
COVID-19:NEC的人造DNA适体:与新的电晕结合
-成功开发空间监控-
NEC:
NEC解决方案创新者:
5月6日,它宣布已成功开发出与SARS-CoV-2结合的人工DNA适体。
开发人造DNA适体,促进空间监测业务。
什么是适体:
病毒,蛋白质等
识别特定目标分子的三维结构,
特异性结合的核酸(DNA或RNA)。
Aptamer这次开发了:
新开发的适体通过结合RBD作为靶标来识别和捕获病毒。
SELEX的人工DNA生产:
查找仅与待检查对象牢固结合的序列的技术(SELEX)
使用SELEX,可以人工生产DNA。
在新电晕的情况下
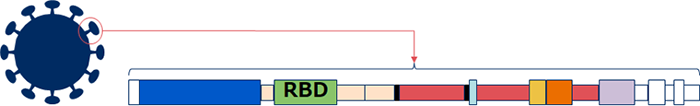
病毒表面:
刺突蛋白“ RBD(受体结合结构域)”侵入人细胞的表面。
人体细胞表面:
该病毒可通过与病毒表面上人类细胞的“ ACE2受体”结合而侵入人类细胞。
与适体结合测试的结果:
NEC集团:
联合研究的学术研究机构:
它具有以下新的冠状病毒。
原始菌株(WK521武汉菌株),
突变株(TY7-501巴西株),
突变株(QK002 UK株),
使用所有三种病毒株进行了与适体的结合评价测试。
在所有三个菌株中均观察到适体和新的冠状病毒之间的强结合。
MSS薄膜型表面应力传感器:
NEC解决方案创新者
MSS(膜表面应力传感器)和
与适体结合
目前,我们正在开发一种可以在空间上监测新冠状病毒的测量设备。
空间监视设备原型:
2021年:
开发固定式空间监视设备的原型。
开始为病毒测量公司和大学研究机构提供监视设备。
2022年:
该产品将作为嵌入式设备出售并作为空调设备提供。
我们提供了可以监测空间的生物传感系统。
科技+
https://news.mynavi.jp/article/20210506-1884404/
NEC contributes to development of artificial DNA aptamer that binds to coronavirus
Tokyo, May 6, 2021
NEC Corporation (NEC; TSE: 6701)
NEC Solution Innovators
today announced the successful development of artificial DNA aptamers (*1) that bind to the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
This breakthrough
stems from the NEC Group’s efforts to promote spatial monitoring business using aptamers, including the development of new biosensing systems,
such as measuring equipment that can monitor spaces where various viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses, are present.
Overview of Aptamers
SARS-CoV-2 enters into human cells
when the spike protein, Receptor-Binding Domain (*2, RBD), on the surface of the virus binds to the ACE2 receptors (*3) on the surface of human cells.
The aptamer developed by NEC Solution Innovators
targets RBD, which is the key to infection, then traps the virus by recognizing the three-dimensional structure of the RBD and binding very strongly to it (*4, a dissociation constant indicating the strength of the binding between molecules is less than 1nM).
This aptamer uses a new modified base called Base appended Base (*5, Patent No. 6763551),
which was developed by NEC Solution Innovators and Gunma University from 2014-2017 supported by a grant for “Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-driven R&D” (A-STEP)
from the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).
Three variants of SARS-CoV-2,
including
the original strain (WK521 Wuhan strain) and two mutant strains (TY7-501 Brazilian and QK002 UK strains)
are being studied by academic laboratories in collaboration with the NEC Group.
The binding assessment tests with aptamers were conducted in a biosafety level 3 (*6, BSL3) laboratory, which is allowed to handle SARS-CoV-2.
Binding assessment tests
were conducted using the Direct ELAA method (*7), in which viruses were adsorbed onto plates and detected with enzyme-labeled aptamers.
As a result, a strong binding of aptamers to SARS-CoV-2 was observed in all three strains.
Future Prospects
NEC is developing a measuring device
that enables spatial monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 by combining MSSs (*8, Membrane-type Surface Stress Sensor) and an aptamer that binds to SARS-CoV-2.
This measuring device
is designed to be used in spaces where people gather and spend time in close proximity, such as
public facilities,
restaurants,
lodging facilities,
event venues and offices.
In fiscal 2021, NEC expects to provide a prototype of a fixed-type spatial monitoring measuring device
for companies,
universities
and other research institutions
that perform virus measurement and other measures.
In addition, in fiscal 2022, NEC aims
to provide a biosensing system that can be used for space monitoring and as an embedded device for equipment such as air conditioners.
Press Releases | NEC