岩手大:’カイコ冬虫夏草’物質が寄与:認知症やアルツハイマー病(動画):
Iwate Univ: ‘Cacerpillar fungus’ substance: dementia、Alzheimer’s disease:
岩手大学:“毛虫真菌”物质的贡献:痴呆症和阿尔茨海默氏病
岩手大:バイオコクーン研究所
カイコのさなぎに寄生するキノコ「カイコ冬虫夏草(とうちゅうかそう)」
「ナトリード」という物質が、認知症やアルツハイマー病などの改善に寄与することがわかった。
岩手大発のベンチャー企業「バイオコクーン研究所」(盛岡市)が発表した。
脳疾患への治療:
今後、「認知症、パーキンソン病や統合失調症といった脳の疾患への治療に活用できる」としている。
- 岩手大のほか、
- 大阪市立大、
- 九州大、
- 岩手医大と共同で実施。
研究成果が米科学誌「プロスワン」(電子版)に1月28日(日本時間)に掲載された。
カイコ冬虫夏草:
バイオコクーン研究所は2010年、カイコ冬虫夏草からの抽出物を、老いたマウスに与えた。
その結果、「記憶をつかさどる脳の海馬にできた傷が、修復された」と発表。
カイコ冬虫夏草に起因物質が含まれるのを確信して研究を進化。
2013年にナトリード (Naturido)を特定した。
ナトリード (Naturido):
その後、約6年間にわたった研究を実施。
「ナトリード (Naturido)に、神経細胞の成長を促進させる効果があること」を突き止めた。
読売新聞オンライン
https://www.yomiuri.co.jp/science/20210203-OYT1T50037/
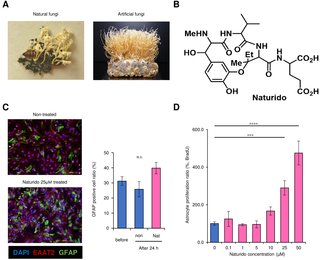
A novel cyclic peptide (Naturido) modulates glia–neuron interactions in vitro and reverses ageing-related deficits in senescence-accelerated mice
The use of agents that target both glia and neurons may represent a new strategy for the treatment of ageing disorders.
Here, we confirmed the presence of the novel cyclic peptide Naturido
that originates from a medicinal fungus (Isaria japonica) grown on domestic silkworm (Bombyx mori).
We found that
Naturido significantly enhanced astrocyte proliferation and activated the single copy gene encoding the neuropeptide VGF and the neuron-derived NGF gene.
The addition of the peptide to the culture medium of primary hippocampal neurons increased dendrite length, dendrite number and axon length.
Furthermore, the addition of the peptide to primary microglial cultures
shifted CGA-activated microglia towards anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective phenotypes.
These findings of in vitro glia–neuron interactions led us to evaluate the effects of oral administration of the peptide on brain function and hair ageing in senescence-accelerated mice (SAMP8).
In vivo analyses revealed that spatial learning ability and hair quality
were improved in Naturido-treated mice compared with untreated mice, to the same level observed in the normal ageing control (SAMR1).
These data suggest that
Naturido may be a promising glia–neuron modulator for the treatment of not only senescence, but also Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0245235#abstract