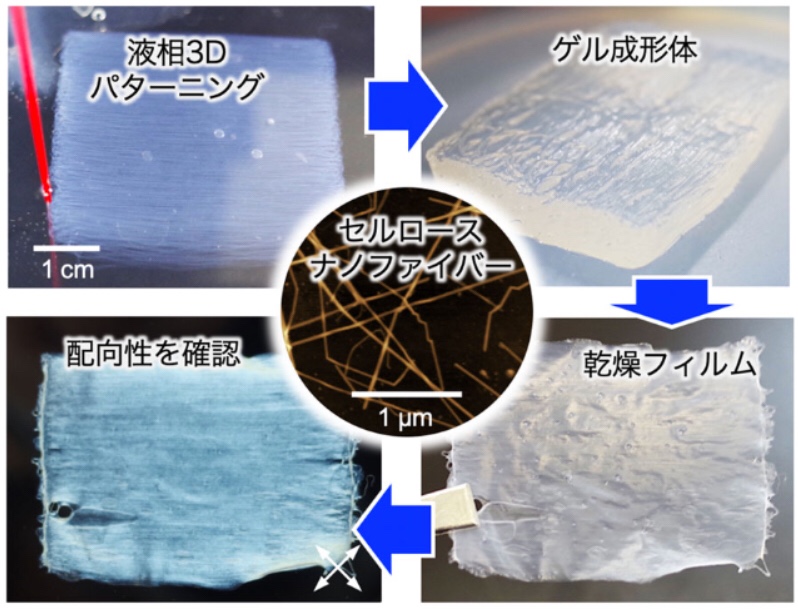
图1液相3D构图技术对纳米纤维素取向膜的开发概念
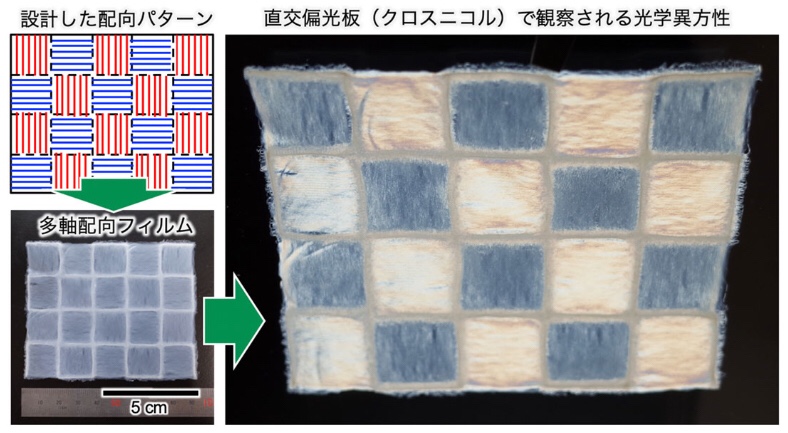
图2开发的纳米纤维素多轴取向薄膜
大阪大学:纳米纤维素的自由布置/组装:液相3D图案开发
大阪大学
宣布“液相纳米3D图案化技术,可将纳米纤维素整合到柔性结构中,同时进行排列”。
开发了纳米纤维素在多个方向排列的多轴取向薄膜。
我们能够确定光学相差,慢轴和传热的可控性。
应用领域:
将使用下一代/光学功能材料和造纸电子/更高性能。
热控制节能
可以进行灯光管理的电影
可以用光管理的纸质材料
RESOU
https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/research/2020/20200520_2
Checkered Films of Multiaxis Oriented Nanocelluloses by Liquid-Phase Three-Dimensional Patterning
May 2020Nanomaterials 10(5):958
DOI: 10.3390/nano10050958
Authors:
Kojiro Uetani
Hirotaka Koga at Osaka University
Masaya Nogi
Abstract and Figures
It is essential to build multiaxis oriented nanocellulose films in the plane for developing thermal or optical management films.
However,using conventional orientation techniques,
it is difficult to align nanocelluloses in multiple directions within the plane of single films rather than in the thickness direction like the chiral nematic structure.
In this study,
we developed the liquid-phase three-dimensional (3D) patterning technique by combining wet spinning and 3D printing.
Using this technique,
we produced a checkered film with multiaxis oriented nanocelluloses.
This film
showed similar retardation levels, but with orthogonal molecular axis orientations in each checkered domain as programmed.
The thermal transport
was enhanced in the domain with the oriented pattern parallel to the heat flow.
This liquid-phase 3D patterning technique
could pave the way for bottom-up design of differently aligned nanocellulose films to develop sophisticated optical and thermal materials.