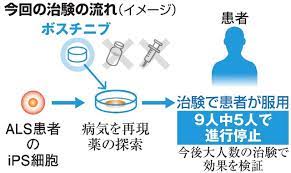
京都大:iPS細胞で難病ALSを再現:治療薬「ボスチニブ」(動画):
Kyoto Univ:Reproduce intractable disease ALS with iPS cells: “Bosutinib”:
京都大学:用 iPS 细胞重现顽固性 ALS:治疗药物“博舒替尼”
ー治療薬に光、京大が治験へー
京都大のチーム:
iPS細胞を使って、難病「筋萎縮性側索硬化症(ALS)」の状態を再現した。
白血病に有効な治療薬発見:
ALS治療薬の候補を探す研究の結果、白血病に有効な治療薬を見つけた。
京大が9月26日、発表した。
京都大のチームが、ALSの治験を始める。
ALSの治験開始:
治験は、公的医療保険適用を受けるために必要な手続きだ。
ALSの治療薬の実用化をめざして、動き出した。
治療薬「ボスチニブ」:
薬は、慢性骨髄性白血病の治療薬「ボスチニブ」
1日1回、12週間にわたって口から飲む。
京大病院など4カ所の医療機関で24人に実施する。
24人のALS患者に投与:
発症後2年以内の20~79歳の患者を対象とする。
- ALS症状は進行しているが、
- 一方、まだ働けたり、
- 家事などができたりする人が対象になる。
日本のALS患者:
ALSの患者は国内に約9千人。
筋力が低下し、体を動かすことが徐々に難しくなっていく。
進行を遅らせる薬はあるが、確立した治療法はない。
朝日新聞デジタル
https://www.asahi.com/articles/ASM3V3S6PM3VPLBJ001.html
Announcement of a clinical trial for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University,
has announced a new Phase 1*1) clinical trial for the drug bosutinib to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the Kyoto University Hospital (KUH).
Leading the project from CiRA is Professor Haruhisa Inoueand from KUH is Professor Ryosuke Takahashi.
This trial has received approval from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA).
News and Events | CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/pressrelease/news/190403-110000.html
Deep learning amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by taking pictures
A team of scientists led by CiRA Professor Haruhisa Inoue
reports the combination of deep learning and iPS cell technology for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Recently, researchers have reported that
deep learning could potentially identify individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease (https://www.nytimes.com/2021/02/01/health/alzheimers-prediction-speech.html).
In the new study on ALS seen in Annals of Neurology,
Inoue and colleagues show how deep learning can be used to identify indications of ALS,
a relentless motor neuron disease, by using iPS cell technology to reprogram patient blood cells into motor neurons, the cells most afflicted by the disease.
Convolutional neural networks
were trained using images of motor neurons prepared from the iPS cells of 15 healthy donors and 15 ALS patients.
Based on just images of motor neurons,
the network could predict with over 0.97 of area under curve (AUC) whether other donors were healthy or ALS patients.
On the other hand,
conventional machine learning with the same images,focusing on soma size, neurite length, and cell number, presented approximately 0.97 of AUC (see figure).
News and Events | CiRA | Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/e/pressrelease/news/210224-100000.html