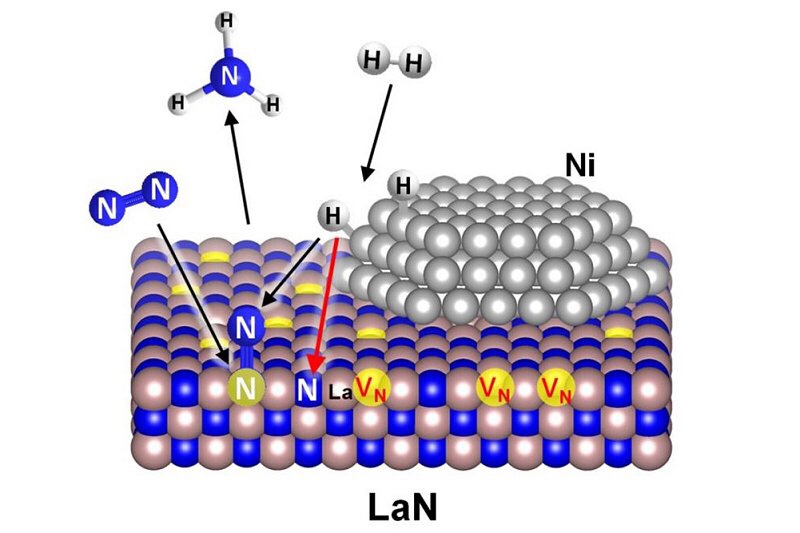
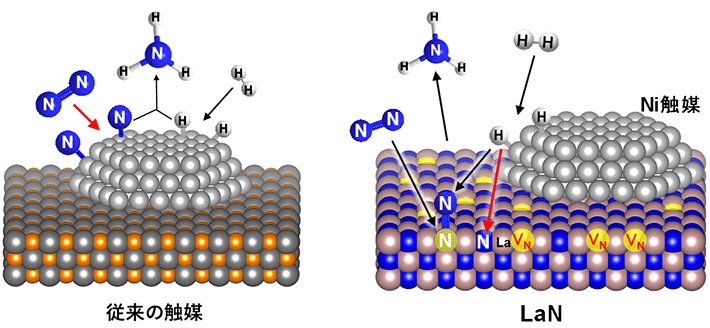
在常规催化剂(左)和已开发的催化剂Ni / LaN(右)上合成氨的反应机理。 VN是在LaN上形成的氮空位,红色箭头是速率确定的反应过程。 N 2的解离不发生在金属表面,而是发生在LaN表面的氮空位上。
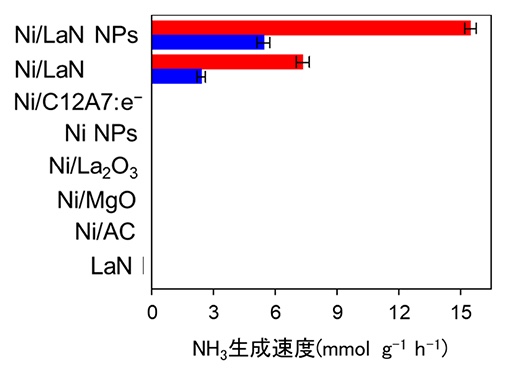
固定化镍和其他催化剂对LaN氨合成活性的比较(反应温度:400℃,压力:1 atm(蓝色),9 atm(红色))
东京工业大学:成功的高效氨合成:使用Ni / LaN催化剂
发行日期:2020年7月20日
要点:
成功地实现了仅使用镍(Ni)和氮化镧(LaN)而不单独显示活性的氨合成方法。
无需使用钌等贵金属即可实现高氨合成活性
演示使用LaN表面的氮空位作为反应场的新概念
概述:
东京工业大学基础策略研究中心
细野荣教授
叶天南助理教授
北野副教授
这次氨合成催化剂:
通过结合自身不显示活性的镍(Ni)和氮化镧(LaN),我们已经实现了与贵金属催化剂(如钌)相当的出色的氨合成催化剂。
常规氨合成催化剂:
常规的氨合成催化剂是
铁在高温高压下用于合成。
在温和的条件下使用钌。
由于两种金属都牢固地与氮结合,因此反应在金属上进行。
另一方面,与氮的键非常弱的镍至今尚未使用,因为它不能活化氮分子。
在这个研究中:
镍上氢分子的活化,
氮分子的激活是通过LaN上的氮空位进行的,
通过这样做,实现了非常高的氨合成活性。
反应场的使用称为氮空位:
结果表明,通过使用单独不显示活性的金属可以实现优异的氨合成。
这是一个推翻传统观点的研究结果。
研究结果:
近年来开发的且在温和条件下具有高合成氨活性的催化剂要求负载作为贵金属的钌。
在这项研究中,重要的是作为一种不使用稀有和昂贵的钌的新型催化剂技术。
这在氨合成过程中带来了新的可能性。
研究结果于7月16日(日本时间)在线发表在英国科学杂志“自然”上。
东京科技新闻|东京工业大学
https://www.titech.ac.jp/news/2020/047268.html
Vacancy-enabled N 2 activation for ammonia synthesis on an Ni-loaded catalyst
Article
Published: 15 July 2020
Vacancy-enabled N2 activation for ammonia synthesis on an Ni-loaded catalyst
Tian-Nan Ye, Sang-Won Park, […]Hideo Hosono
Nature volume 583, pages391–395(2020)Cite this article
Abstract
Ammonia (NH3) is pivotal to the fertilizer industry and one of the most commonly produced chemicals1.
The direct use of atmospheric nitrogen (N2)
had been challenging, owing to its large bond energy (945 kilojoules per mole)2,3, until the development of the Haber–Bosch process.
Subsequently, many strategies
have been explored to reduce the activation barrier of the N≡N bond and make the process more efficient.
These include using alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides as promoters to boost the performance of traditional iron- and ruthenium-based catalysts4,5,6 via electron transfer from the promoters to the antibonding bonds of N2 through transition metals7,8.
An electride support further lowers the activation barrier because its low work function and high electron density enhance electron transfer to transition metals9,10.