping the human immune system through mutations of genomic RNA, thereby causing local outbreaks and global pandemics of emerging or re‐emerging viral diseases.
While specific therapeutics and vaccines
are being developed, a broad‐spectrum therapeutic agent for RNA viruseswould be beneficial for targeting newly emerging and mutated RNA viruses.
In this study,
we conducted a screen of repurposed drugs using Sendai virus (an RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae),with human‐induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to explore existing drugs that may present anti‐RNA viral activity.
Selected hit compounds
were evaluated for their efficacy against two important human pathogens:
Ebola virus (EBOV) using Huh7 cells
and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) using Vero E6 cells.
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), including raloxifene,
exhibited antiviral activities against EBOV and SARS‐CoV‐2.
Pioglitazone, a PPARγ agonist, also exhibited antiviral activities against SARS‐CoV‐2,
and both raloxifene and pioglitazone presented a synergistic antiviral effect.
Finally,
we demonstrated that SERMs blocked entry steps of SARS‐CoV‐2 into host cells.These findings suggest that
the identified FDA‐approved drugs can modulate host cell susceptibility against RNA viruses.
Abbreviations
DAPI 4’6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole
EBOV Ebola virus
EGFP enhanced green fluorescent protein iPSCs induced pluripotent stem cells
MOI multiplicity of infection
SARS‐CoV‐2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
SERMs selective estrogen receptor modulators
VSV vesicular stomatitis virus
ZIP zero interaction potency
https://febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2211-5463.13153