
名古屋大学:开发超小型天线:兼容Wi-Fi
-由一根 1nm 碳纳米管制成-
名古屋大学:
11 月 17 日,
用一根碳纳米管,
可接收大规模数字数据,
我们开发了一种非常小的天线。
虽然是纳米级,但可以实现稳定、高精度的数据传输。
什么是碳纳米管?
六边形碳网络,是一个直径约为 1 纳米(十亿分之一米)的圆柱体。
名古屋大学未来材料研究所
丰田中央研发实验室
研究人员的联合研究。
由于物联网使用的扩大
多种信息同时高精度
需要检测。
在一个系统中安装大量传感器已成为必要。
因此,需要传感器的小型化。
这就是这项研究的背景。
超小型天线特点:
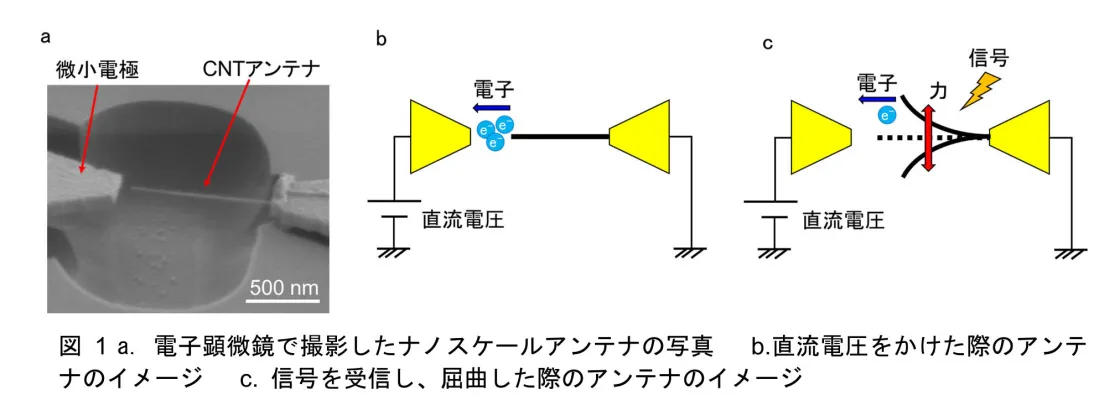
它将电磁波转换为机械振动,并将其转换为电信号。
使用机械强度高、电性能优良的碳纳米管。
将尺寸减小到纳米级已经成为可能。
通讯速度为70Mbps:
还可以支持当前主流的Wi-Fi环境(80MHz带宽)。
通信速度为70Mbps,性能足够。
超小型天线的应用:
可应用于图像数据、视频通话等大容量数据通信。
此外,可以直接检测生物体和大气中的信息。
TechCrunch 日本
https://jp.techcrunch.com/2021/11/18/nagoya-univ-cnt-antenna/
Carbon Nanotube-Based Nanomechanical Receiver for Digital Data Transfer
ACS Applied Nano Materials
Abstract
The evolution of carbon nanomaterials can provide tremendous advantages in sensing, computation, and functional materials.
A carbon nanotube (CNT)
has outstanding thermal and electrical conductivity features and is one of the most promising nanoscale carbon materials.It has a hardness of up to 1 TPa.
Exploiting these features, nanomechanical systems with CNTs
have been reported to achieve ultrasensitive sensors for mass, force, and electromagnetic waves owing to their outstanding elastic and electric properties.
Some research groups
have attempted to achieve digital data transfer in potential nanoscale wireless terminals with carbon nanomaterials.Although conceptual demonstrations have been reported,
the fundamental capability of the transfer, particularly in the presence of noise, is yet to be explained.
Here,
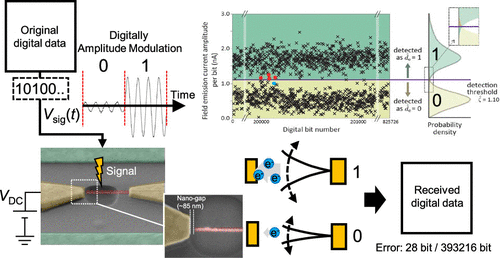
we experimentally demonstrate for the first time thatan ultrasmall digital receiver with a nanomechanical nanoantenna can transfer a vast amount of digital data, up to 1 Mbit, even in the presence of noise.
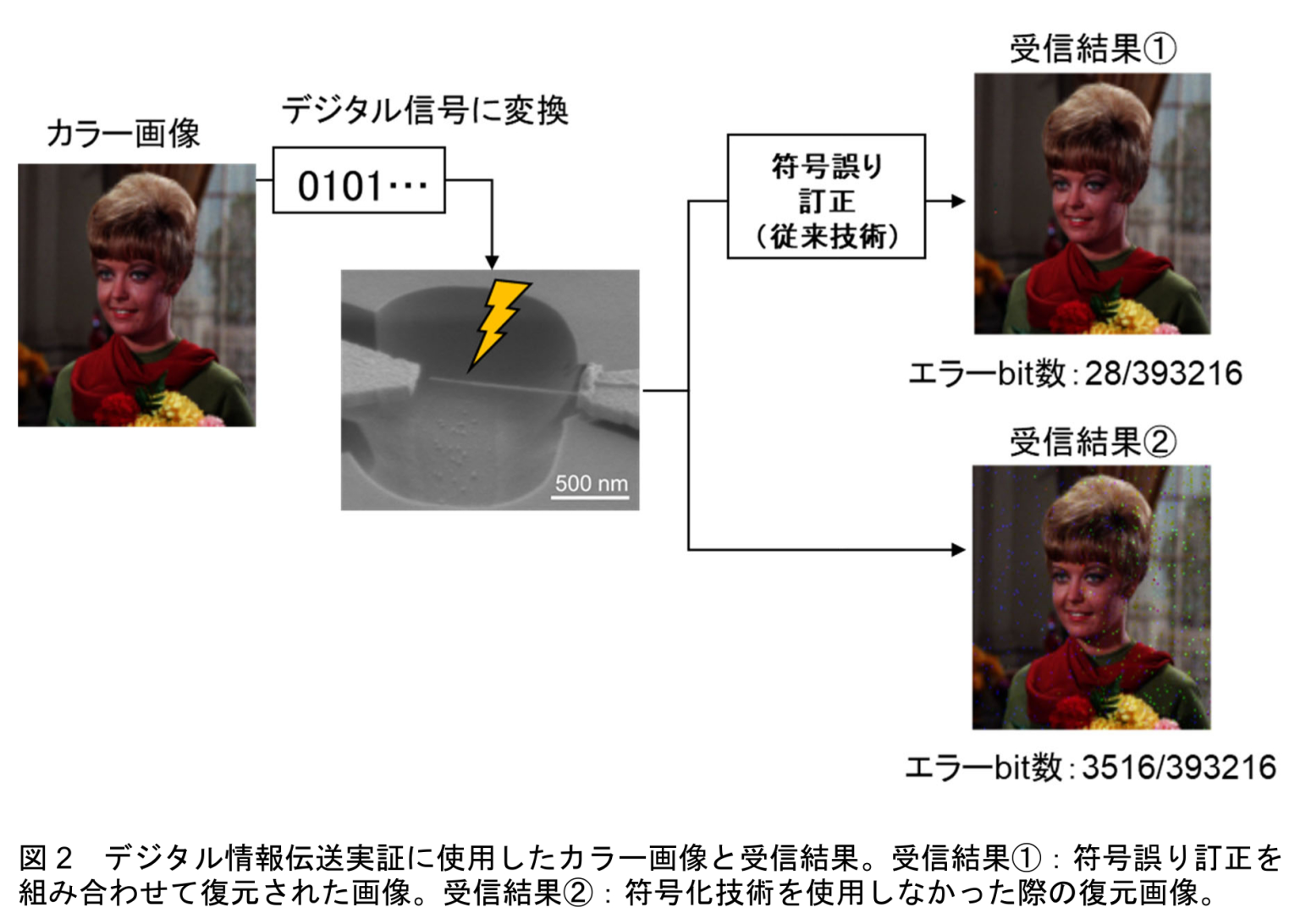
We successfully transfer a digital image data with 393 216 bits.
This demonstration proves that
the data-transfer capability is close to the theoretical limit established in information theory and channel capacity.This small but robust nanomechanical receiver
will contribute to the forthcoming data-oriented age of Internet of things (IoT)- and artificial intelligence (AI)-based systems.