韩国:中美产大米致癌物:高毒DMMTA
-去年进口49万吨=韩国-
韩国进口大米:
中国和美国生产的大米每年有50万吨进口到韩国。
有人提出,从韩国进口的大米可能含有As成分。
包含 As 组件的可能性:
急需做好有害物质检查、标准值设定等对策的准备工作。
中国南京农业大学,
德国拜罗伊特大学,
澳大利亚昆士兰大学
国际研究团队通过环境科学技术做了报告。
演讲稿:
中国及全球水稻中DMMTA剧毒成分分析结果已出炉。
产于中国和美国和欧洲:
大米产于中国部分地区和美国、欧洲等地。
据说二甲基化单硫代砷酸盐 (DMMTA) 的测量值很高。
DMMTA 污染:
这是对 DMMTA 污染的首次广泛调查。
DMMTA 是一种有机砷。
有机砷的 DMMTA:
与有机砷 DMA(二甲基化砷酸盐)不同,它具有剧毒。
它的毒性是无机砷的3-10倍。
美国最高:
美国制造,DMMTA浓度最高
研究团队分析:
酶提取法在中国采集的103份大米样品,
从全球6大洲16个国家的市场征集而来,
分析了 130 个大米样品。
中国分析:
在中国的 103 个样品中,有 14 个样品(13%)超过了无机砷 200 ppb 的标准值。
北美分析:
美国的 DMMTA 平均浓度为 29.3 ppb,中国的平均浓度为 12.1 ppb。
DMMTA 最大值在中国产品中超过 20 ppb 的情况并不少见。
DMMTA浓度排名:
北美生产的稻米的平均 DMMTA 浓度最高,平均为 25.7 ppb。
欧洲平均为 18.9ppb,
亚洲平均为 5.01 ppb,
据解释,非洲平均为 3.11 ppb。
中央日报
https://s.japanese.joins.com/JArticle/288047?sectcode=400&servcode=400
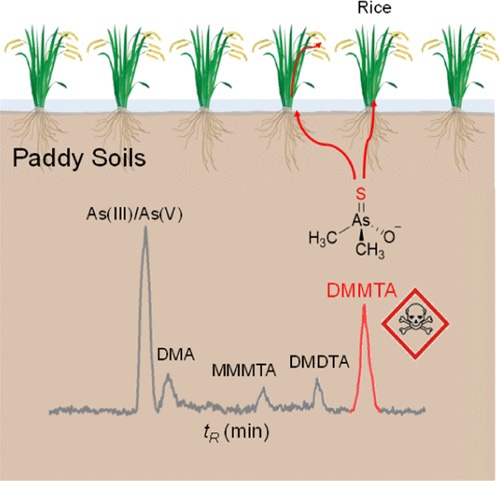
Dynamics of Dimethylated Monothioarsenate (DMMTA) in Paddy Soils and Its Accumulation in Rice Grains
Environmental Science & Technology
Abstract
Arsenic species transformation in paddy soils has important implications for arsenic accumulation in rice grains and its safety to the consumers.
Methylated thioarsenates including highly toxic dimethylated monothioarsenate (DMMTA)
have been detected in paddy soils, but their production and dynamics remain poorly understood.
In the present study,
we first optimized a HPLC-ICP-MS method to quantify methylated thioarsenate species.Using this method together with 10 mM diethylenetriamine pentaacetate (DTPA) to preserve As speciation,
we investigated methylated thioarsenate species in porewaters of seven As-contaminated soils incubated under flooded conditions and of two paddy fields.
DMMTA was the main methylated thioarsenate species in the porewaters in both incubated soils and paddy fields,
with concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 36.2 μg/L and representing ca.
58% of its precursor dimethylarsenate (DMA).
The temporal production and dynamics of DMMTA were linked with the DMA concentrations.
When soils were drained, DMMTA was converted to DMA.
In the two paddy fields,
DMMTA concentrations in rice grains were 0.4–10.1 μg/kg.Addition of sulfur fertilizer and rice straw incorporation increased grain DMMTA by 9–28%.
These results suggest that DMMTA is an important As species in paddy soils and can accumulate in rice grains,
presenting a risk to food safety and human health.